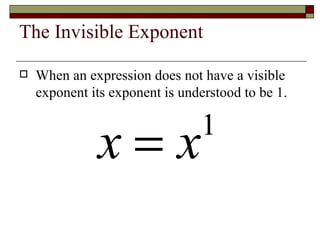
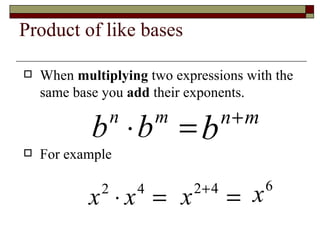
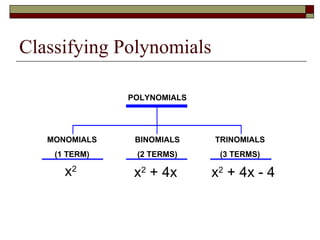
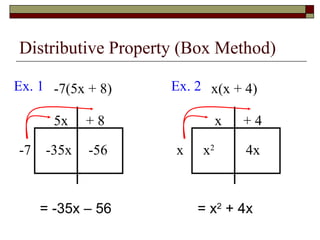
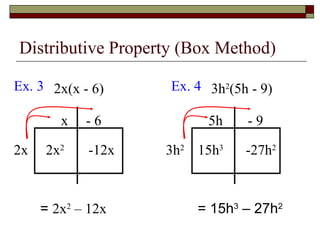
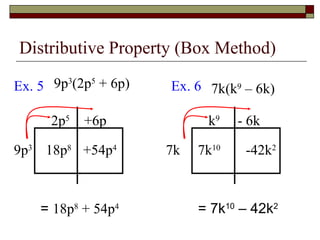
This document reviews rules of exponents and introduces multiplying polynomials using the distributive property and box method. It defines monomials, binomials, and trinomials. Examples are provided of distributing a monomial over a binomial using the box method, including rewriting the expression by combining like terms.