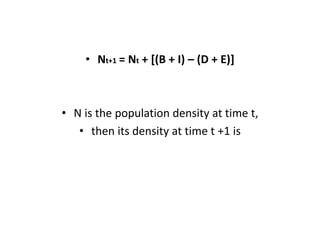Embed presentation





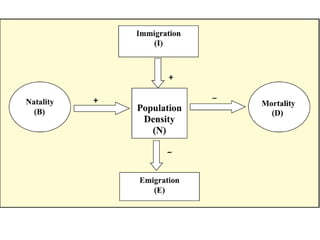
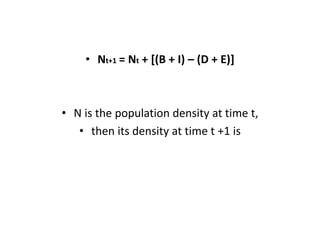







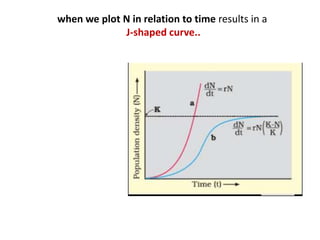




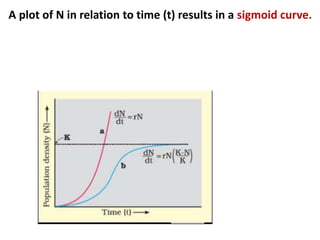






This document discusses population growth models, including exponential and logistic growth. Exponential growth occurs when resources are unlimited and the population grows rapidly in a J-shaped curve. Logistic growth occurs when resources are limited, causing the population to initially grow rapidly then slow down, reaching an asymptote as the carrying capacity is approached. Key factors that influence population growth are birth rates, death rates, immigration, emigration, food availability, and competition for limited resources. Governments have implemented controls to limit unsustainable human population growth.