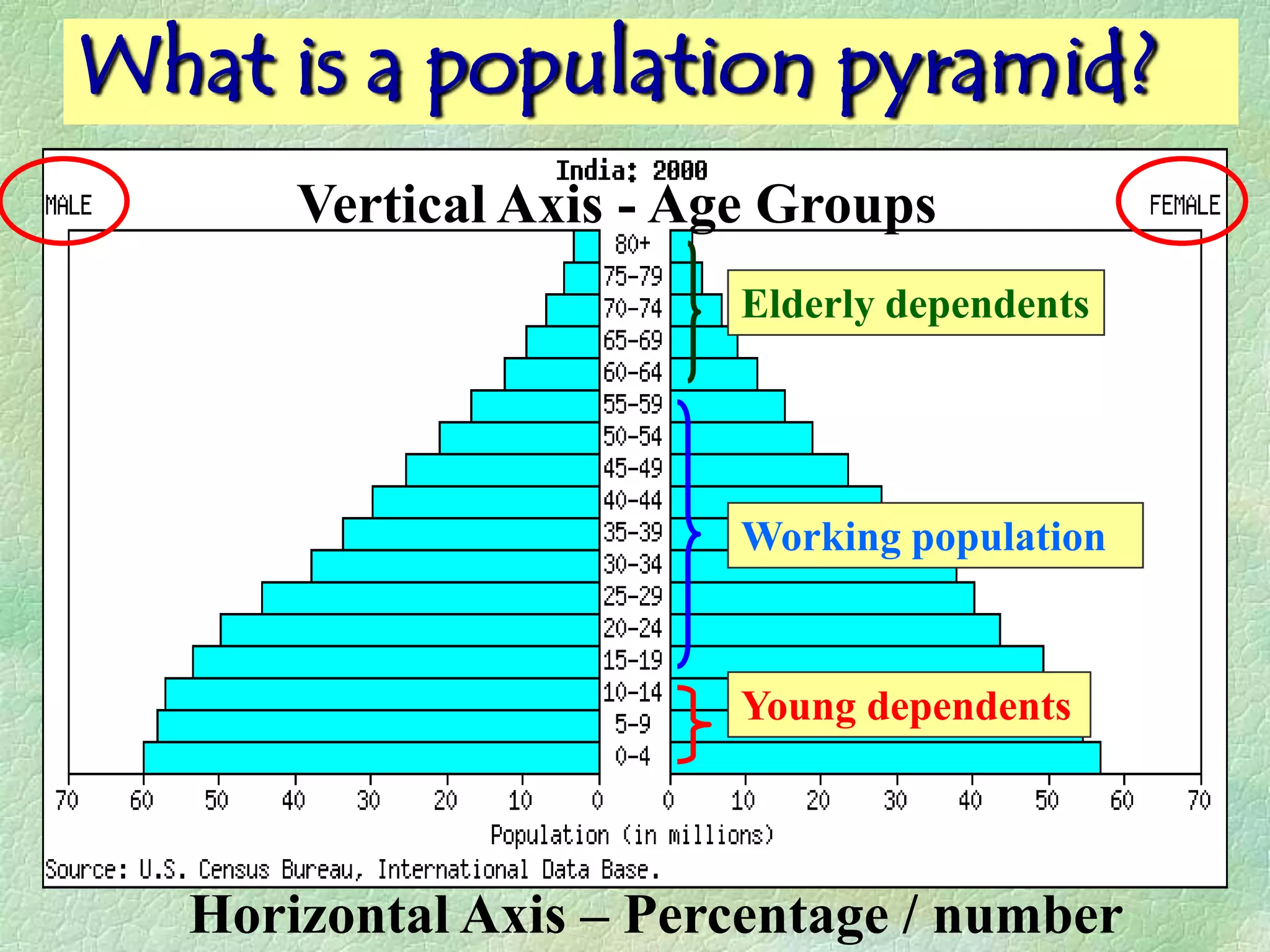
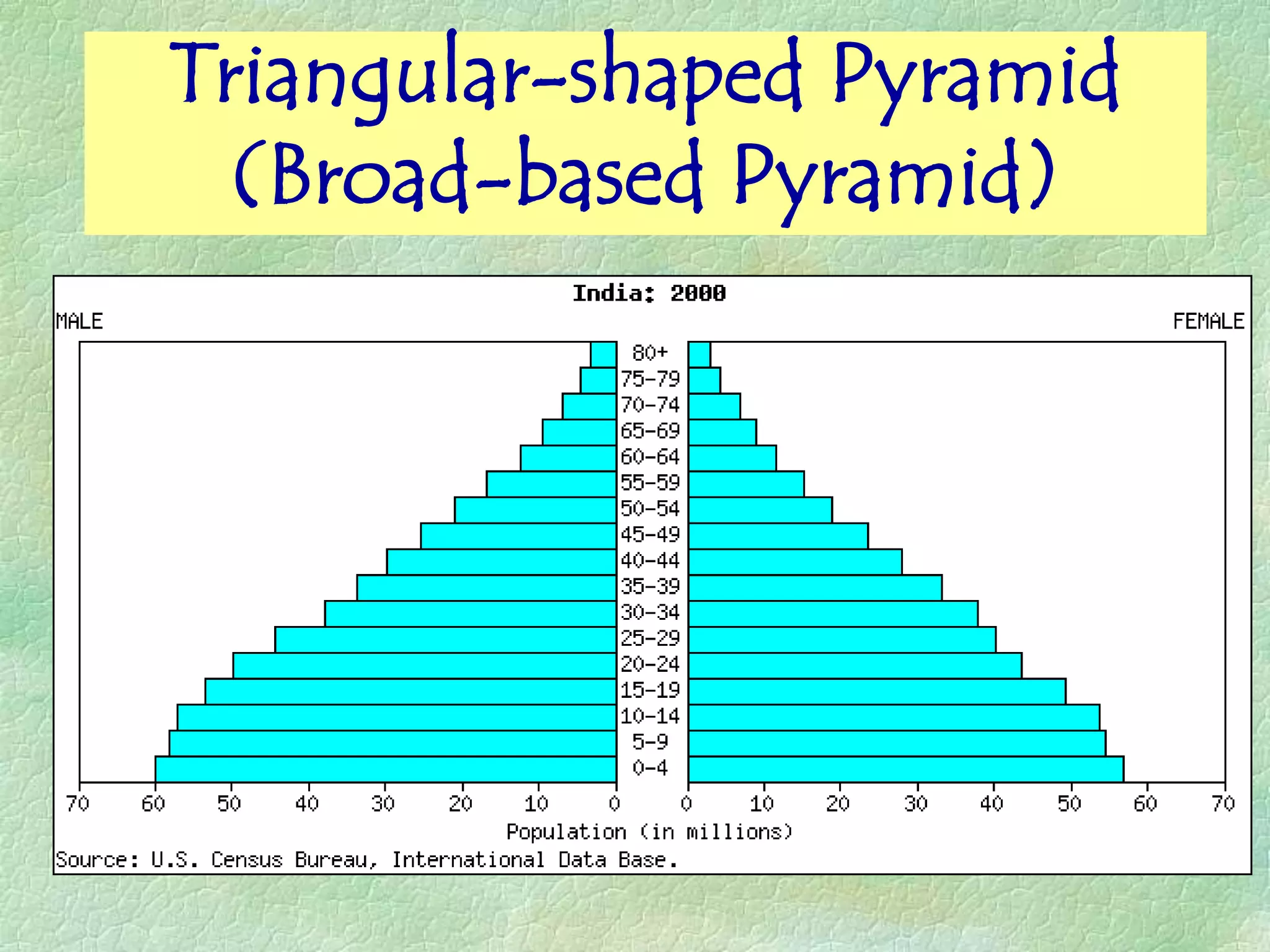
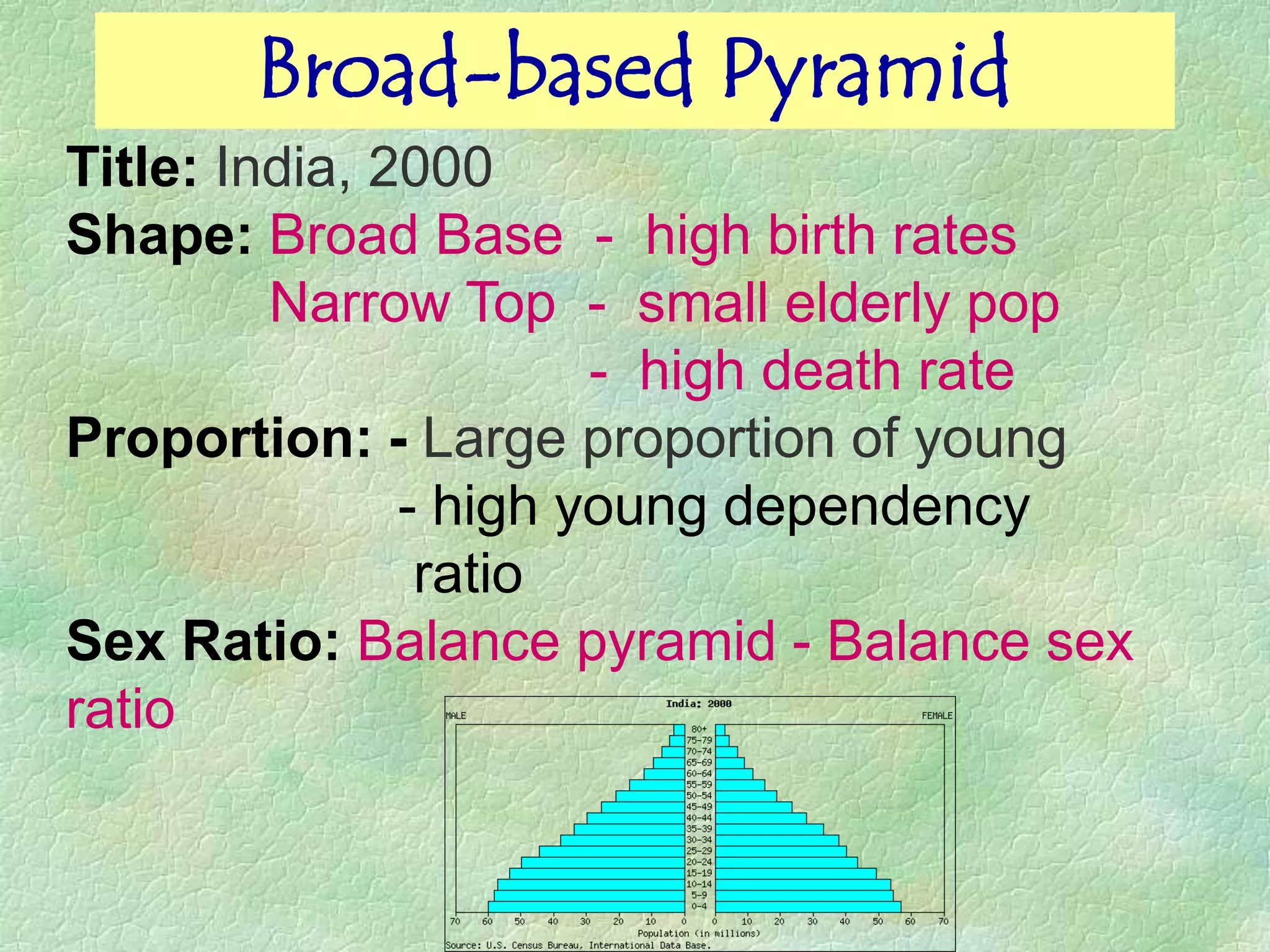
