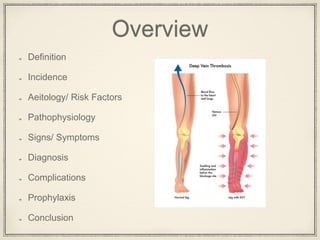
This document discusses deep vein thrombosis (DVT) prophylaxis. It defines DVT as clot formation in the deep veins of the legs, with an annual incidence of 1-2 per 1000 people in the US. Risk factors include surgery, injury, prolonged bed rest, estrogen use, and inherited clotting disorders. Signs and symptoms include leg pain, swelling, and difficulty breathing. Diagnosis involves duplex ultrasound and other imaging tests. Complications include pulmonary embolism and post-thrombotic syndrome. Prophylaxis includes mechanical methods, aspirin, anticoagulants, and stratified prophylaxis based on patient risk factors. The goal of prophylaxis is to prevent DVT and its