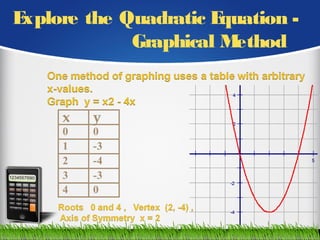
The document provides an extensive overview of solving quadratic equations, detailing various forms and methods including standard form, factoring, and the quadratic formula. It discusses the significance of coefficients a, b, and c, along with the discriminant's role in determining the nature of roots. Examples illustrate completing the square, factoring techniques, and graphical representation of quadratic functions.














![• By using quadratic formula –
• Substitute a=6, b=5 and c=−6 into the formula:
• x = (−b ± √[b2
− 4ac]) / 2a
• x = (−5 ± √[52
− 4×6×(−6)]) / 2×6
• = (−5 ± √[25 + 144]) / 12
• = (−5 ± √169) / 12
• = (−5 ± 13) / 12
• So the two roots are:
• x = (-5 + 13) / 12 = 8/12 = 2/3,
• x = (-5 − 13) / 12 = −18/12 = −3/2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mathutkarshfa3-160309163744/85/Quadratic-Equation-16-320.jpg)