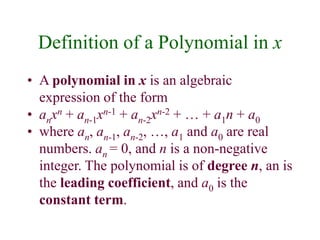
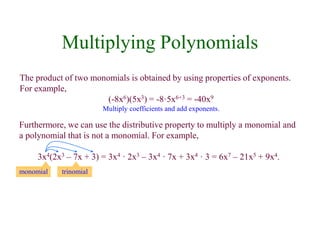
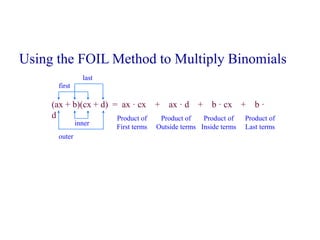
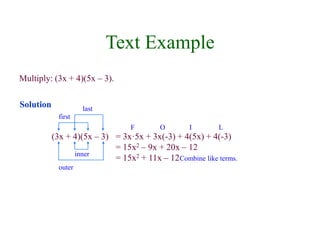
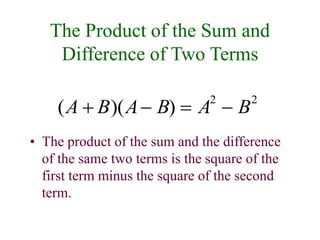
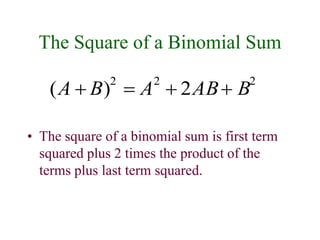
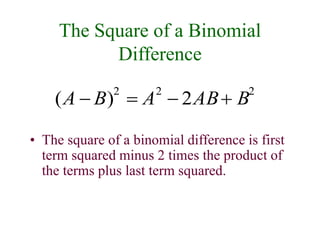
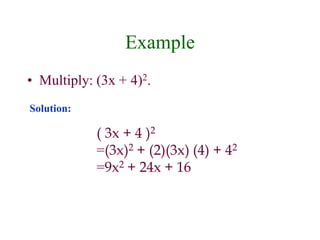
This document discusses polynomials and their properties. It defines polynomials as algebraic expressions involving terms of varying degrees, and defines the degree of a polynomial. It then covers operations like addition, multiplication, and factoring of polynomials using various properties and methods like FOIL. Examples are provided to demonstrate multiplying binomials and special products involving sums and differences of terms.