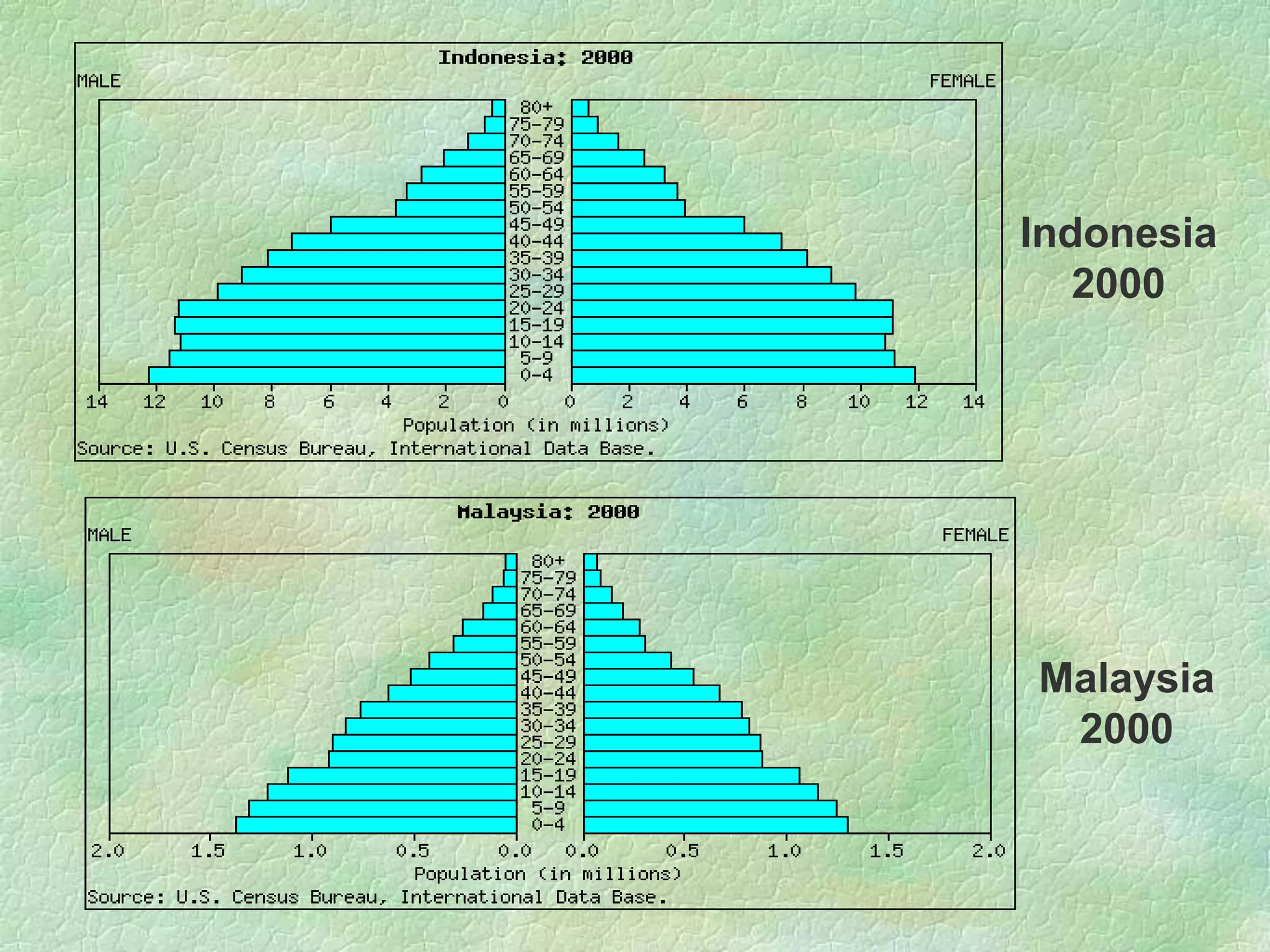
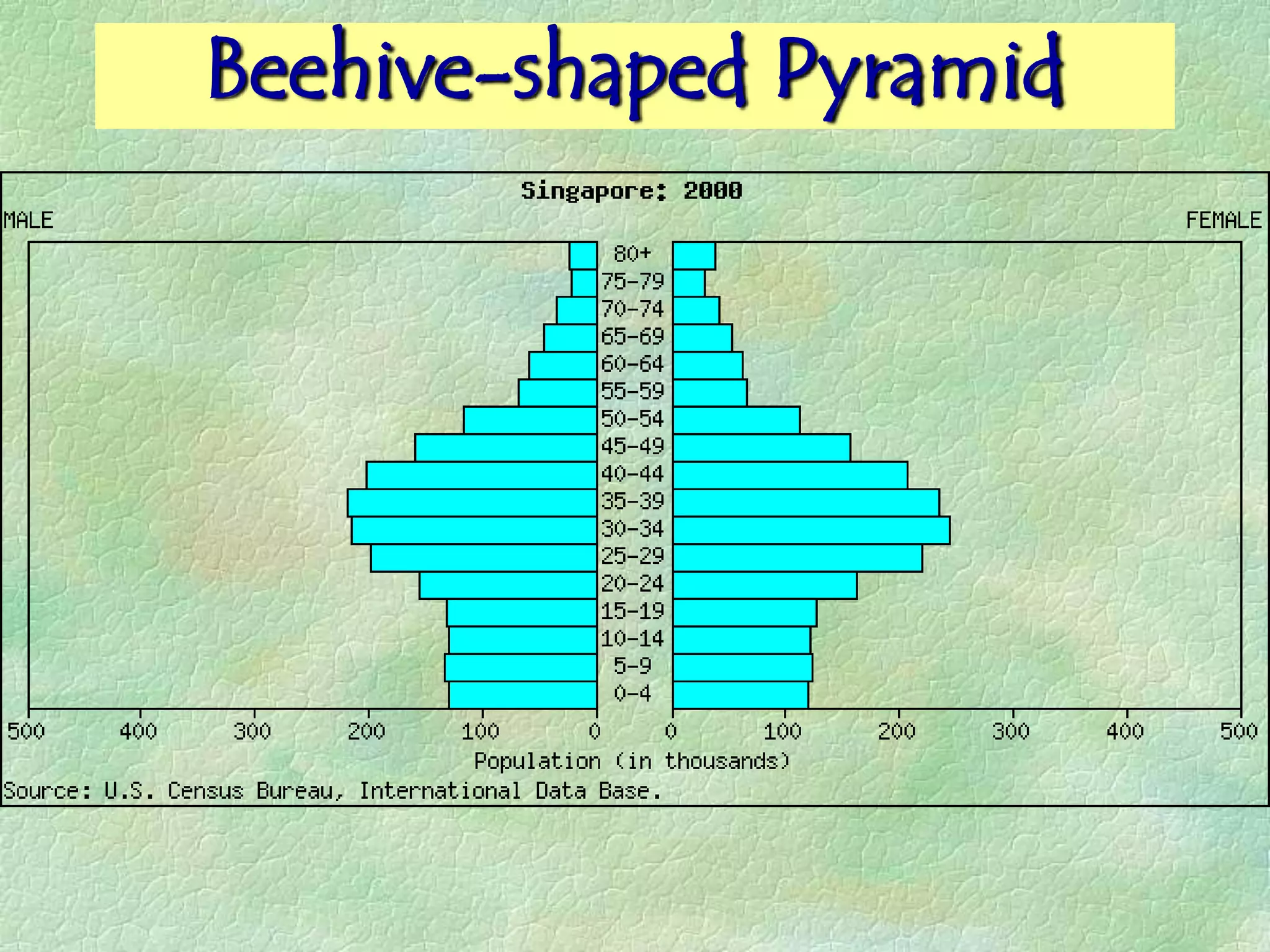
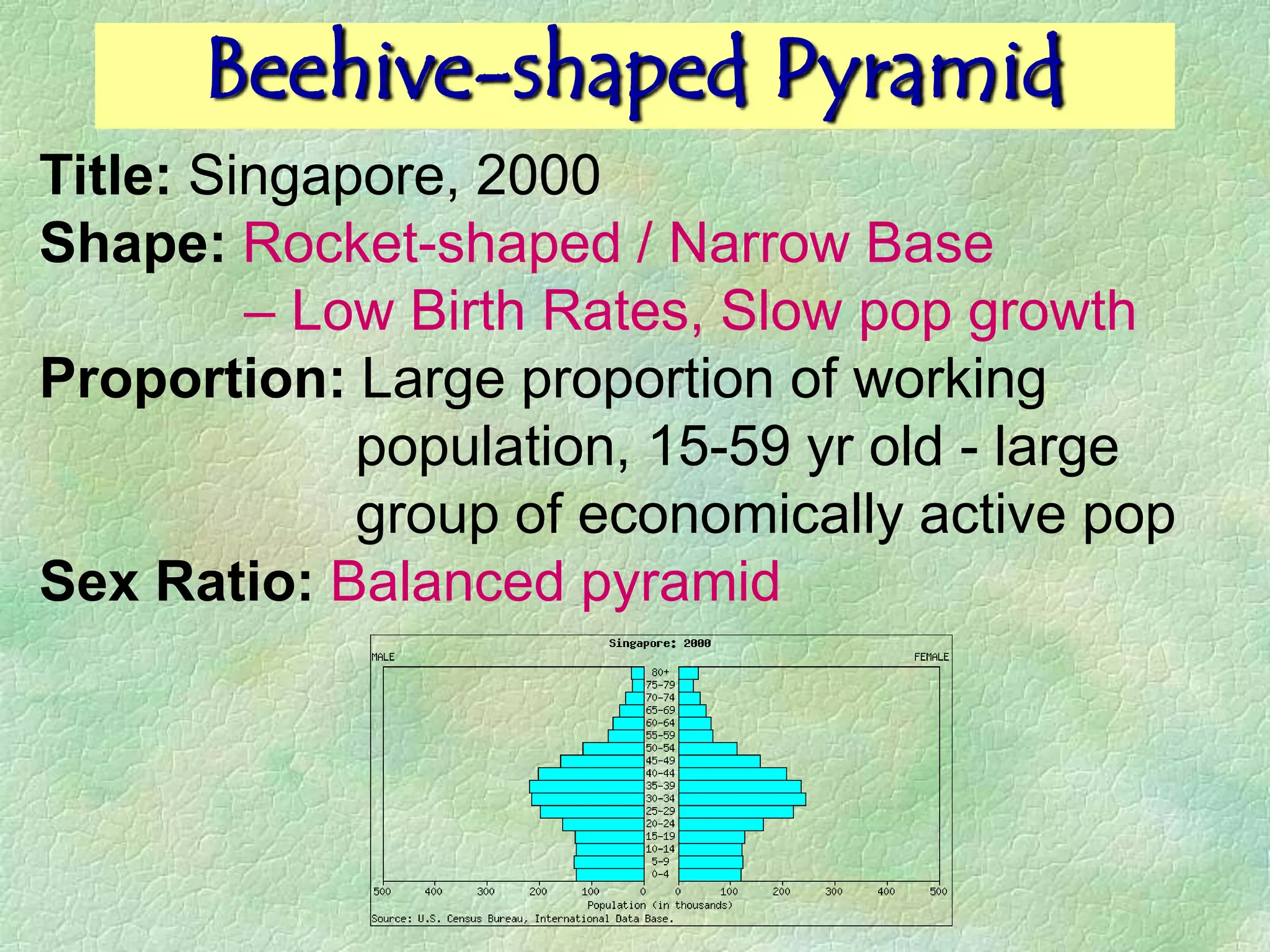
