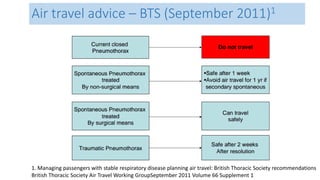
This document provides an overview of pneumothorax, including:
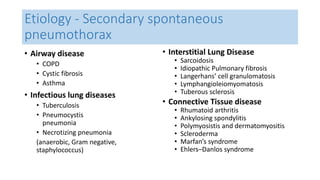
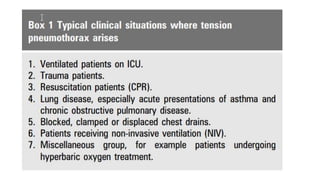
- Classification as spontaneous (primary or secondary), traumatic, or iatrogenic
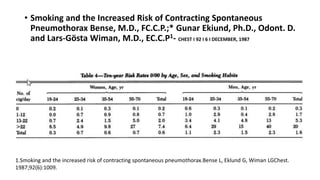
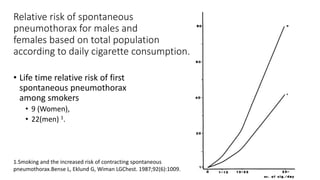
- Risk factors like smoking, COPD, and connective tissue diseases for secondary spontaneous pneumothorax
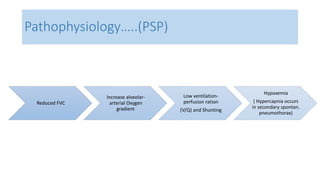
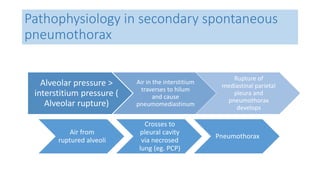
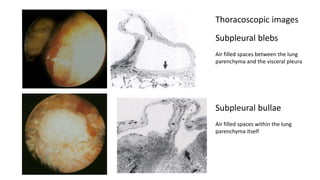
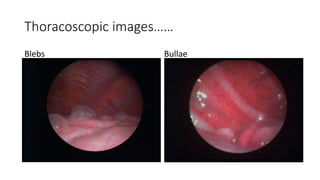
- Pathophysiology involving bleb/bullae rupture and air migration into the pleural space
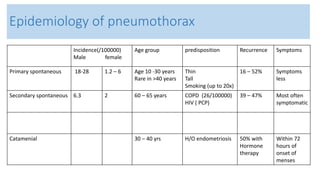
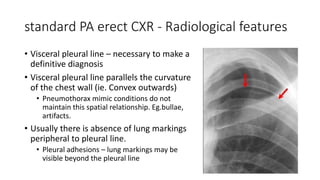
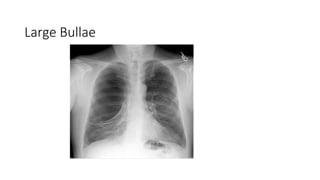
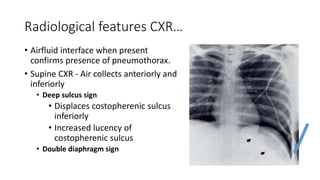
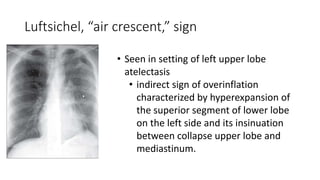
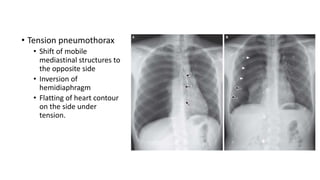
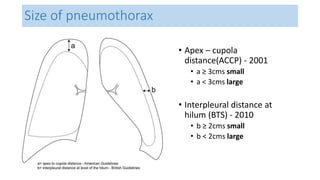
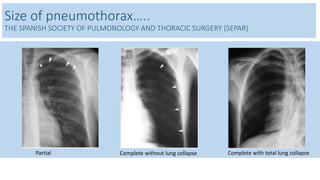
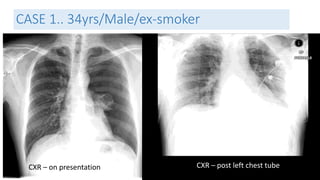
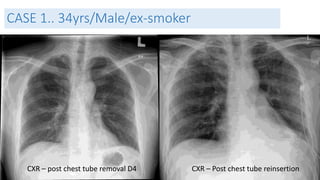
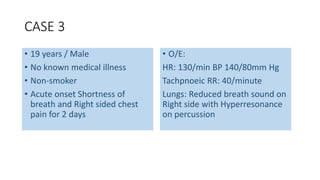
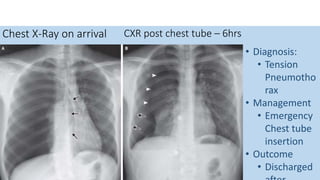
- Clinical features like chest pain and shortness of breath, and radiological findings on CXR and CT scans
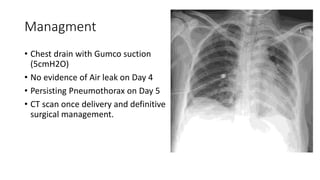
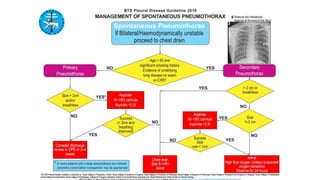
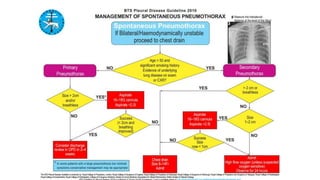
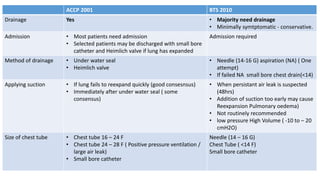
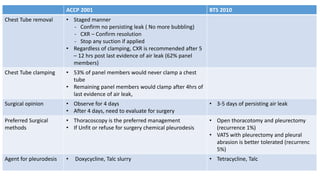
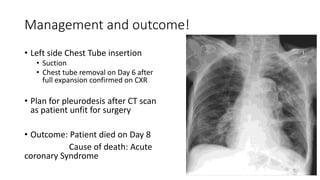
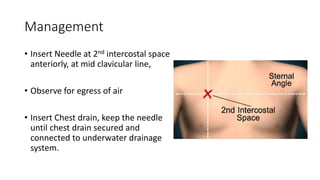
- Management approaches like chest tube insertion, pleurodesis, and VATS for recurrent or large pneumothoraces.









