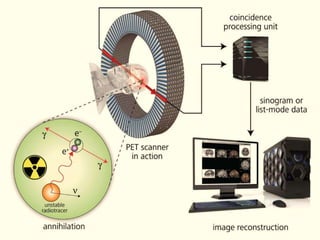
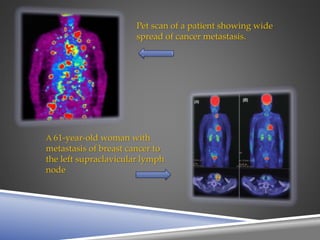
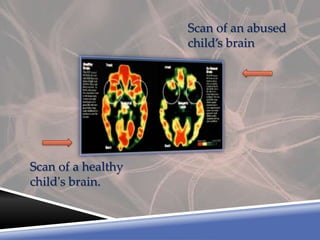
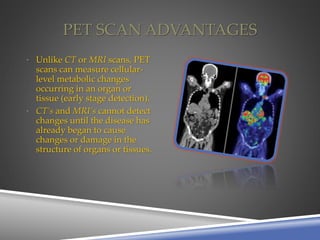
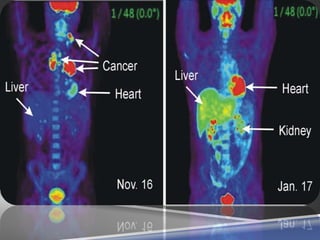
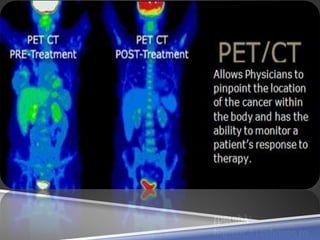
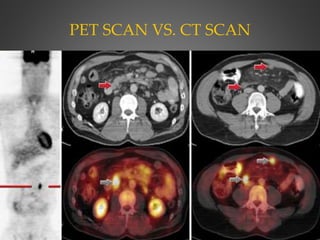
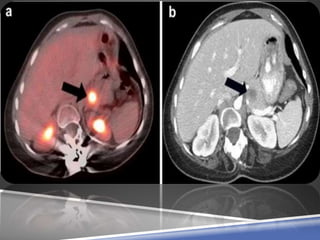
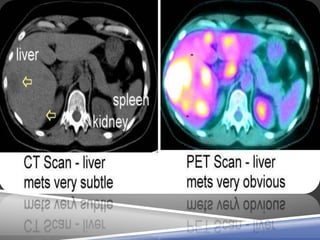
A PET scan uses radioactive tracers to detect disease in the body at a cellular level. It works by injecting a small amount of radioactive sugar molecule called FDG into the bloodstream. Cancer cells absorb more FDG than normal cells, allowing cancers to be seen as hot spots on PET images. PET scans are useful for detecting cancer, epilepsy, Alzheimer's disease, and evaluating treatment response. While exposing patients to radiation, PET scans provide metabolic imaging to detect diseases earlier than other scans.