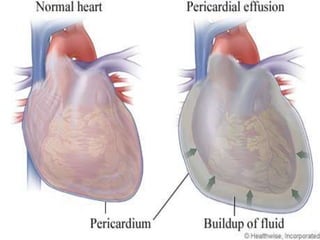
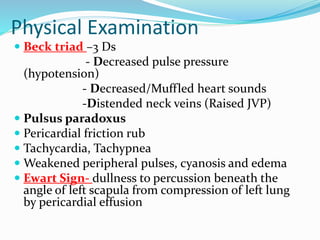
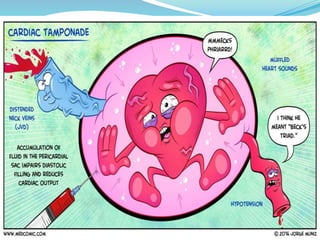
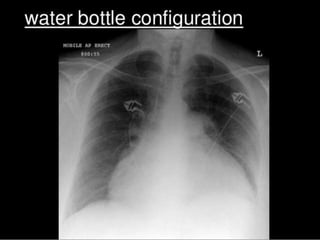
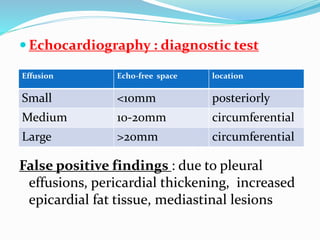
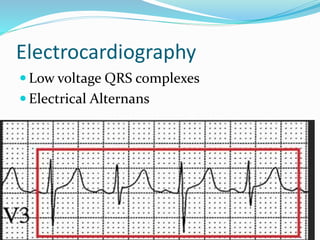
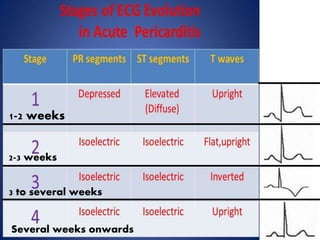
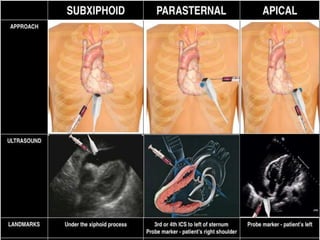
This document defines pericardial effusion and cardiac tamponade, discusses their pathophysiology, etiology, clinical presentation, investigations, and management. Pericardial effusion is an abnormal amount of fluid in the pericardial space, while cardiac tamponade is acute heart failure caused by compression of the heart from a large or rapidly developing effusion. Clinical manifestations depend on the rate of fluid accumulation and include chest pain, lightheadedness, and decreased pulse pressure. Investigations include echocardiography, electrocardiography, and pericardiocentesis. Management involves bed rest, medications, drainage procedures, and surgery in severe cases.