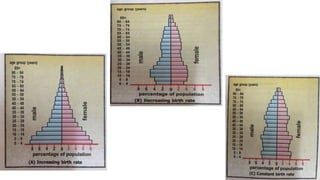
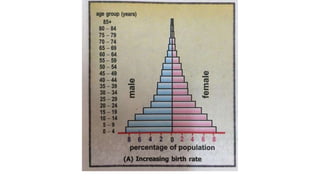
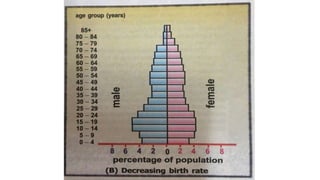
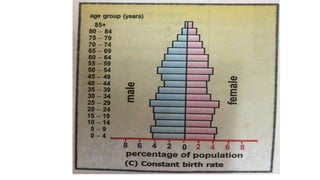
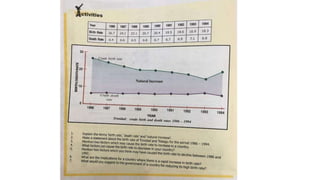
There are three types of population pyramids: expansive, slow growth, and no growth. A population pyramid graphically represents the age and sex composition of a population based on census data. Pyramid A represents a developing country with a high and increasing birth rate seen in its large 0-4 age group. Pyramid B shows a developed country with a decreasing birth rate seen by comparing age groups. Pyramid C has a birth rate that is neither increasing nor decreasing significantly.