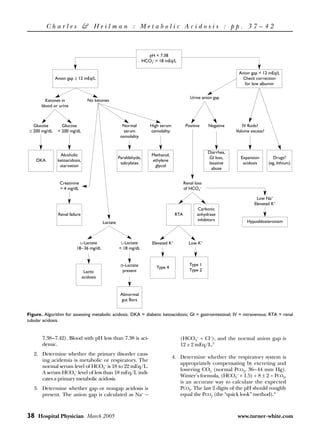
1. Metabolic acidosis is a common acid-base disorder caused by excessive acid production, reduced acid excretion, or loss of alkali in the body.
2. It is diagnosed based on arterial blood gas analysis showing a pH below 7.35 and serum bicarbonate below 18 mEq/L, along with a high anion gap.
3. Left untreated, metabolic acidosis can have serious hemodynamic effects and lead to right heart failure, hypotension, and respiratory failure. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are important.

![Charles & Heilman : Metabolic Acidosis : pp. 37 – 42
Table 1. Causes of Increased Anion Gap Metabolic Acidosis Table 2. Causes of Normal Anion Gap Metabolic Acidosis
Increased acid production Hypokalemia-associated causes
Alcoholic ketoacidosis Diarrhea
Diabetic ketoacidosis Renal tubular acidosis types 1 and 2
Starvation ketoacidosis (mild acidosis only) Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (eg, acetazolamide)
Lactic acidosis Ureteral diversions
Type A (with tissue hypoxia) Post-hypocapnic conditions
Circulatory and respiratory failure Laxative abuse
Sepsis Hyperkalemia-associated causes
Myocardial infarction Acid loads and total parenteral nutrition
Severe anemia Obstructive uropathy
Massive hemorrhage Cholestyramine
Carbon monoxide poisoning Addison disease (hypoaldosteronism)
Ischemia of large and small bowels Renal tubular acidosis type 4
Ascites and other third-spacing of fluids Sulfur toxicity
Type B (without tissue hypoxia) 21-Hydroxylase deficiency
Liver failure Potassium-sparing diuretics (eg, triamterene)
Enzyme defects of childhood Chlorine gas exposure
Leukemia, lymphoma, solid tumors
Seizures
Poorly controlled diabetes mellitus serum must equal the sum of the negatively charged
Severe burns anions. The cations are primarily sodium and potassi-
Parenteral nutrition um. The major anions are chlorine and bicarbonate.
Epinephrine and norepinephrine infusions Increased anion gap acidosis is generally more severe
Idiopathic (in terms of potentially fatal outcome) than normal
Bronchodilator
anion gap acidosis. The causes of increased and nor-
mal anion gap metabolic acidosis are summarized in
Drugs and toxins (aspirin, ethylene glycol, methanol, paraldehyde)
Tables 1 and 2.
Renal failure
Gastrointestinal loss can be differentiated from
Dilutional (large volume of intravenous fluid replacement)
renal pathologies as a cause of normal gap acidosis by
using the urinary anion gap ([urine Na+ + urine K+] −
urine Cl–), an indirect measure of ammonium secre-
5. Determine whether another metabolic disorder
tion.7,8 A negative urinary anion gap (< 0) suggests
is present in patients with a high anion gap aci-
dosis. Calculate the delta anion gap5 as follows: appropriate renal excretion of ammonium and points
delta gap = (anion gap − 10)/(24 − HCO3–). to gastrointestinal loss as the cause of the acidosis.
The normal value is between 1 and 1.6. A low Conversely, a zero or positive anion gap suggests
delta gap suggests the presence of a concomi- impaired ammonia production and a renal etiology for
tant nongap acidosis, whereas a delta gap the acidosis.
greater than 1.6 suggests the presence of a con- Calculation of an osmolar gap in a patient with a
comitant metabolic alkalosis. metabolic acidosis is essential if the clinical scenario sug-
gests ingestion or poisoning. Osmolality is a measure of
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS solute particles in a solution. Plasma osmolality reflects
Metabolic acidoses can be classified clinically as an both the intracellular and extracellular compartments
increased anion gap acidosis or a normal anion gap because they are in osmotic equilibrium. Osmolality can
acidosis (hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis). As a be measured or calculated as follows: 2 × Na+ (mEq/L) +
concept, the anion gap has shortcomings; nonethe- (blood urea nitrogen [mg/dL]/2.8) + (glucose
less, it is a useful clinical tool in developing a differen- [mg/dL]/18). This formula reflects the major solutes in
tial diagnosis of metabolic acidosis.6 The concept of extracellular fluid. The calculated plasma osmolality
the anion gap is derived from the law of electrical neu- should be within 10 mOsm/L water of the measured
trality. The sum of the positively charged cations in the plasma osmolality. If unmeasured solutes are present in
www.turner-white.com Hospital Physician March 2005 39](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metabolicacidosis-121127074715-phpapp02/85/Metabolic-acidosis-3-320.jpg)


![Charles & Heilman : Metabolic Acidosis : pp. 37 – 42
benefit.23,24 Coronary perfusion pressure, not myocar- bolic acidosis. N Engl J Med 1988;318:594–9.
dial pH, seems to determine the success of resuscita- 8. Goldstein MB, Bear R, Richardson RM, et al. The urine
anion gap: a clinically useful index of ammonium excre-
tion. Efforts are best directed at establishing adequate
tion. Am J Med Sci 1986;292:198–202.
oxygenation and effective circulation.
9. Figge J, Jabor A, Kazda A, Fencl V. Anion gap and
Dilutional Acidosis hypoalbuminemia. Crit Care Med 1998;26:1807–10.
