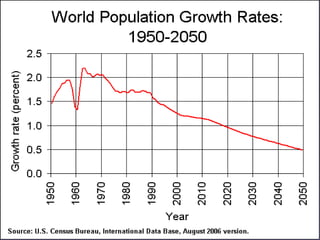
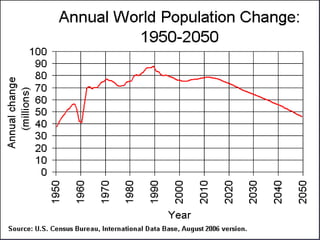
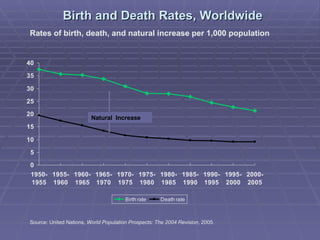
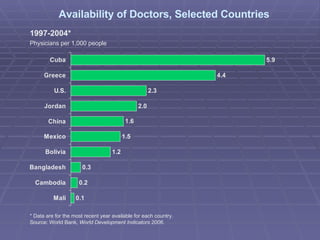
The document provides information about world population trends, including definitions of key demographic concepts. It discusses topics like population growth rates, birth and death rates, life expectancy, fertility rates, rural vs urban populations, and UN Millennium Development Goals. Data on population figures, distributions and projections for different countries and world regions are presented.