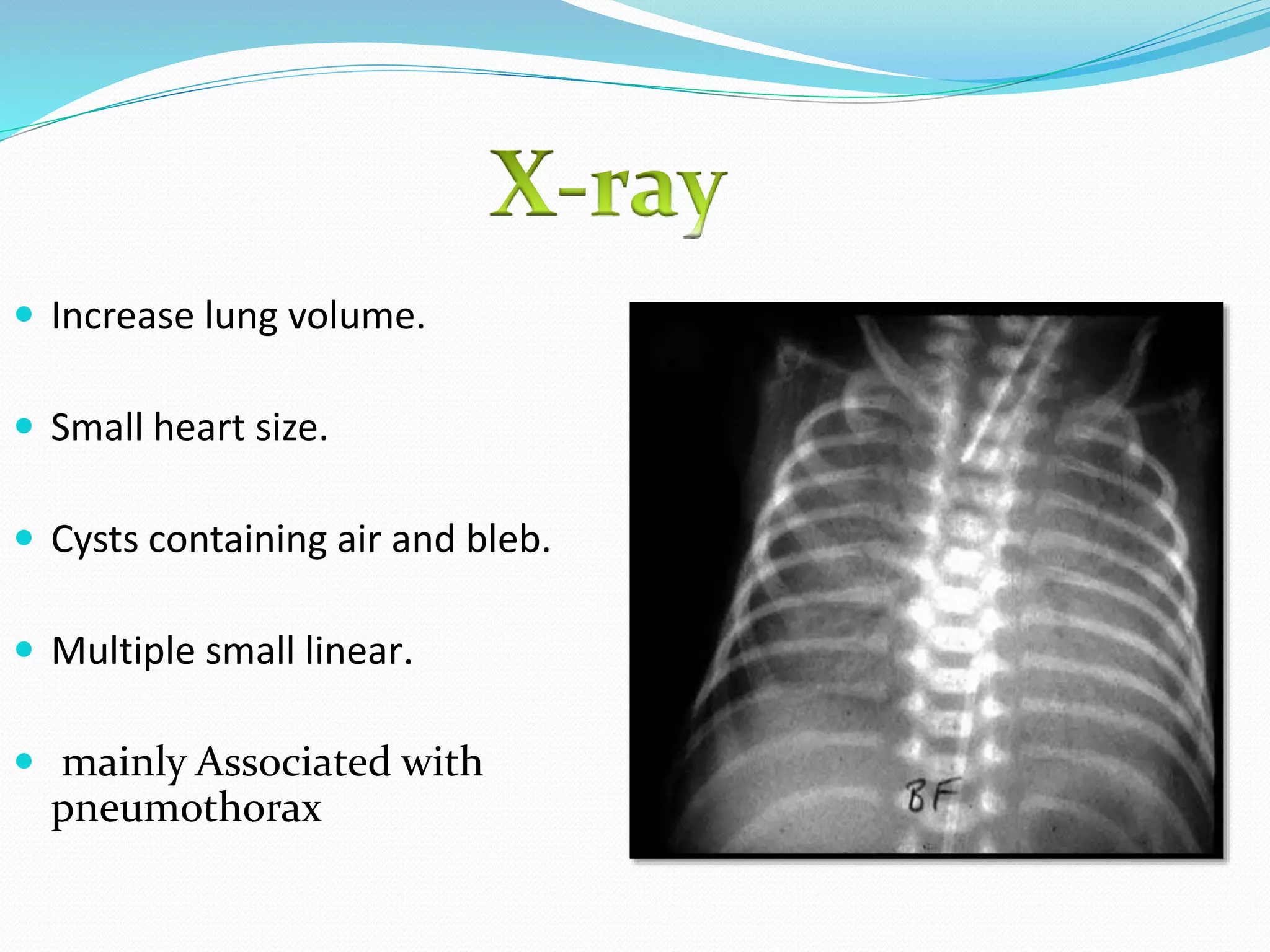
This document discusses air leak syndrome, which refers to the escape of air from the lungs into other tissues. It can include pulmonary interstitial emphysema, pneumothorax, pneumomediastinum, pneumopericardium, pneumoperitoneum, and subcutaneous emphysema. Pneumothorax, or air in the pleural space between the lung and chest wall, is the most common type. Risk factors include prematurity, mechanical ventilation, and diseases that damage lung tissue. Symptoms depend on the location and amount of air, and treatment ranges from supportive care to needle aspiration or chest tube insertion for more severe cases.