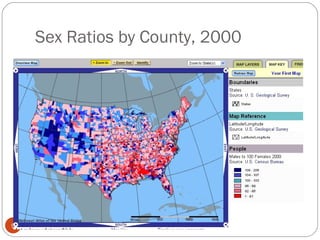
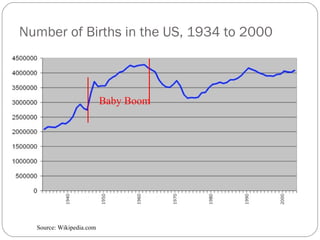
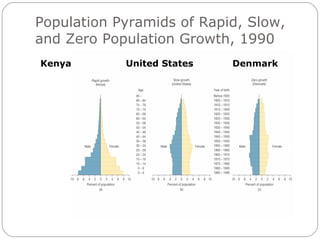
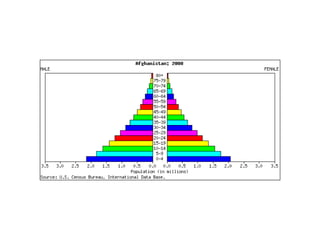
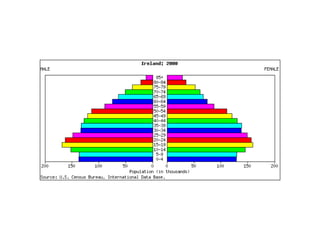
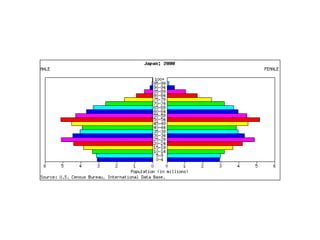
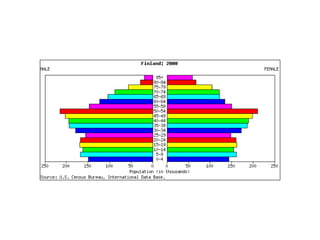
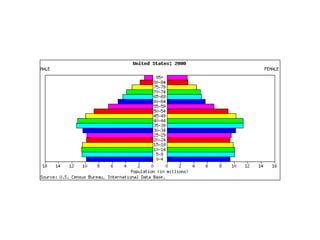
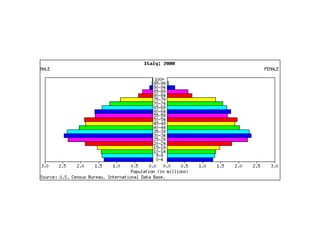
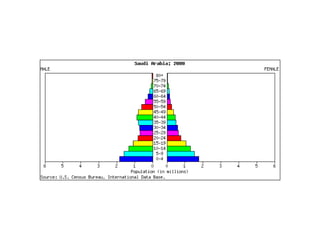
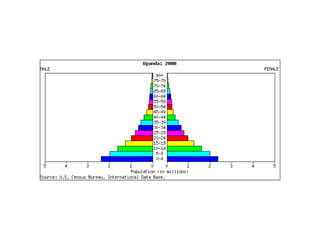
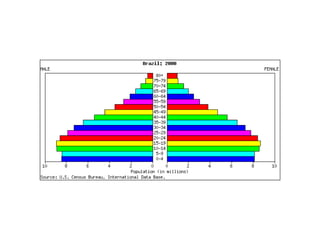
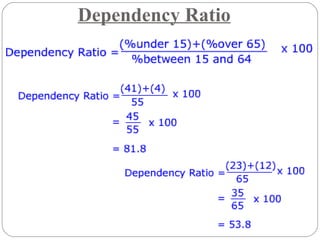
The document discusses key elements of population composition and structure, including sex ratio and age structure. It defines sex ratio as the number of males per 100 females in a population. Age structure is analyzed using population pyramids that show cohorts in 5-year age groups. The postwar US baby boom from 1946 to 1964 significantly increased births, affecting age structure. Analysis of population composition and structure is important for understanding future population growth patterns and the dependency ratio.