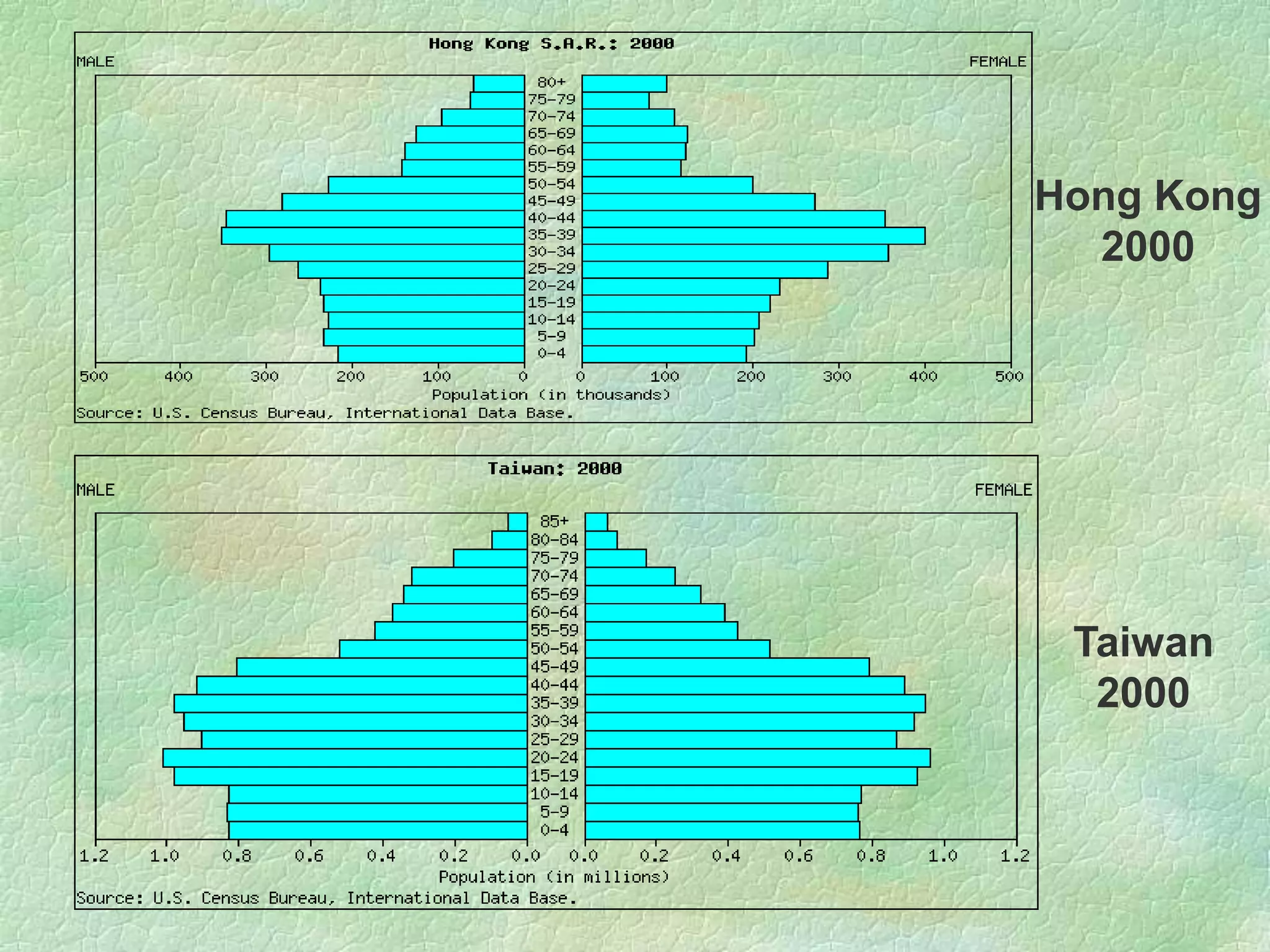
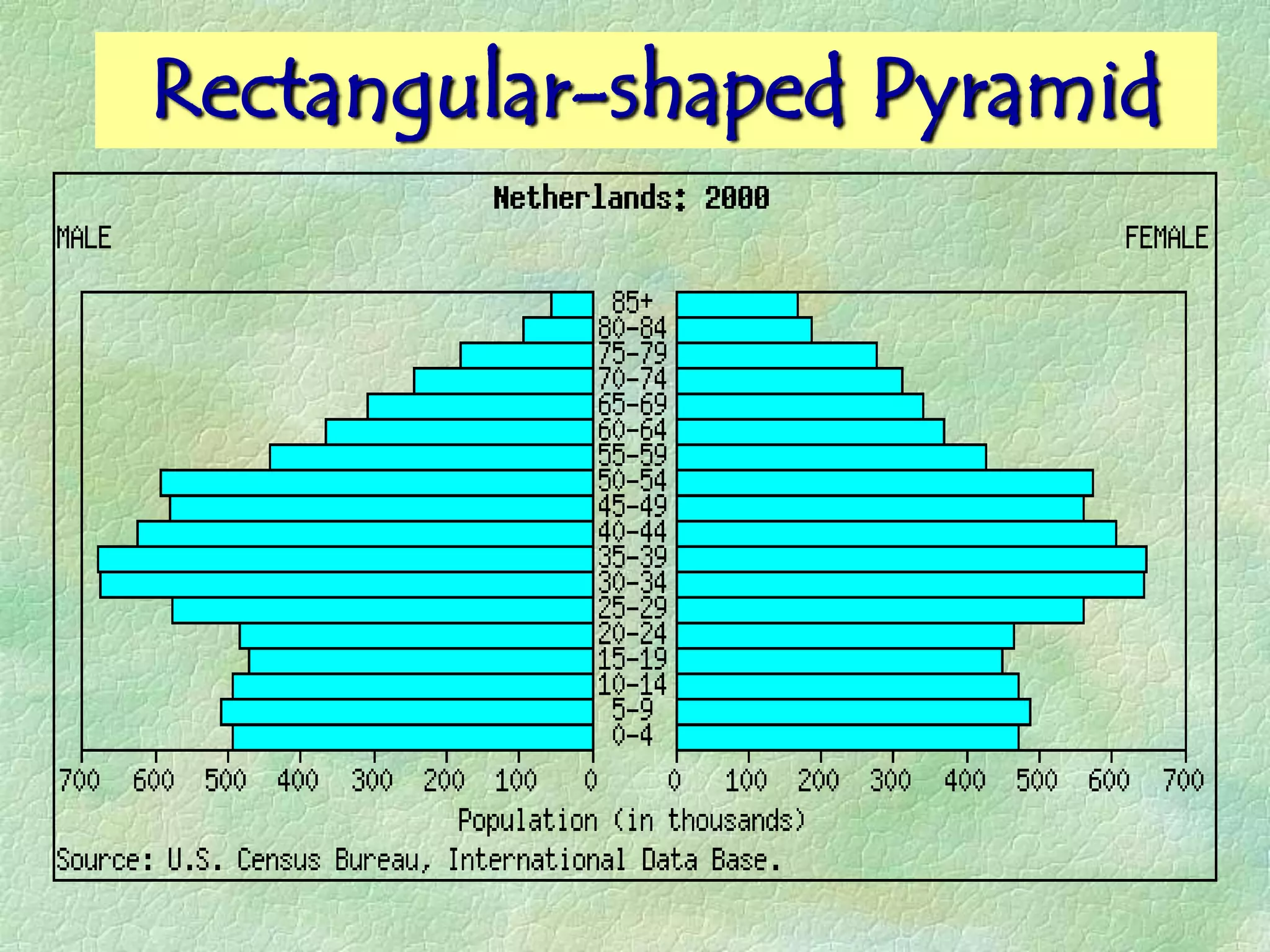
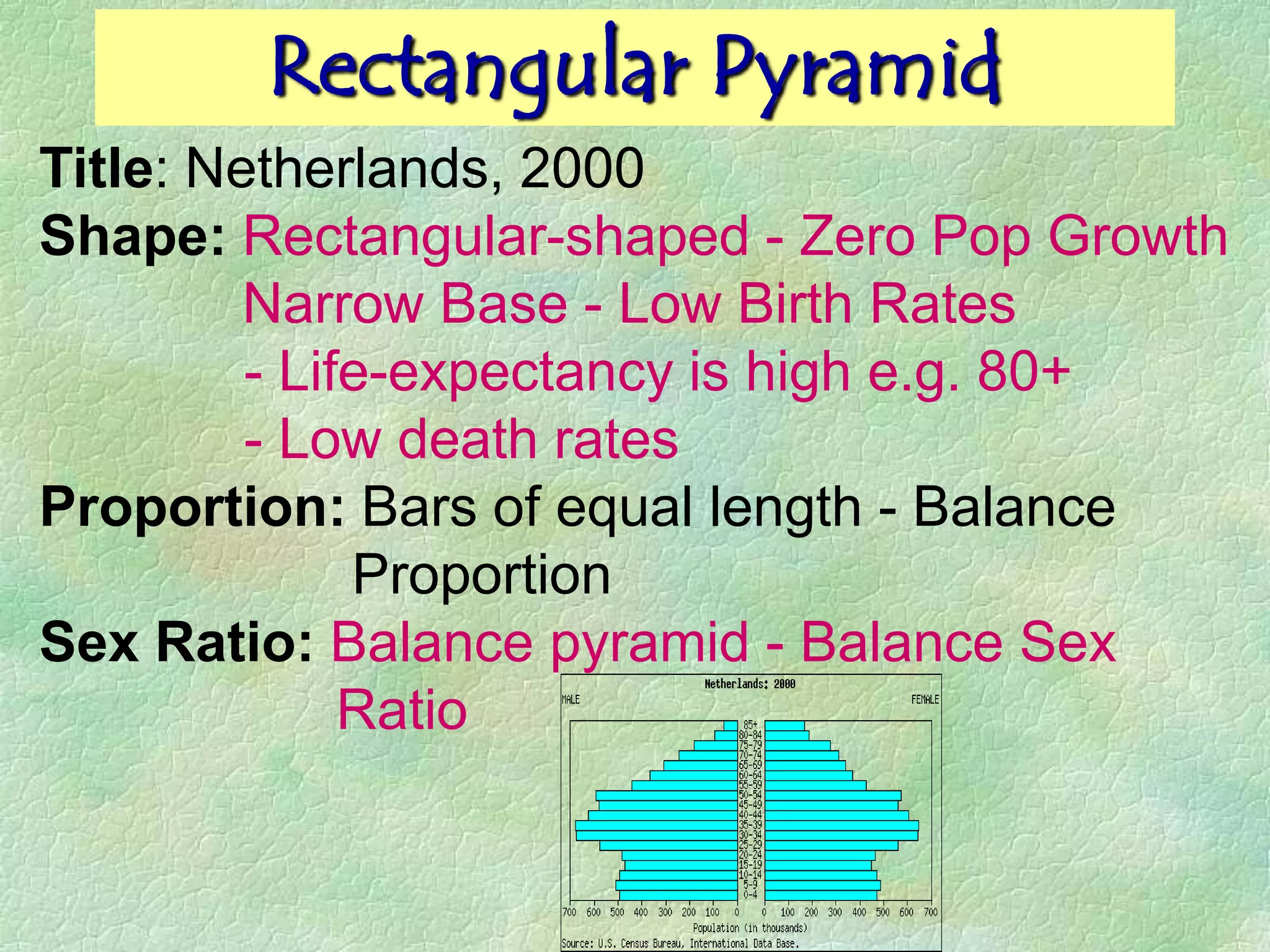
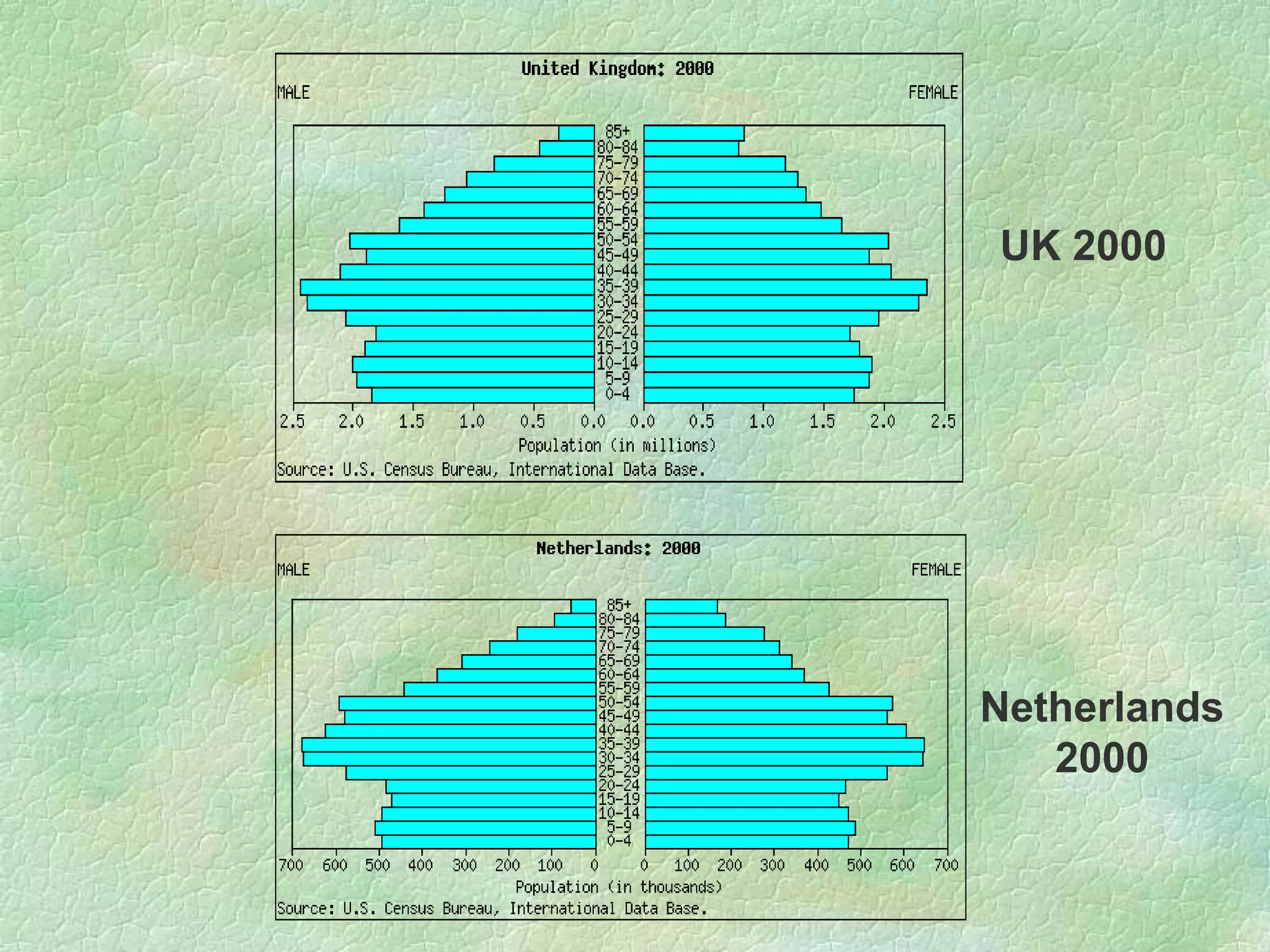