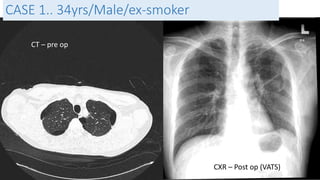




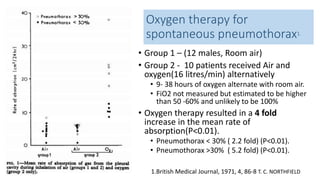
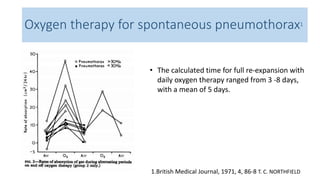
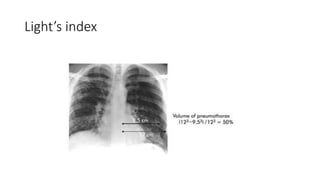


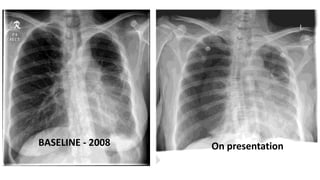
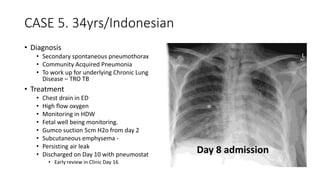
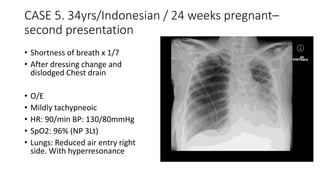
![CASE 5
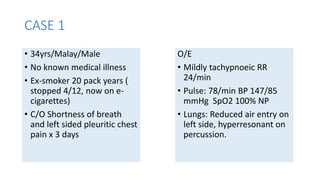
• 34 yrs / Indonesian / Female
• G4 P2 L1 [21 weeks pregnant]
• BGHx:
• PDA under cardio follow up detected
2006 during 3rd pregnancy
• ECHO: PDA 0.47cm, Left to Right shunt,
No evidence of Pulm. HTN
• Detected to have ? Lung disease in
2008 not worked up.
• Presented with Shortness of breath
for 10/7 and cough x 3/7
• O/E
• Mildy tachpneoic, RR 24/min
• Speaking in full sentences
• Pulse: 88/min
• BP: 130/70 mmHg
• sPO2: 97% Room air
• Lungs: Reduced air entry on
the right side with
hyperresonant on right side](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pneumothorax-casebased-141110144104-conversion-gate02/85/Pneumothorax-case-based-51-320.jpg)