10. Gabow PA. Sodium bicarbonate: a cure or curse for
In patients receiving intravenous solutions of lactate, metabolic acidosis? J Critical Illness 1989;4(5):13–28.
acetate, or citrate in large volumes, an increased gap aci- 11. Bersin RM, Arieff AI. Improved hemodynamic function
dosis can develop as a result of incomplete conversion to during hypoxia with Carbicarb, a new agent for the
bicarbonate. The addition of bicarbonate to the infu- management of acidosis. Circulation 1988;77:227–33.
sion prevents this. By a similar mechanism, the negative- 12. Leung JM, Landow L, Franks M, et al. Safety and efficacy
ly charged salts of some antibiotics (eg, carbenicillin) of intravenous Carbicarb in patients undergoing surgery:
given in large quantities can cause a metabolic acidosis. comparison with sodium bicarbonate in the treatment of
mild metabolic acidosis [published erratum appears in
CONCLUSION Crit Care Med 1995;23:420]. SPI Research Group. Study
of Perioperative Ischemia. Crit Care Med 1994;22:1540–9.
Metabolic acidosis may be the result of a transient
13. Brasch H, Thies E, Iven H. Pharmacokinetics of TRIS
and easily reversible condition such as a seizure. More (hydroxymethyl-)aminomethane in healthy subjects and
severe metabolic acidoses require precise diagnosis and in patients with metabolic acidosis. Eur J Clin Pharmacol
timely treatment of the underlying condition. The 1982;22:257–64.
focus of any treatment plan is the underlying disease 14. Bjerneroth G. Alkaline buffers for correction of metabol-
process; however, if the pH is lower than 7.2, the effects ic acidosis during cardiopulmonary resuscitation with
of acidemia can dominate clinical decision making. focus on Tribonat—a review. Resuscitation 1998;37:
The goal of alkali therapy is to reverse severe acidemia 161–71.
and protect against the detrimental effects on the car- 15. Mitch WE. Uremia and the control of protein metabo-
diovascular system. Intravenous sodium bicarbonate is lism. Nephron 1988;49:89–93.
the mainstay of alkali therapy and is given as a continu- 16. Walls J. Effect of correction of acidosis on nutritional sta-
ous infusion to prevent the effects of “overshoot” alka- tus in dialysis patients. Miner Electrolyte Metab 1997;
23:234–6.
losis. Alternative alkalizing agents such as sodium lac-
17. Wrenn KD, Slovis CM, Minion GE, Rutkowski R. The
tate and citrate are not as reliable because their effects syndrome of alcoholic ketoacidosis. Am J Med 1991;91:
depend on oxygenation to bicarbonate. Research 119–28.
efforts aimed at finding alternatives to bicarbonate 18. Viallon A, Zeni F, Lafond P, et al. Does bicarbonate ther-
therapy continue, as do studies to better identify those apy improve the management of severe diabetic ketoaci-
subgroups of metabolic acidosis that benefit from alka- dosis? Crit Care Med 1999;27:2690–3.
linization therapy. HP 19. Carlisle EJ, Donnelly SM, Vasuvattakul S, et al. Glue-
sniffing and distal renal tubular acidosis: sticking to the
REFERENCES facts. J Am Soc Nephrol 1991;1:1019–27.
1. Hamblin PS, Topliss DJ, Chosich N, et al. Deaths associ- 20. Adrogue HJ, Madias NE. Management of life-threatening
ated with diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar coma. acid-base disorders. First of two parts [published erratum
1973-1988. Med J Aust 1989;151:439, 441–2, 444. appears in N Engl J Med 1999;340:247]. N Engl J Med
2. Orchard CH, Cingolani HE. Acidosis and arrhythmias 1998;338:26–34.
in cardiac muscle. Cardiovasc Res 1994;28:1312–9. 21. Stacpoole PW, Lorenz AC, Thomas RG, Harman EM.
3. Winter SD, Pearson JR, Gabow PA, et al. The fall of the Dichloroacetate in the treatment of lactic acidosis. Ann
serum anion gap. Arch Intern Med 1990;150:311–3. Intern Med 1988;108:58–63.
4. Fulop M. A guide for predicting arterial CO2 tension in 22. Stacpoole PW, Wright EC, Baumgartner TG, et al. A
metabolic acidosis. Am J Nephrol 1997;17:421–4. controlled clinical trial of dichloroacetate for treatment
5. Fall PJ. A stepwise approach to acid-base disorders. Prac- of lactic acidosis in adults. The Dichloroacetate-Lactic
tical patient evaluation for metabolic acidosis and other Acidosis Study Group. N Engl J Med 1992;327:1564–9.
conditions. Postgrad Med 2000;107:249–50, 253–4, 23. Shapiro JI. Pathogenesis of cardiac dysfunction during
257–8. metabolic acidosis: therapeutic implications. Kidney Int
6. Emmett M, Narins RG. Clinical use of the anion gap. Suppl 1997;61:S47–51.
Medicine (Baltimore) 1977;56:38–54. 24. Kette F, Weil MH, von Planta M, et al. Buffer agents do
7. Batlle DC, Hizon M, Cohen E, et al. The use of the uri- not reverse intramyocardial acidosis during cardiac re-
nary anion gap in the diagnosis of hyperchloremic meta- suscitation. Circulation 1990;81:1660–6.
Copyright 2005 by Turner White Communications Inc., Wayne, PA. All rights reserved.
42 Hospital Physician March 2005 www.turner-white.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metabolicacidosis-121127074715-phpapp02/85/Metabolic-acidosis-6-320.jpg)