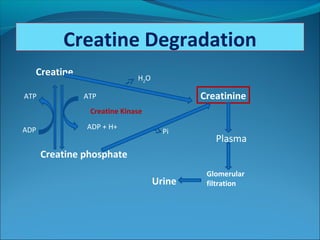
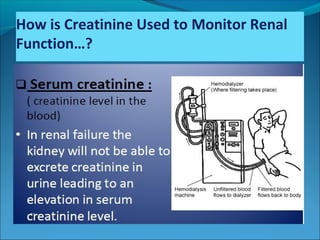
This document discusses creatine, creatinine, and creatine kinase (CK). It explains that creatine is synthesized in the liver and kidneys and stored in muscles, where it is converted to phosphocreatine to provide energy. Creatinine is a breakdown product of creatine and phosphocreatine. Serum creatinine levels indicate kidney function, while CK levels indicate damage to heart and skeletal muscles. The document outlines creatine synthesis and breakdown, the roles and clinical importance of creatinine and CK, and how they are used as biomarkers.





















![What is the purpose of assaying for CK over
a period of time?
Isozymes creatine kinase are tissue specific CK is a
dimer of MM, MB, BB isozymes, and only MB is present in
the myocardium (15% TOTAL CK)
MB-CK: myocardial specific injury
- 100% increase in MB-CK within 4 hr
- Peaks at 8-24 hr then decreases, with aminotranserase
change much slower peak ~ 60 hrs , LDH is the best
indicator to follow the MI from third day(To maximize
treatment, prompt recognition essential)
- Usually [CK] cardium & % MB/total CK are constant,
[MB-CK↑] is proportional to degree injury to myo cardium](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/creatinemetabolism-140616021837-phpapp02/85/Creatine-metabolism-24-320.jpg)

