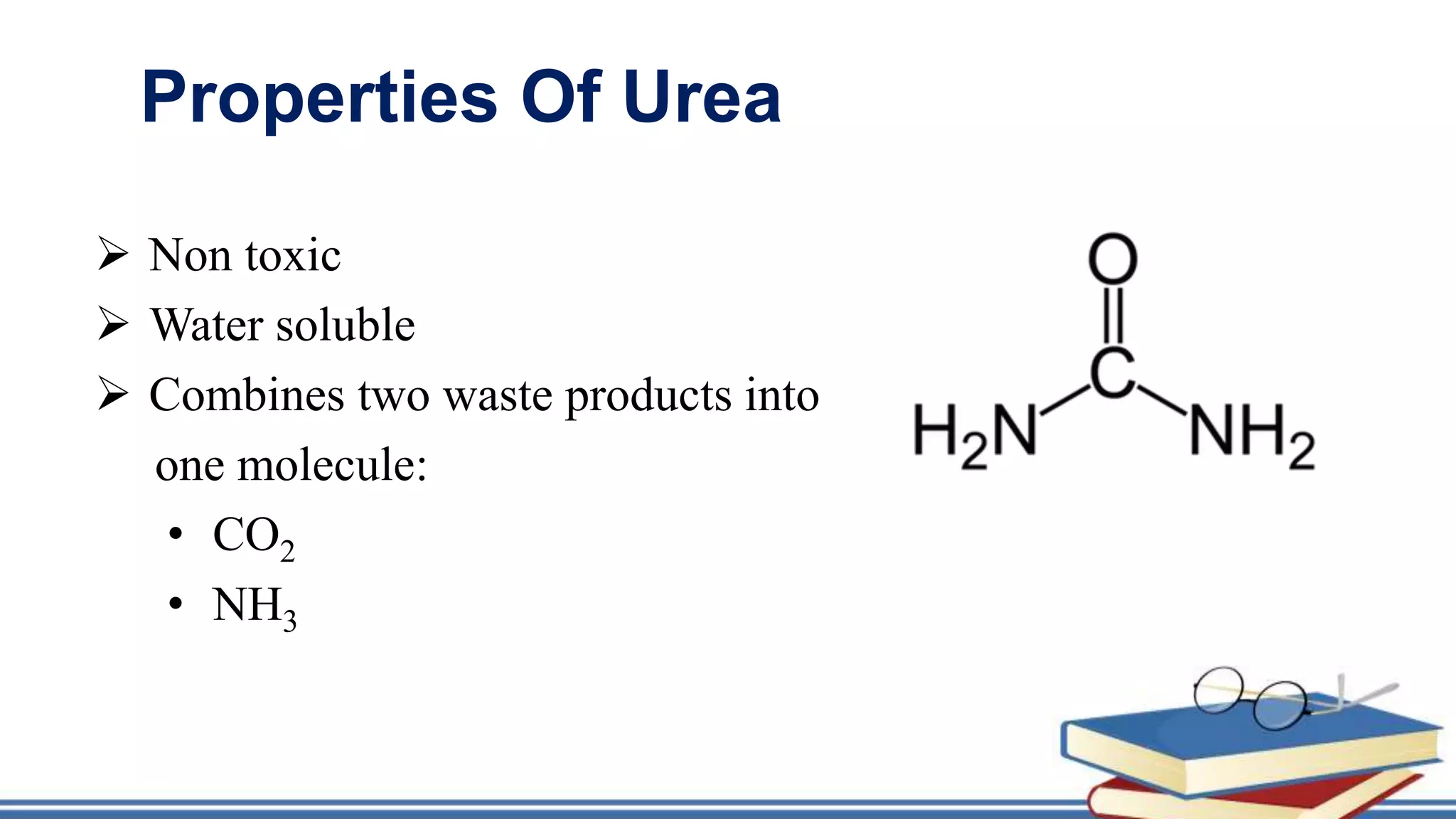
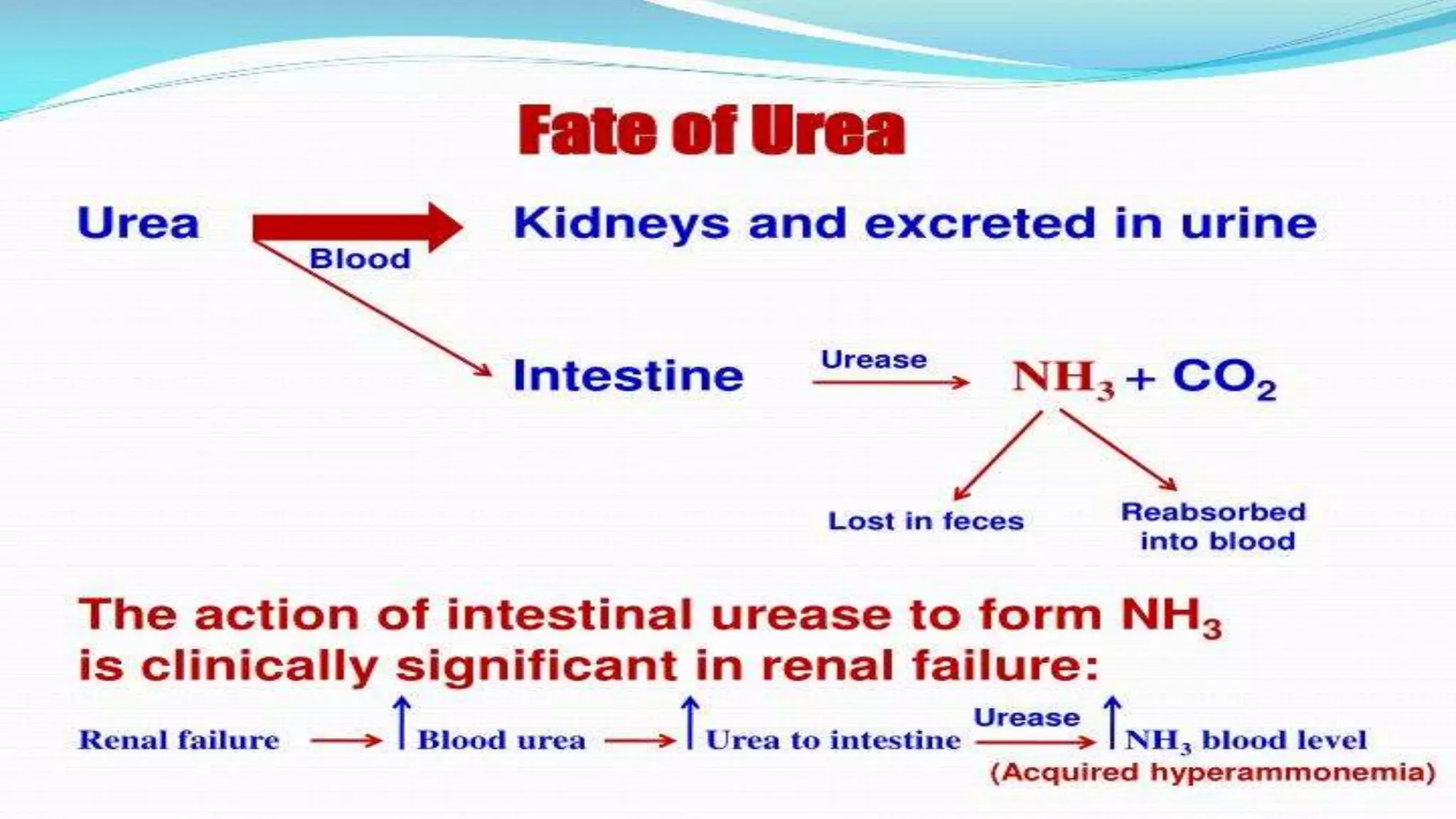
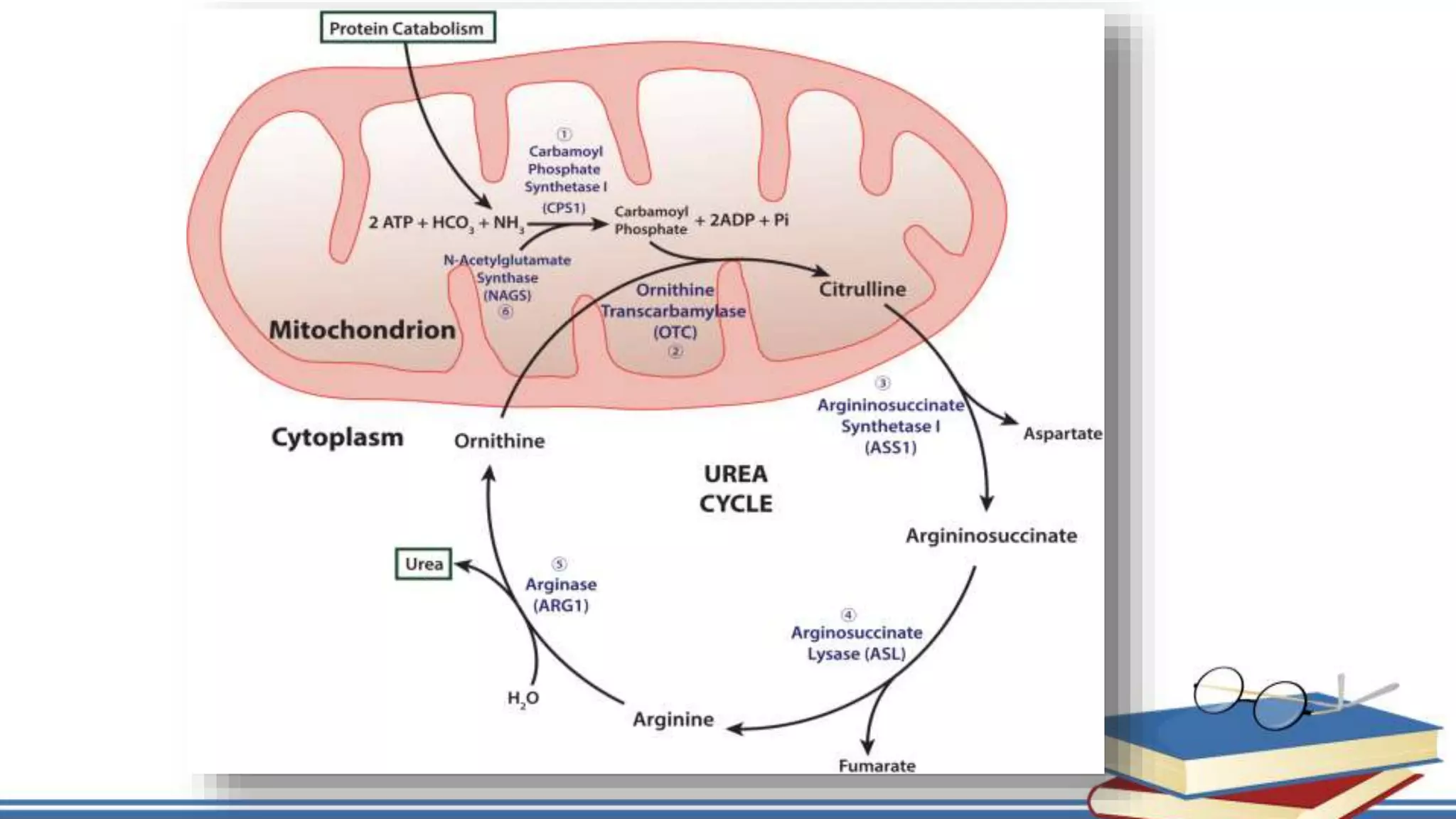
