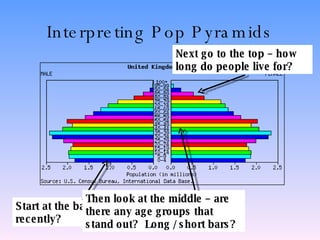
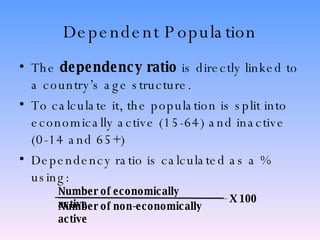
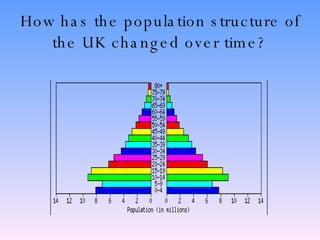
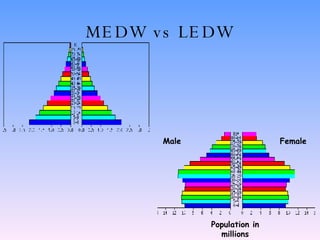
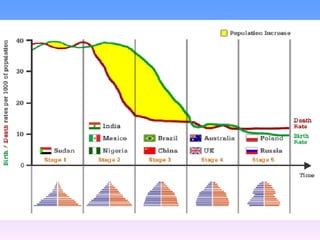
The document discusses population structure and how it can be analyzed using population pyramids. It explains that population structure looks at a country's population grouped by age and sex. Interpreting a population pyramid involves looking at recent birth rates at the base, life expectancy at the top, and any prominent age groups in the middle. It also introduces the dependency ratio, which compares economically active vs inactive portions of a population. The UK's population structure has changed from large families and high birth rates in the past to lower rates today, resulting in an aging population. Less developed countries typically have wider bases on their pyramids indicating high birth rates, while more developed countries have stabilized birth rates and more balanced age distributions.