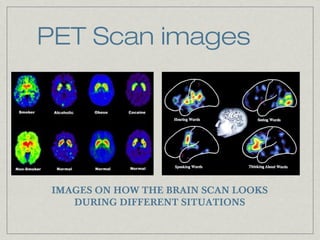
A PET scan uses radioactive tracers injected into the body to produce 3D images showing functional processes. A short-lived radioactive tracer, FDG, is injected and detected as it breaks down, showing glucose metabolism levels in tissues. Different metabolism levels appear as different colors, allowing the computer to generate images of functional abnormalities like cancers or brain disorders. PET scans can detect diseases earlier than other scans and help avoid unnecessary surgery by precisely identifying areas needing treatment.