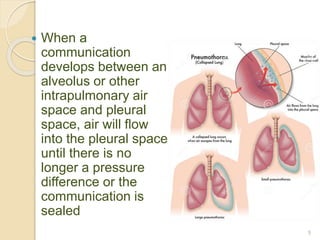
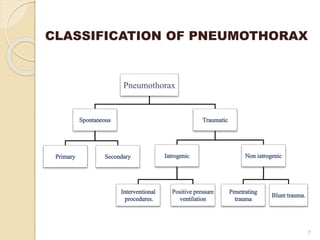
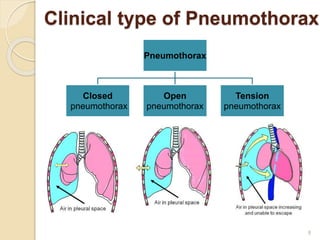
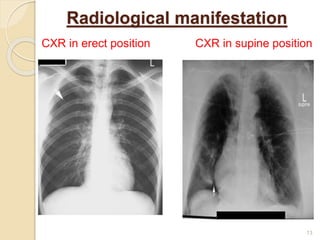
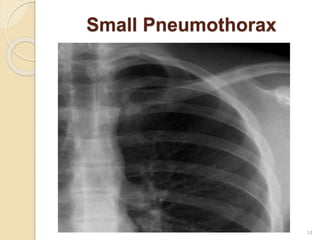
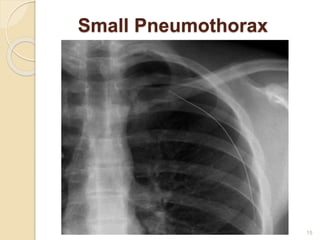
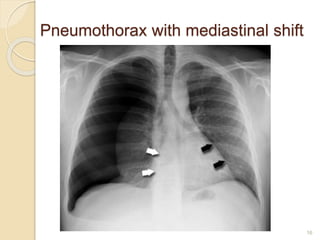
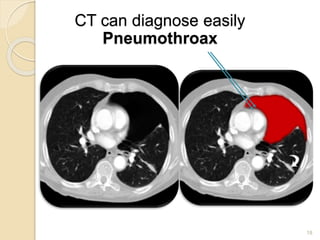
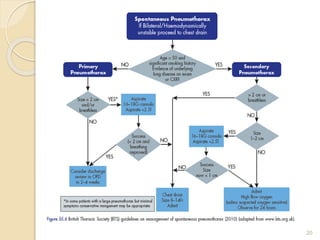
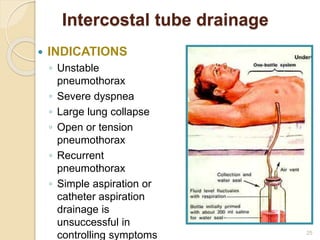
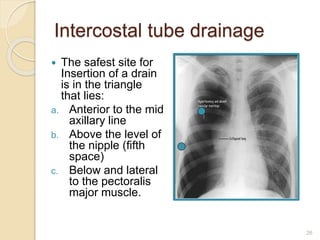
This document provides an overview of pneumothorax, including its definition, classification, mechanisms, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and management. Pneumothorax is defined as the presence of air in the pleural space, and can be spontaneous, traumatic, or iatrogenic. It presents with symptoms like dyspnea and chest pain. Diagnosis is typically made through chest x-ray or CT scan. Management depends on the type and severity, and may include oxygen therapy, needle aspiration, chest tube drainage, or surgery like pleurodesis for recurrent cases.