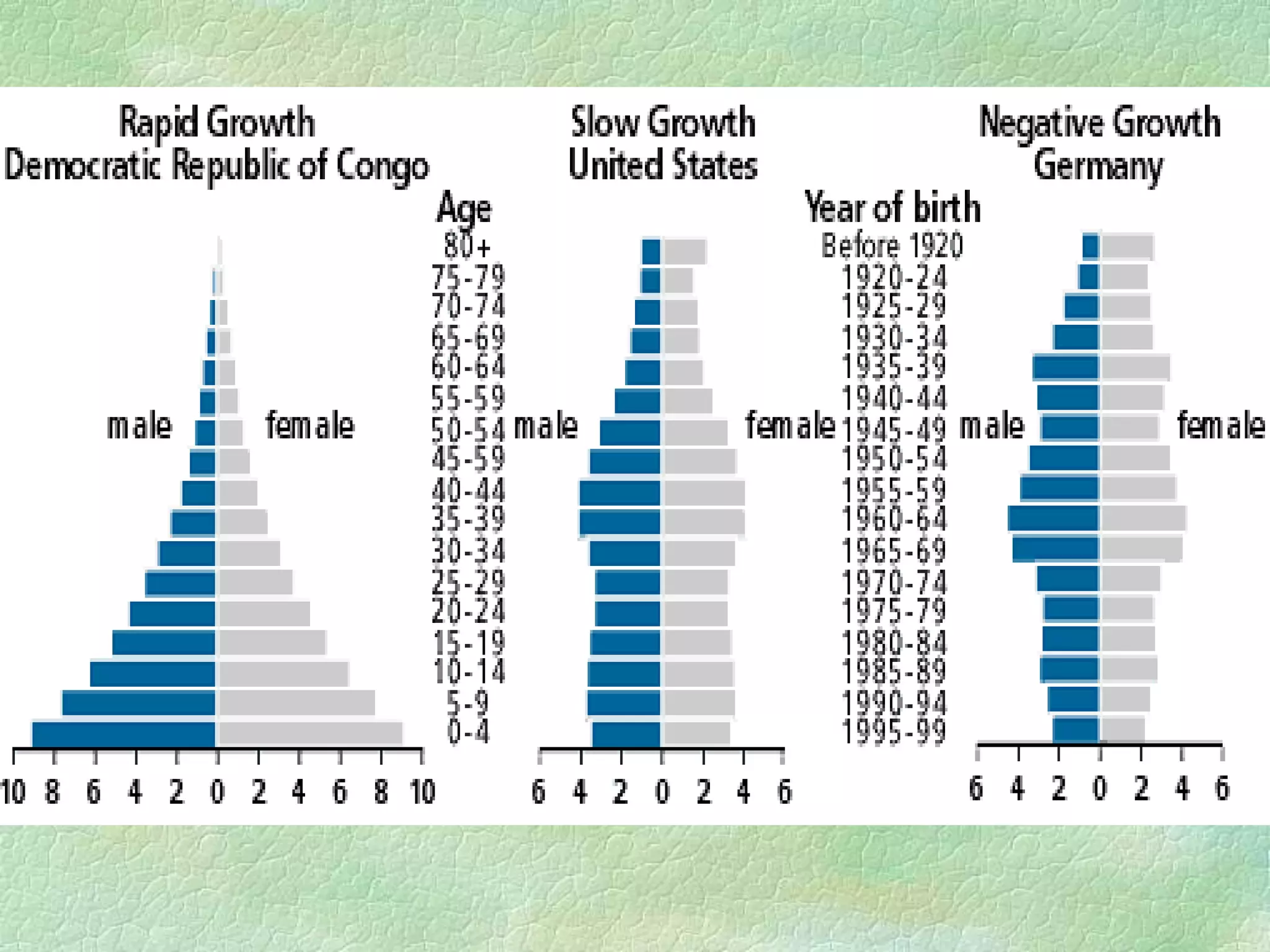
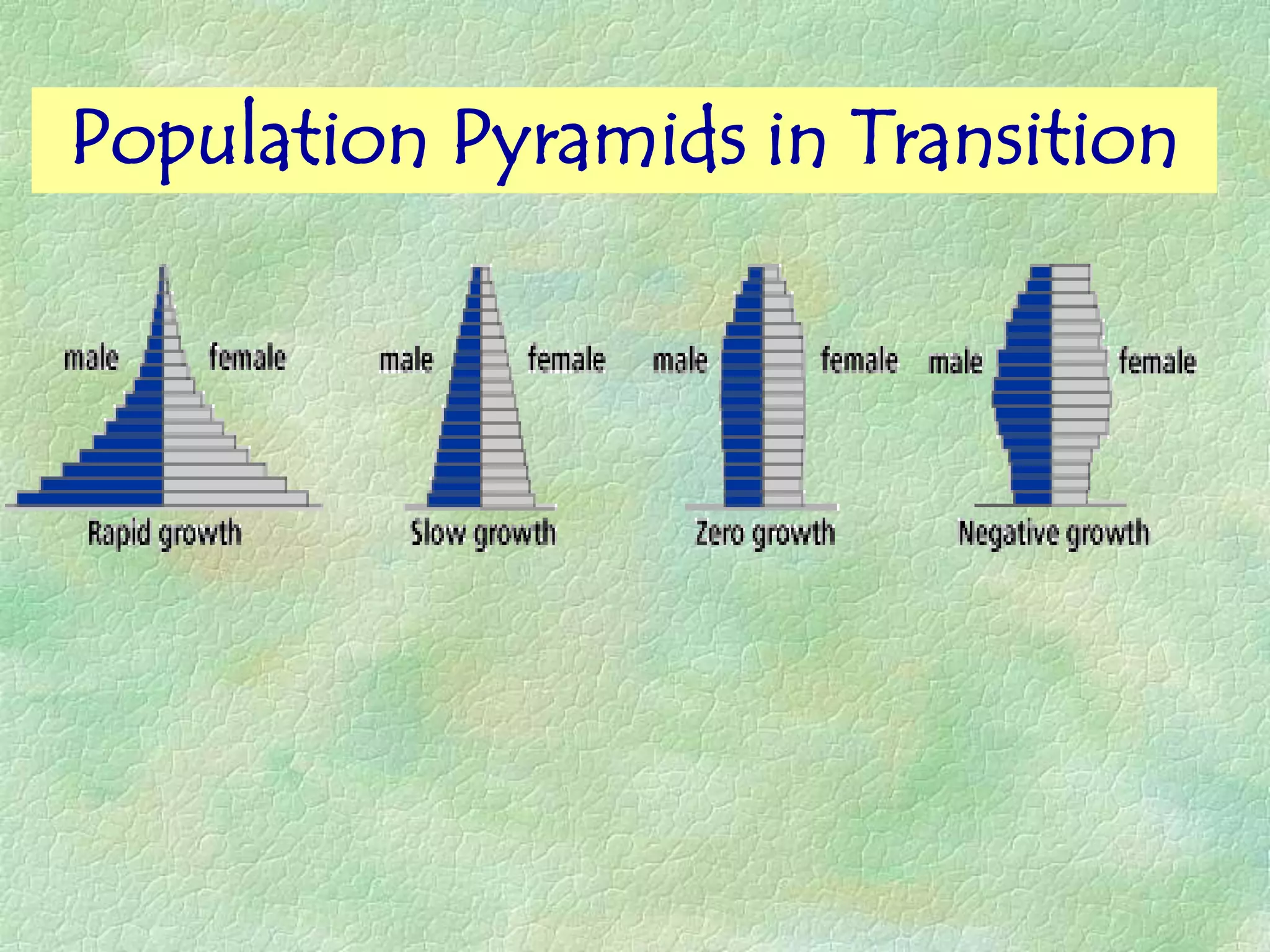
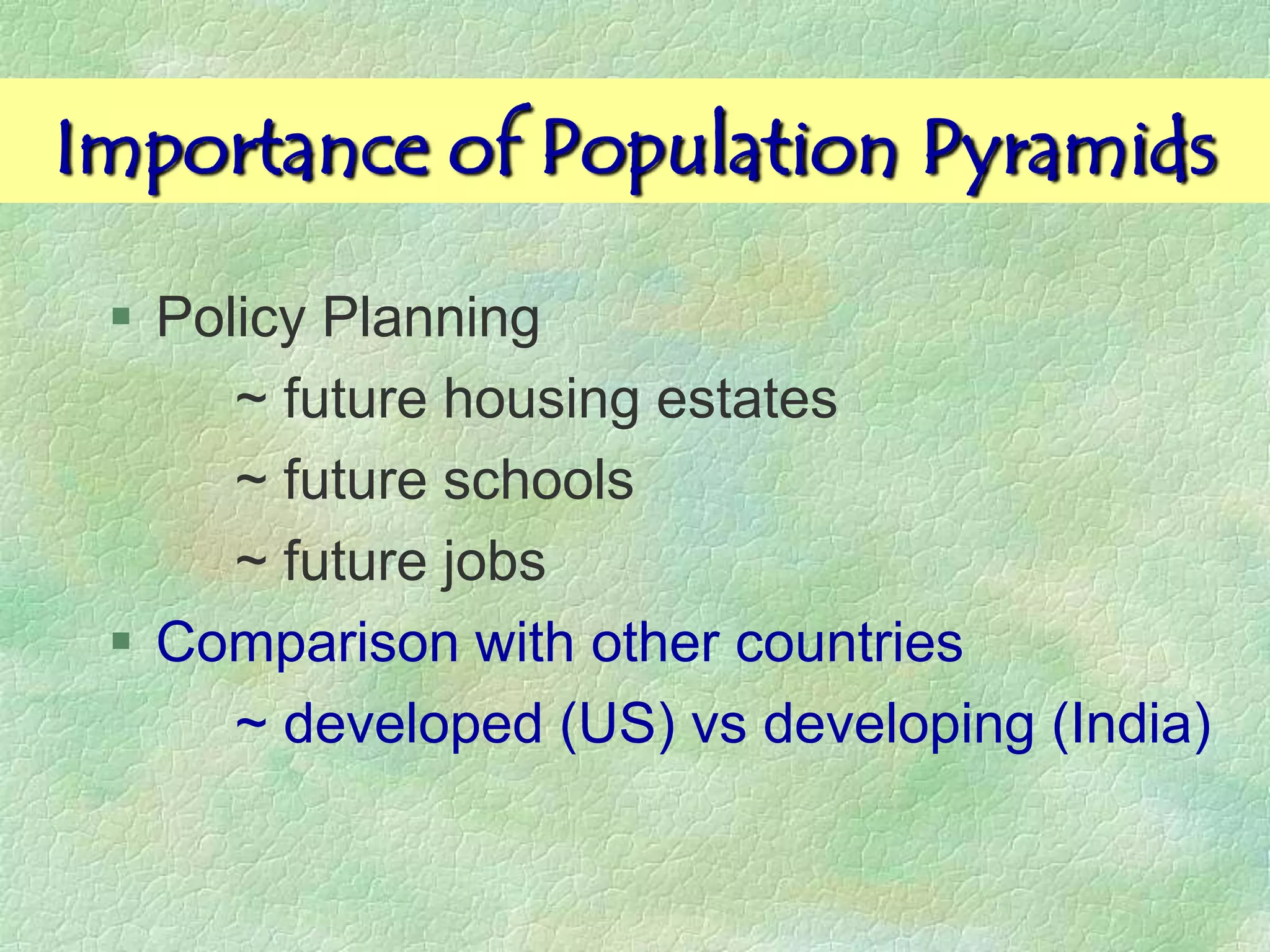
A population pyramid provides information about the proportion of males and females in different age groups. It shows the proportion of young, working-age, and elderly populations. Population pyramids can have triangular, beehive, or rectangular shapes depending on birth rates, death rates, and migration patterns. The shape and proportions revealed in a population pyramid tell the story of a country's demographic past, present, and possible future, making them important tools for policy planning and comparing countries.