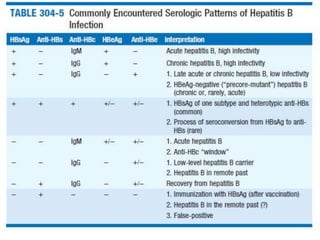
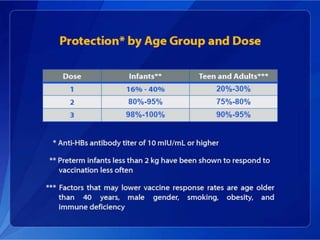
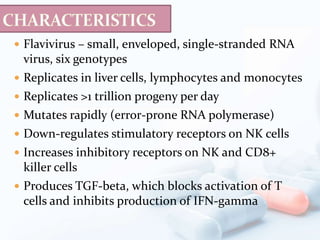
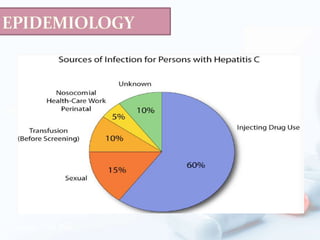
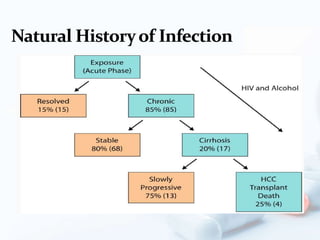
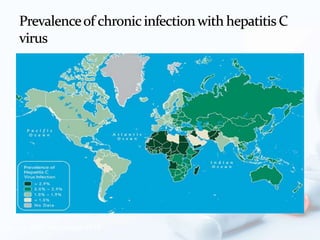
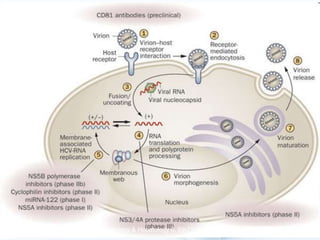
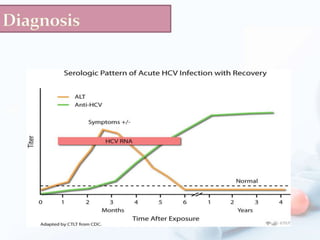
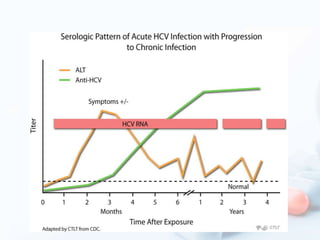
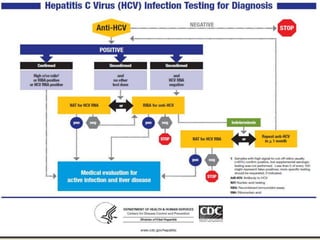
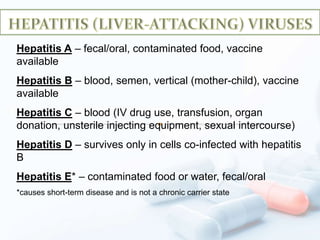
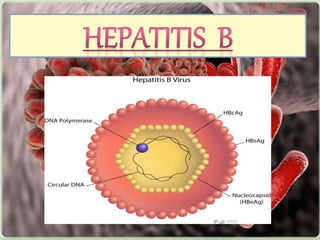
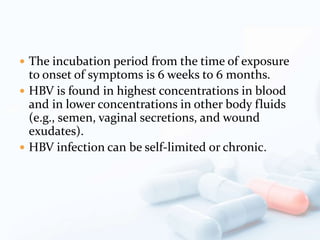
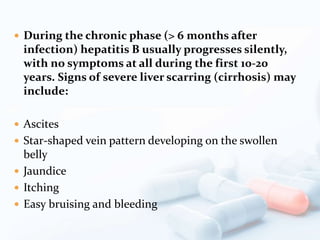
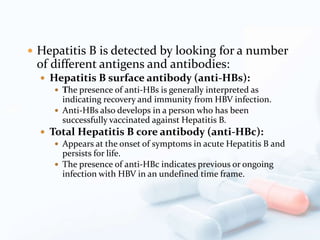
Viral hepatitis, particularly types B and C, is a major global health issue, leading to liver cancer and the need for liver transplants, with millions unaware of their infections. Chronic hepatitis B affects around 800,000–1.4 million Americans, leading to significant morbidity and mortality, while hepatitis C is the most common chronic blood-borne infection in the U.S., with 3.2 million cases. Both infections require careful monitoring and treatment, with various antiviral medications available for chronic cases, but there is currently no vaccine for hepatitis C.













![ Aminotransferase elevations tend to be modest for chronic
hepatitis B but may fluctuate in the range of 100–1,000
units.
(ALT) tends to be more elevated than aspartate
aminotransferase (AST); however, once cirrhosis is
established, AST tends to exceed ALT.
Levels of alkaline phosphatase activity tend to be normal
or only marginally elevated. In severe cases, moderate
elevations in serum bilirubin [51.3–171 mol/L (3–10 mg/
dL)] occur.
Hypoalbuminemia and prolongation of the prothrombin
time occur in severe or end-stage cases.
Hyperglobulinemia and detectable circulating
autoantibodies are absent in chronic hepatitis B (in
contrast to autoimmune hepatitis).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hbvhcv-200809043824/85/Viral-hepatitis-B-and-C-20-320.jpg)