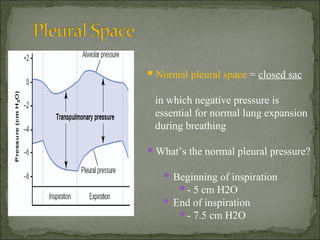
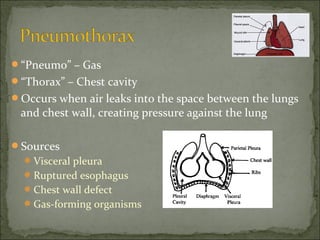
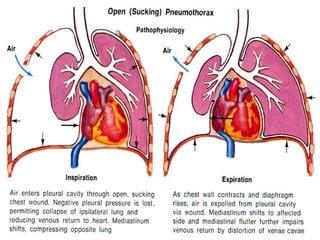
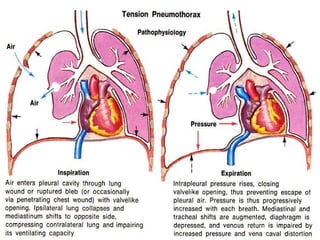
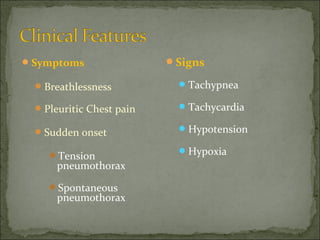
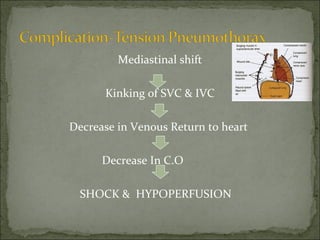
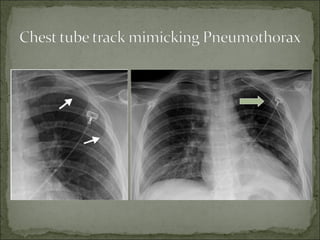
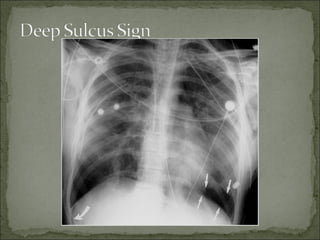
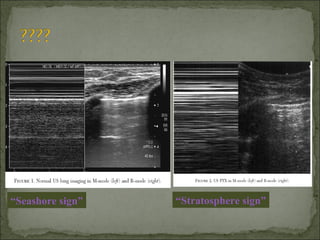
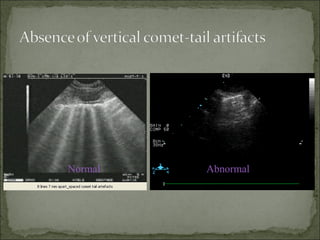
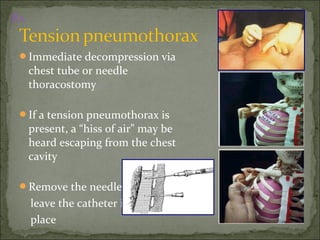
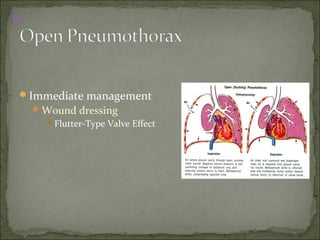
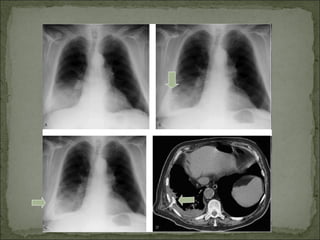
The document discusses pneumothorax, which is air in the pleural space between the lungs and chest wall. It notes that the normal pleural pressure is -5 cm H2O at the beginning of inspiration and -7.5 cm H2O at the end. Pneumothorax can be caused by trauma, medical procedures, or underlying lung conditions. Signs include shortness of breath, chest pain, and decreased breath sounds on examination. Treatment involves needle aspiration or chest tube placement to remove air and re-expand the lung. Recurrent or tension pneumothorax may require surgery.