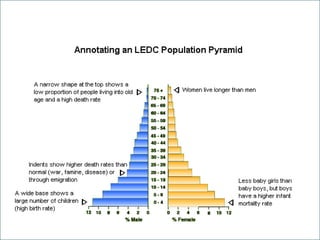
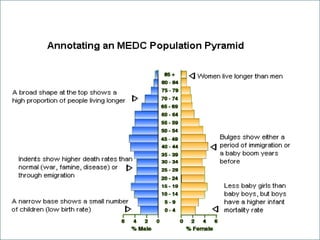
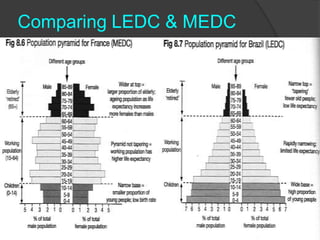
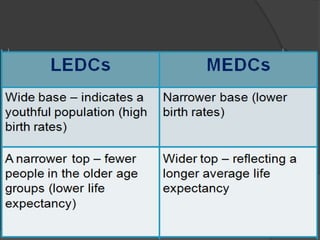
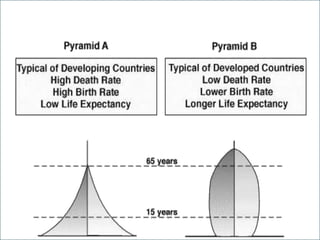
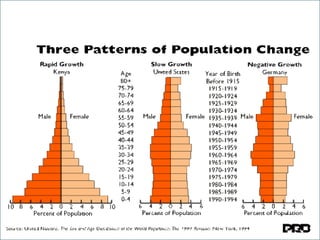
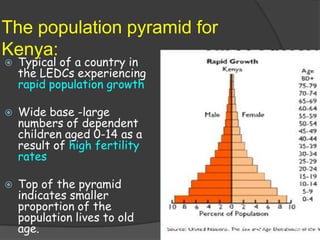
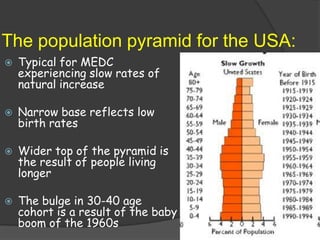
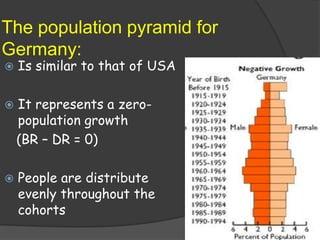
The document discusses population pyramids and the information they provide about a population. Population pyramids show the number of males and females in different age groups through side-by-side bar graphs. They can reveal a population's birth and death rates, life expectancy, and whether it is experiencing rapid growth, slow growth, or is stable or decreasing. Pyramids for less economically developed countries typically have a wide base indicating high fertility rates and dependency, while developed countries have narrow bases and wider tops due to lower birth rates and longer lifespans. The shape of the pyramid provides implications for a country's resources, jobs, and future population growth.