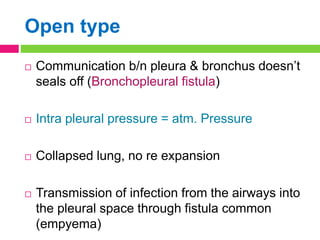
This document discusses pneumothorax, which is the presence of air in the pleural space. It can be spontaneous, due to underlying lung disease or trauma, or iatrogenic due to medical procedures. The types are described as closed, open, or tension pneumothorax. Clinical features include chest pain and breathlessness. Diagnosis is made through chest x-ray or CT scan. Treatment depends on the type and severity, ranging from needle aspiration for minor cases to chest tube drainage or surgery for more severe or recurrent cases.













![Clinical features
Sudden onset of unliateral pleuritic chest pain
Breathlessness
[In pts with a small pneumothorax, physical
examination may be normal ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pneumothorax-141022120943-conversion-gate02-181207022132/85/Pneumothorax-A-quick-Review-15-320.jpg)






![Investigations
Chest x ray
Shows : increased radiolucency, with absence of
bronchovascular markings
extend of mediastinal shift.
pleural fluid ,if present .
underlying pulmonary disease .
(costophrenic angles are clear)
[care must be taken to differentiate b/n a large pre-existing bulla &
a pneumothorax to avoid misdirected attempts at aspiration]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pneumothorax-141022120943-conversion-gate02-181207022132/85/Pneumothorax-A-quick-Review-22-320.jpg)







![Secondary pneumothorax
Even a small secondary pneumothorax may
cause respiratory failure, so all such patients require
↓
Intercostal tube drainage
[Intercostal drains are inserted in the 4th ,5th or 6th
intercostal space in the midaxillary line ,connected
to an under waterseal]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pneumothorax-141022120943-conversion-gate02-181207022132/85/Pneumothorax-A-quick-Review-30-320.jpg)






