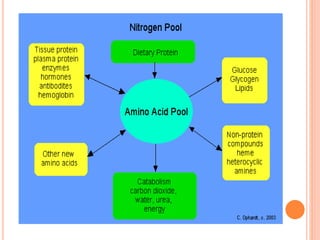
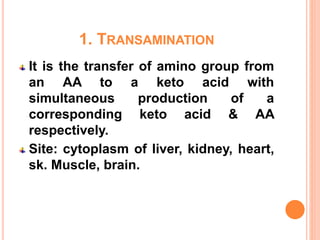
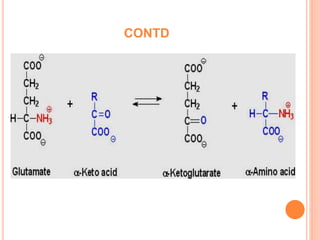
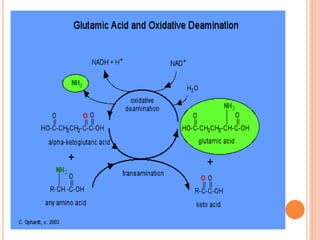
1. Protein metabolism involves the breakdown of amino acids into ammonia and carbon skeletons, and the reuse of these components for new protein synthesis or energy production. Amino acids undergo transamination, deamination, and are metabolized through the urea cycle to dispose of ammonia.
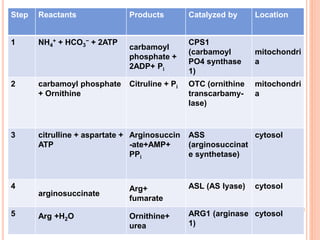
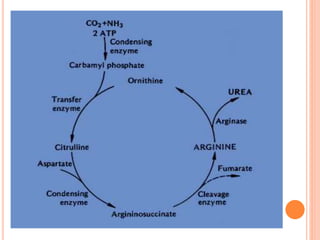
2. The urea cycle is a series of chemical reactions that converts ammonia into urea for excretion. It occurs primarily in the liver and involves five enzymatic steps to incorporate ammonia and carbon into the relatively non-toxic urea molecule.
3. Defects in protein metabolism can cause inborn errors such as phenylketonuria, maple syrup urine disease, and defects in the urea cycle, which






![PROTEIN TURNOVER
It is the rate at which proteins are
constantly being degraded & again
resynthesized. It is 150-300gm/D (i.e.1-
2% of total body protein) in adult.
[Total body protein in 70kg adult is 12-
14kg]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/proteinmetabolism-150827042433-lva1-app6891/85/Protein-metabolism-8-320.jpg)