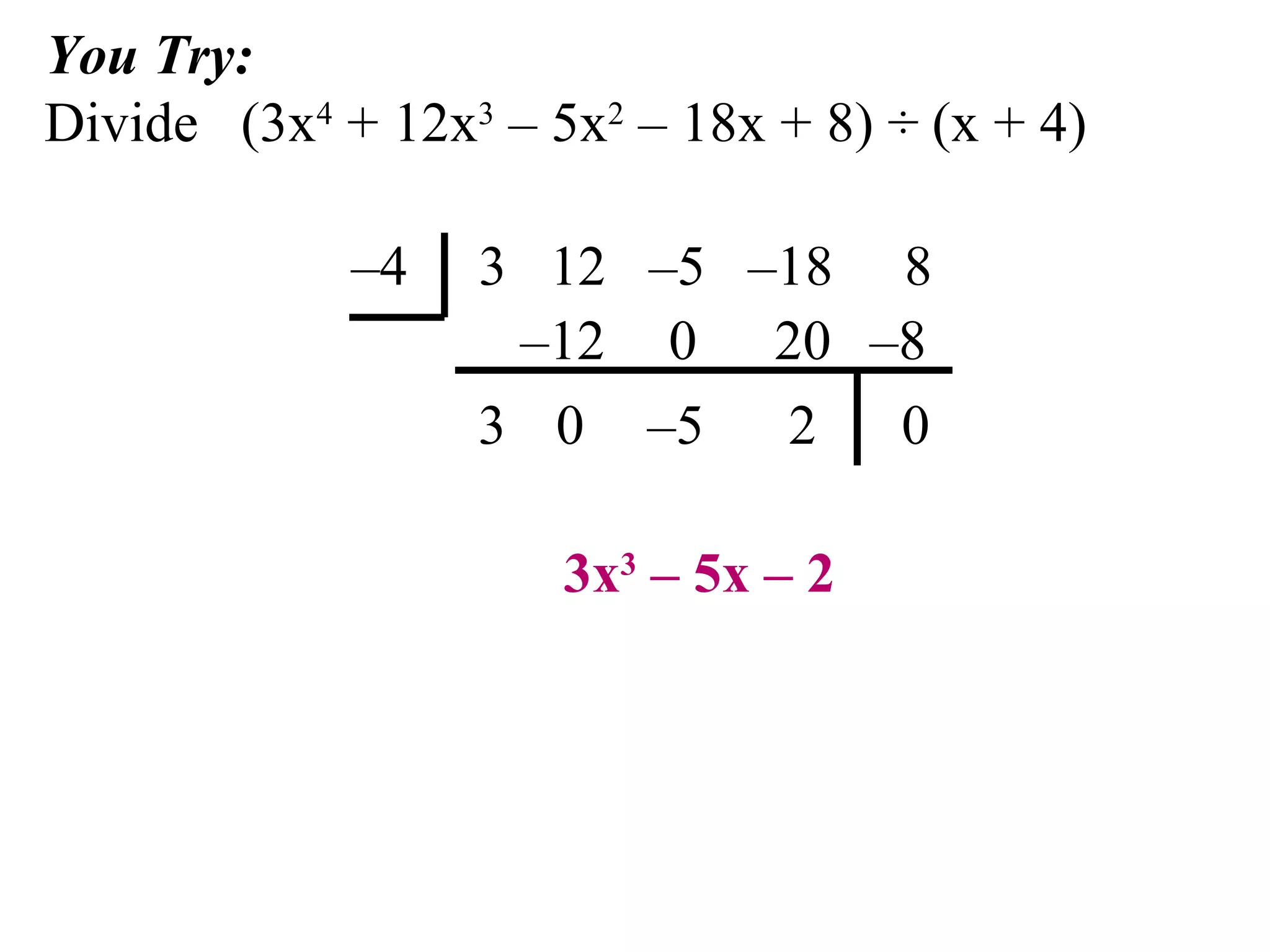Embed presentation
Downloaded 123 times
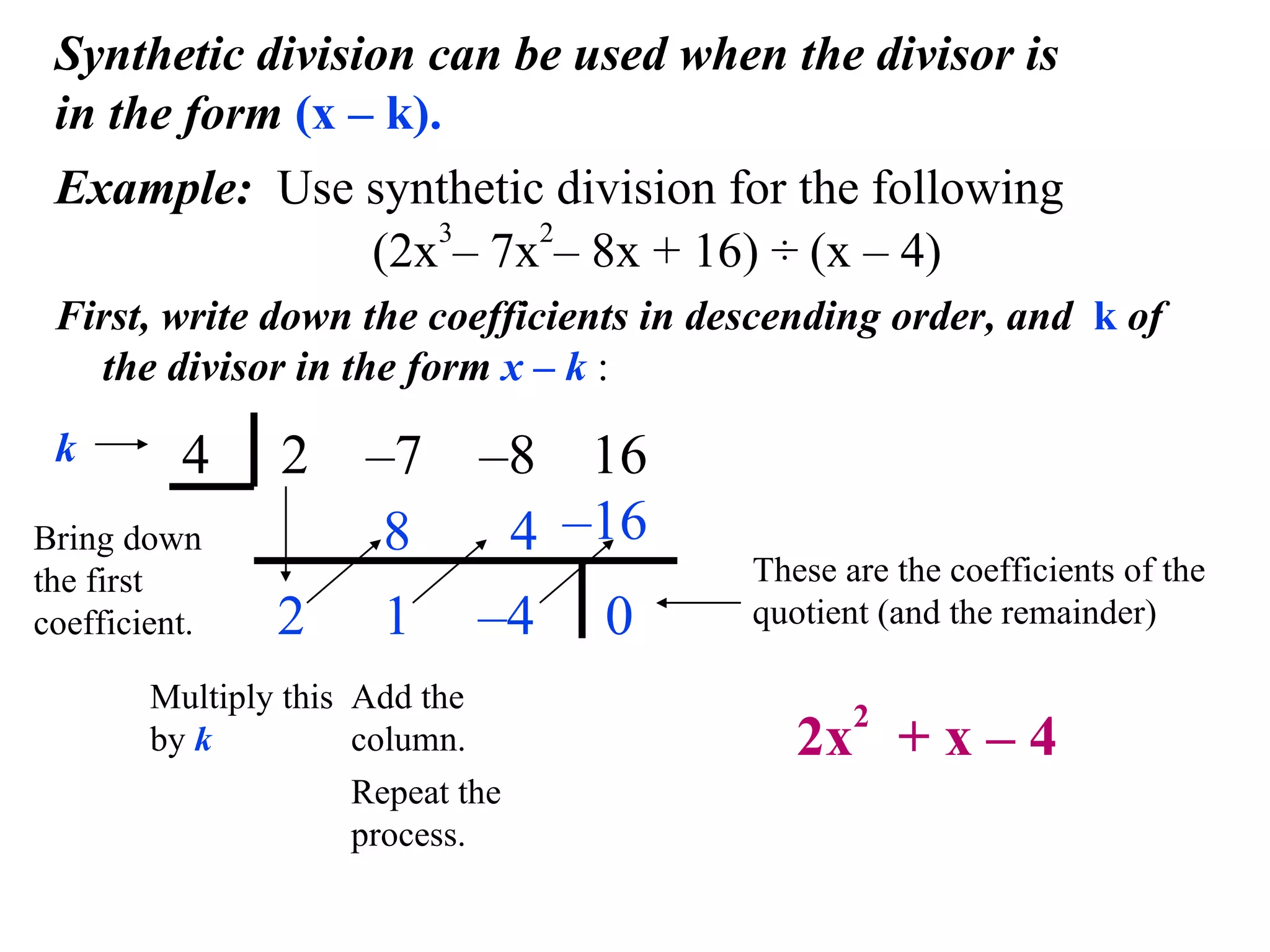
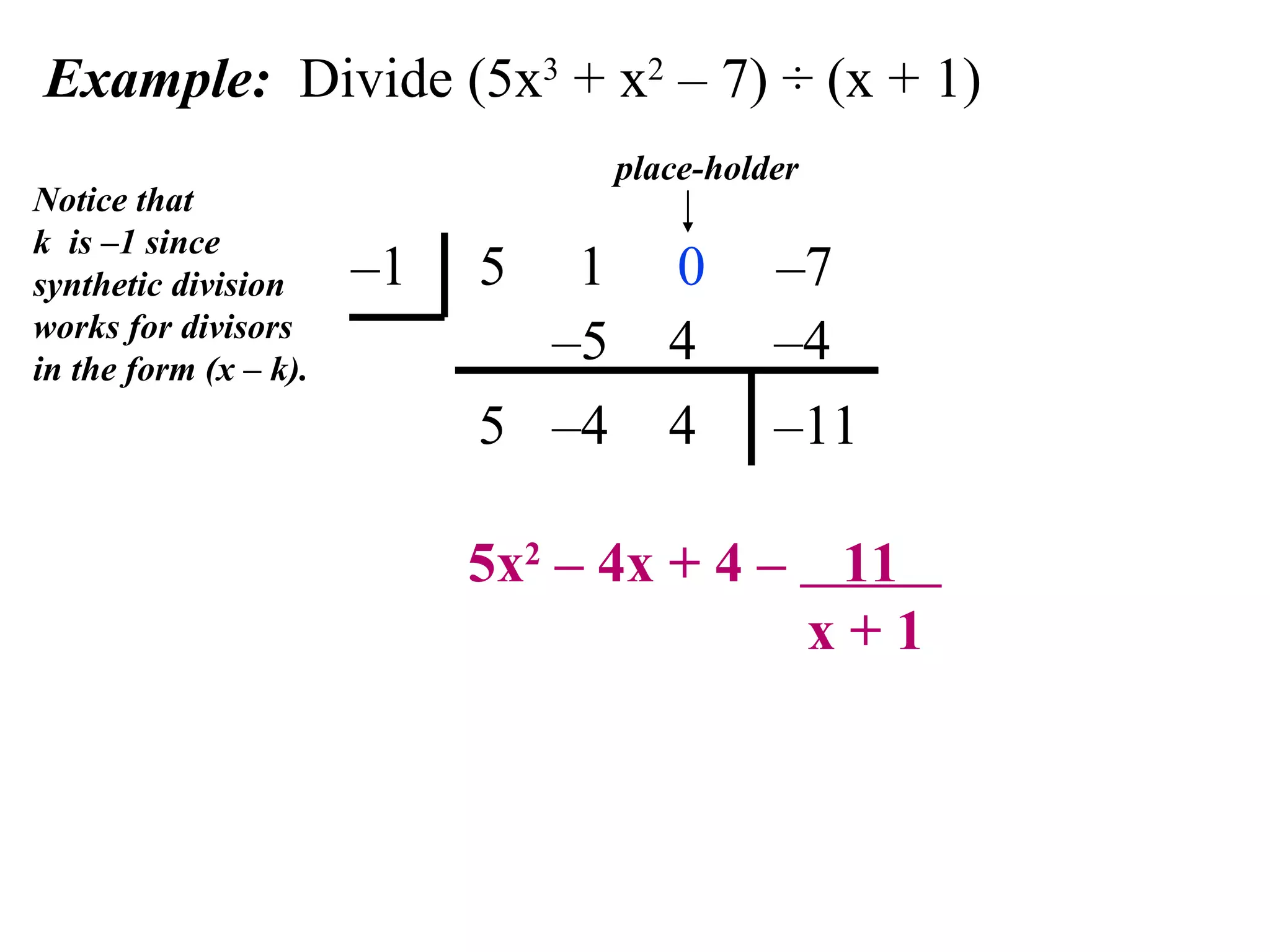
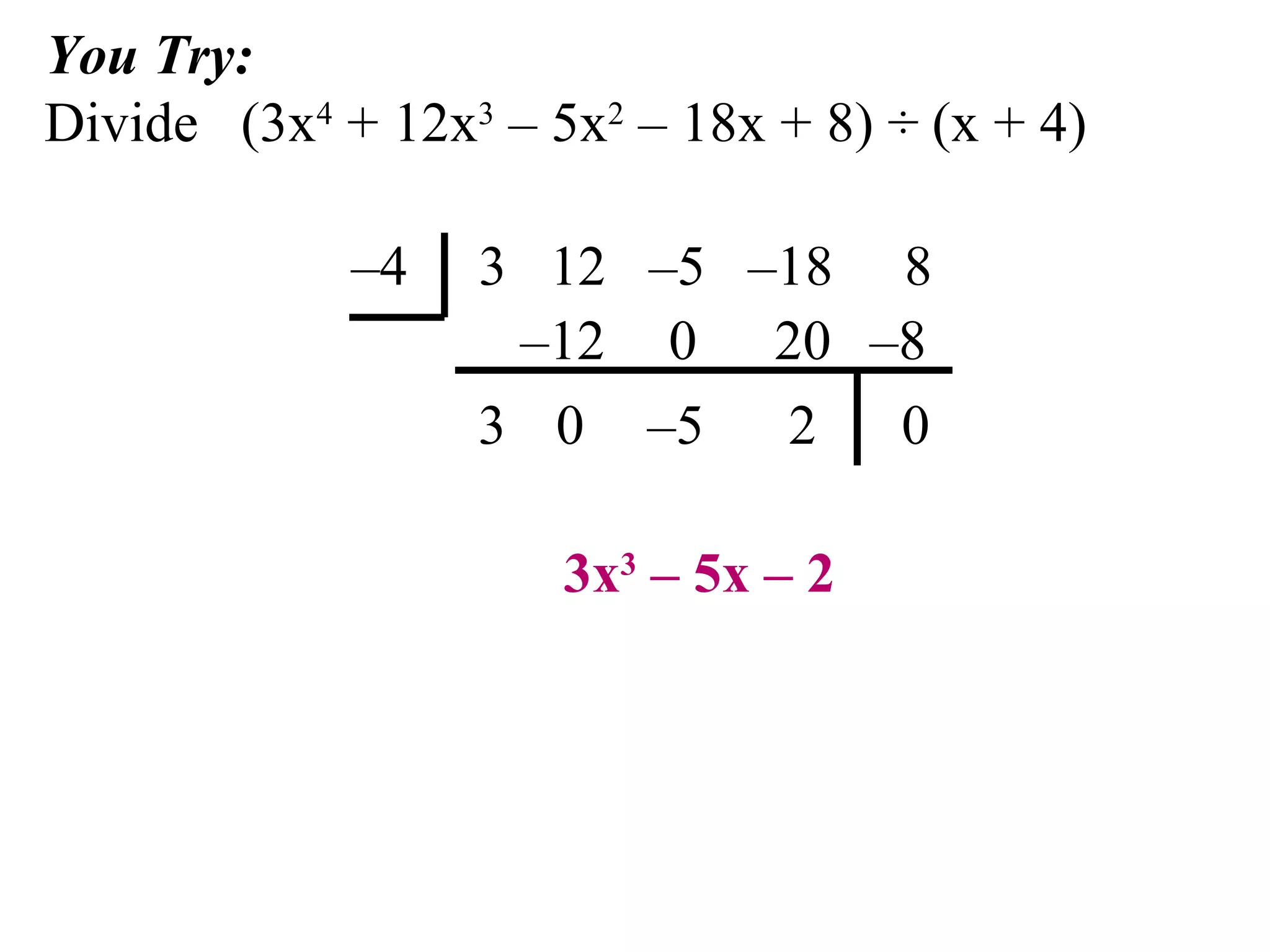
The document provides an explanation and examples of using synthetic division to divide polynomials. Synthetic division allows dividing a polynomial by a divisor of the form (x - k). The process involves writing the coefficients of the dividend in descending order and placing k below. Then, successive multiplication and addition steps provide the coefficients of the quotient polynomial and remainder. Two examples are worked through to demonstrate synthetic division for (2x^3 - 7x^2 - 8x + 16) / (x - 4) and (5x^3 + x^2 - 7) / (x + 1).