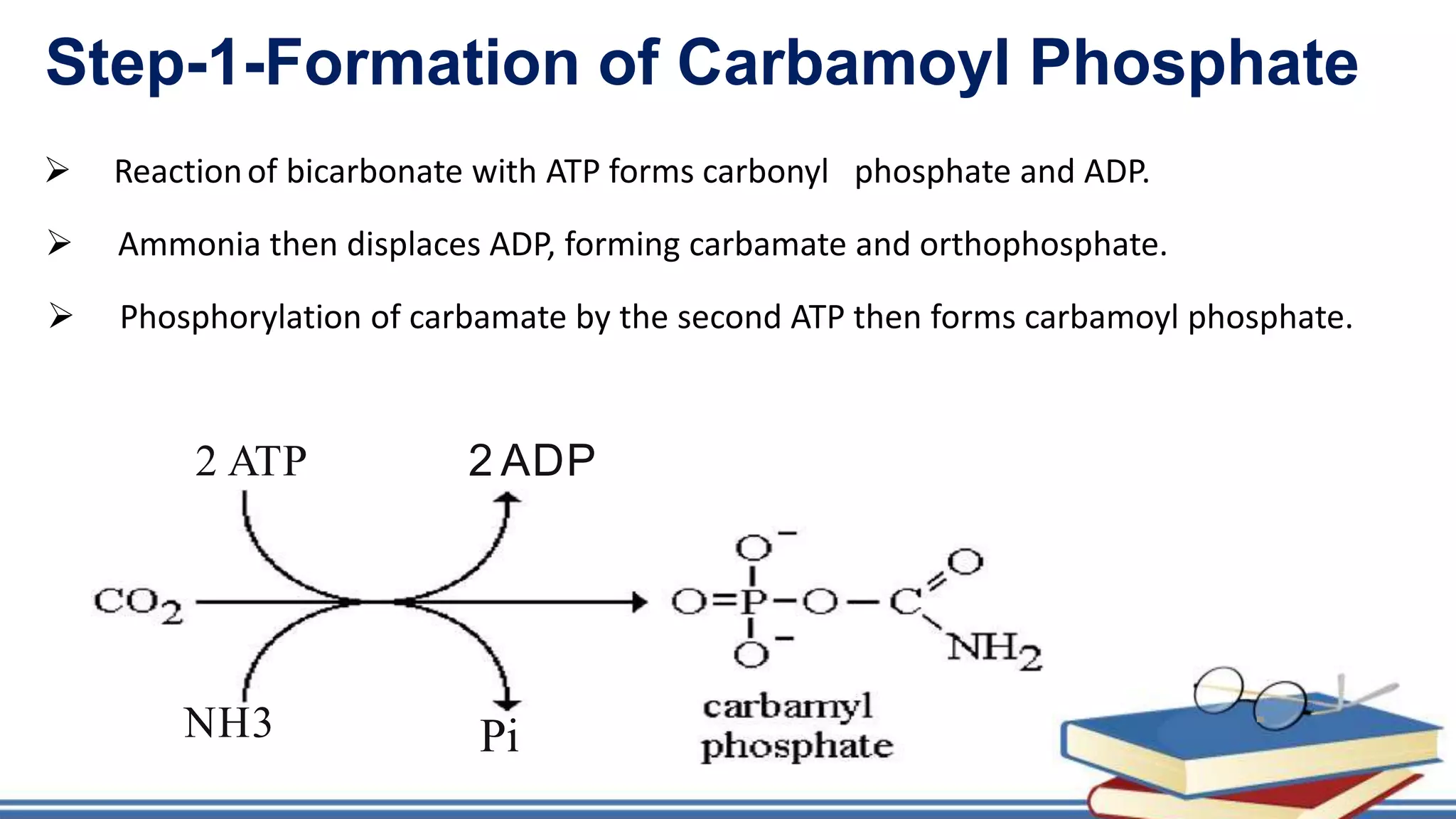
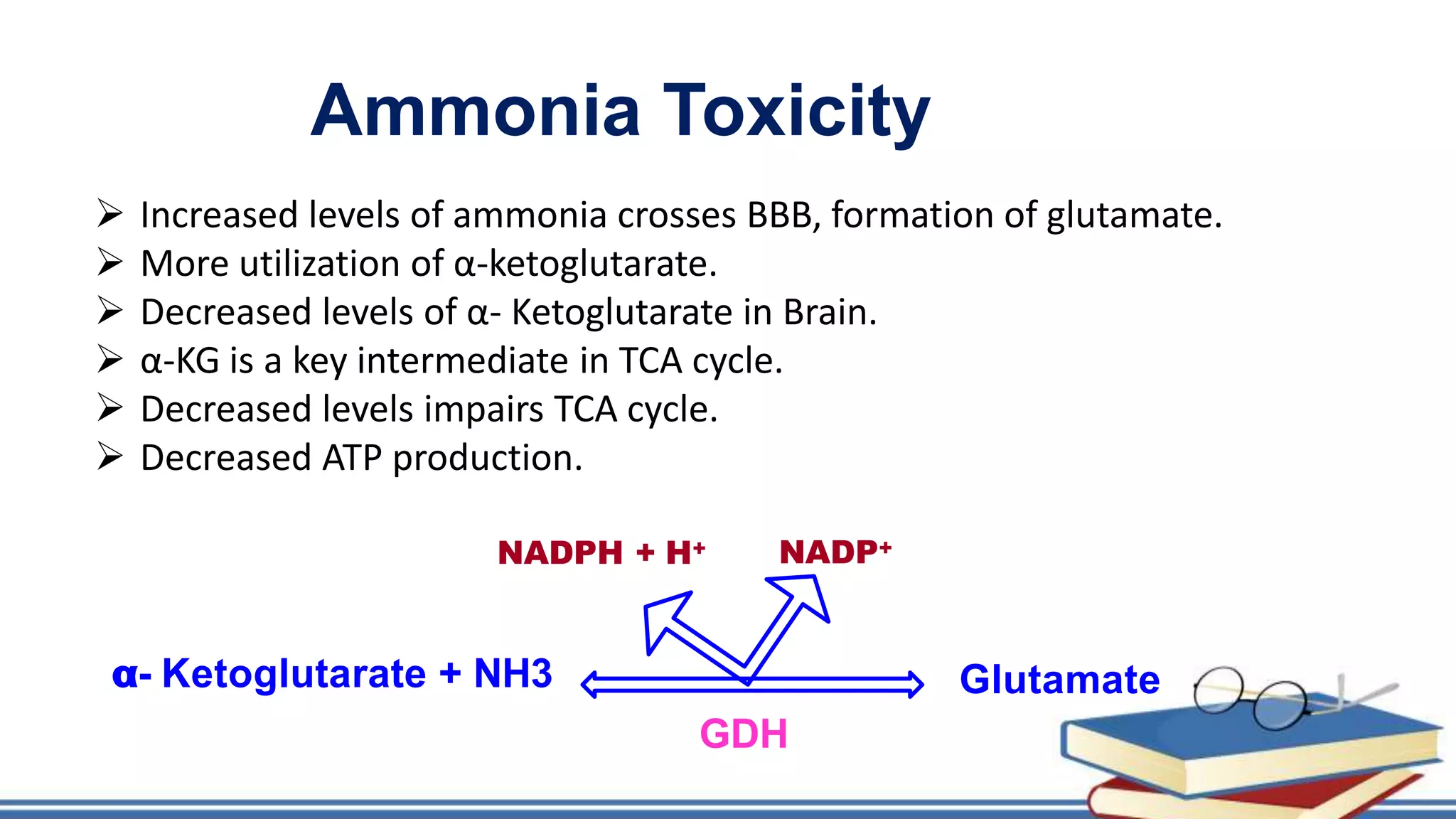
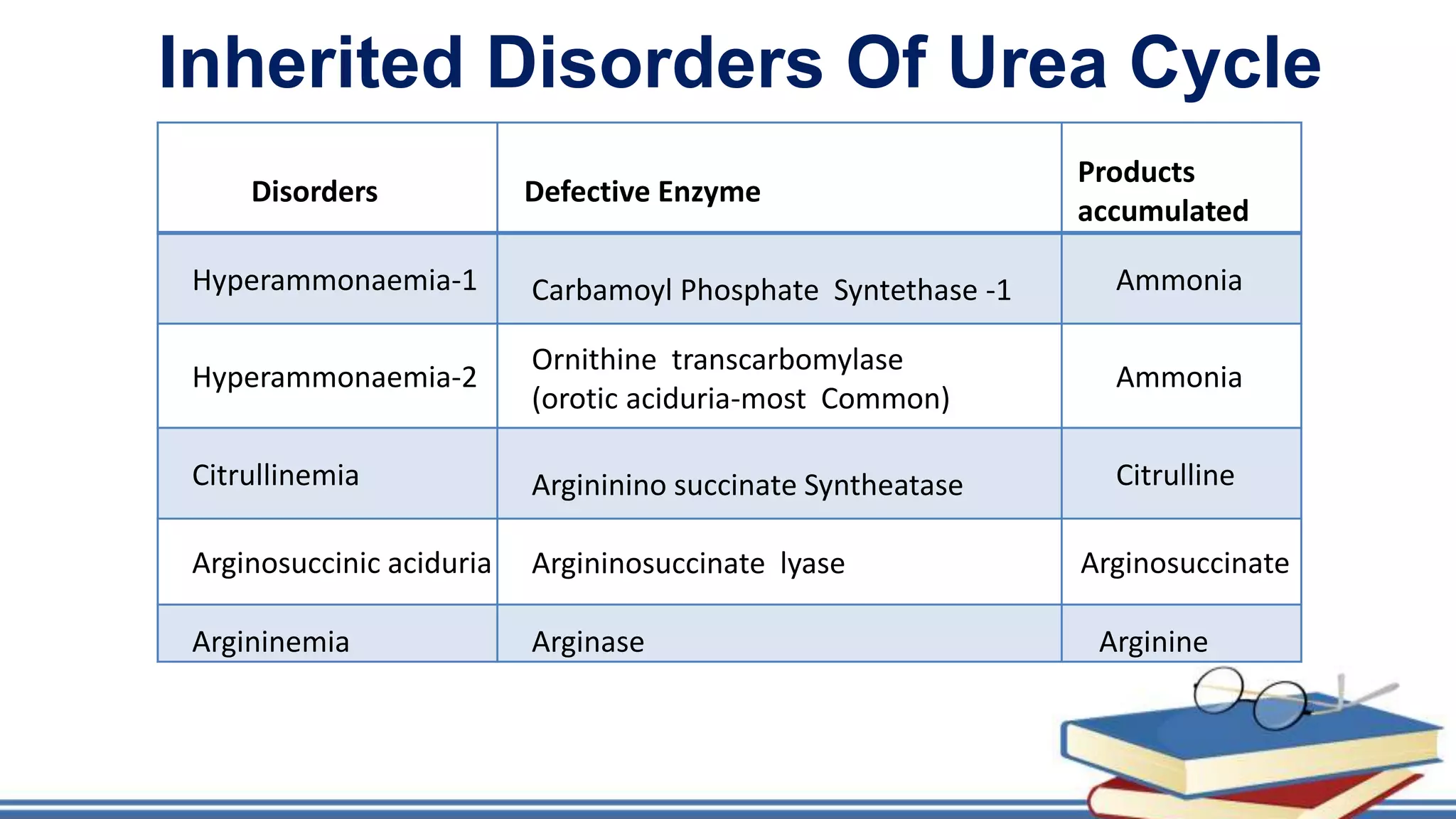
The urea cycle is a cyclic process that occurs primarily in the liver to convert toxic ammonia into urea for excretion. It involves 5 enzyme-catalyzed reactions, 3 in the mitochondria and 2 in the cytosol. The cycle uses 3 ATP and produces 1 molecule of urea while recycling ornithine. Defects in urea cycle enzymes can cause hyperammonemia, which can be toxic if ammonia levels rise and impair the tricarboxylic acid cycle in the brain. The presentation provided details on the individual reactions, regulation, energetics, disorders like hepatic coma, and inherited urea cycle defects.