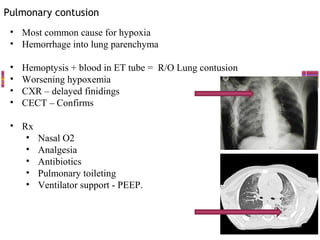
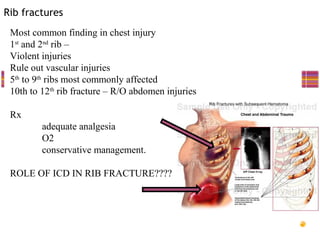
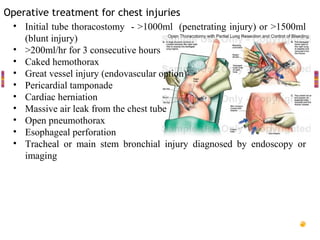
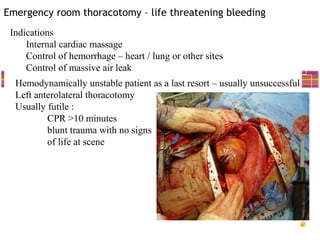
This document provides an overview of chest trauma, including:
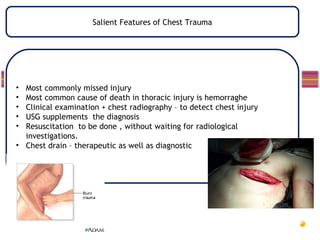
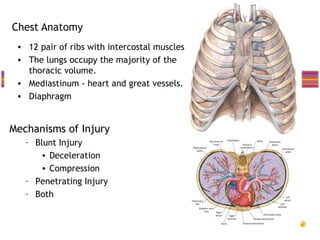
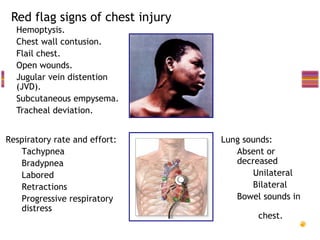
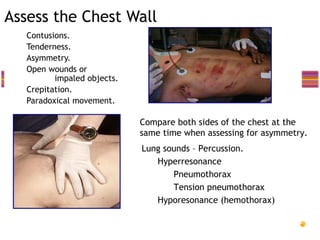
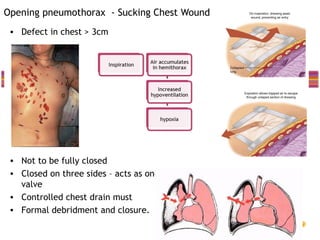
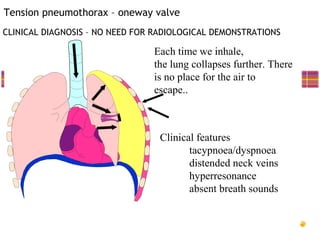
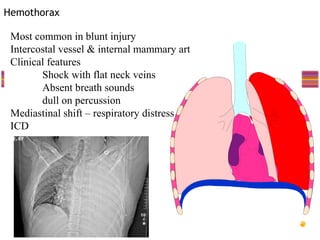
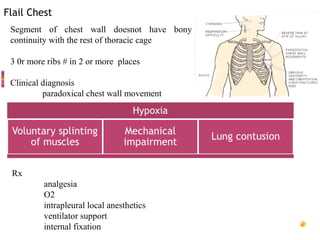
- Common injuries like pneumothorax, hemothorax, flail chest and their signs and symptoms.
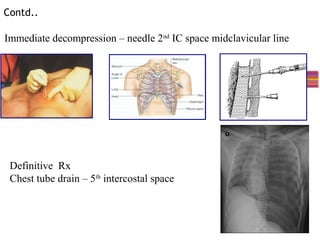
- Assessment involves clinical exam, chest x-ray and ultrasound to detect injuries. Chest tube insertion can be both therapeutic and diagnostic.
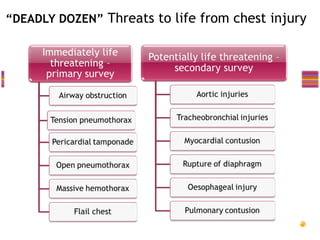
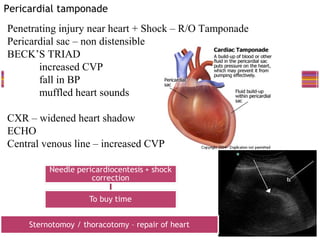
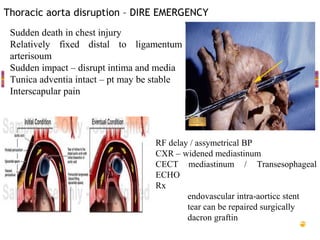
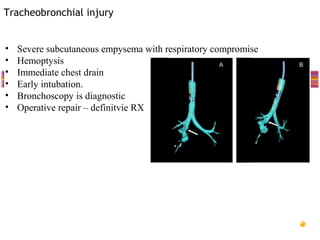
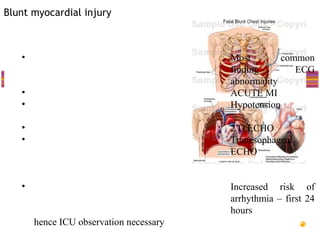
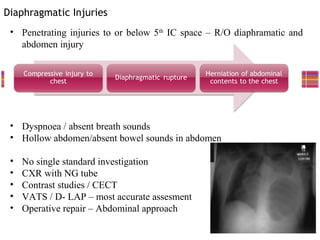
- "Deadly dozen" life-threatening injuries from chest trauma include tension pneumothorax, cardiac tamponade, aortic disruption and others that often require emergency procedures or surgery.
- Management involves airway control, ventilation, chest tube drainage, analgesia and monitoring for complications like respiratory failure. Operative treatment is indicated for severe injuries or those not responding to initial management.