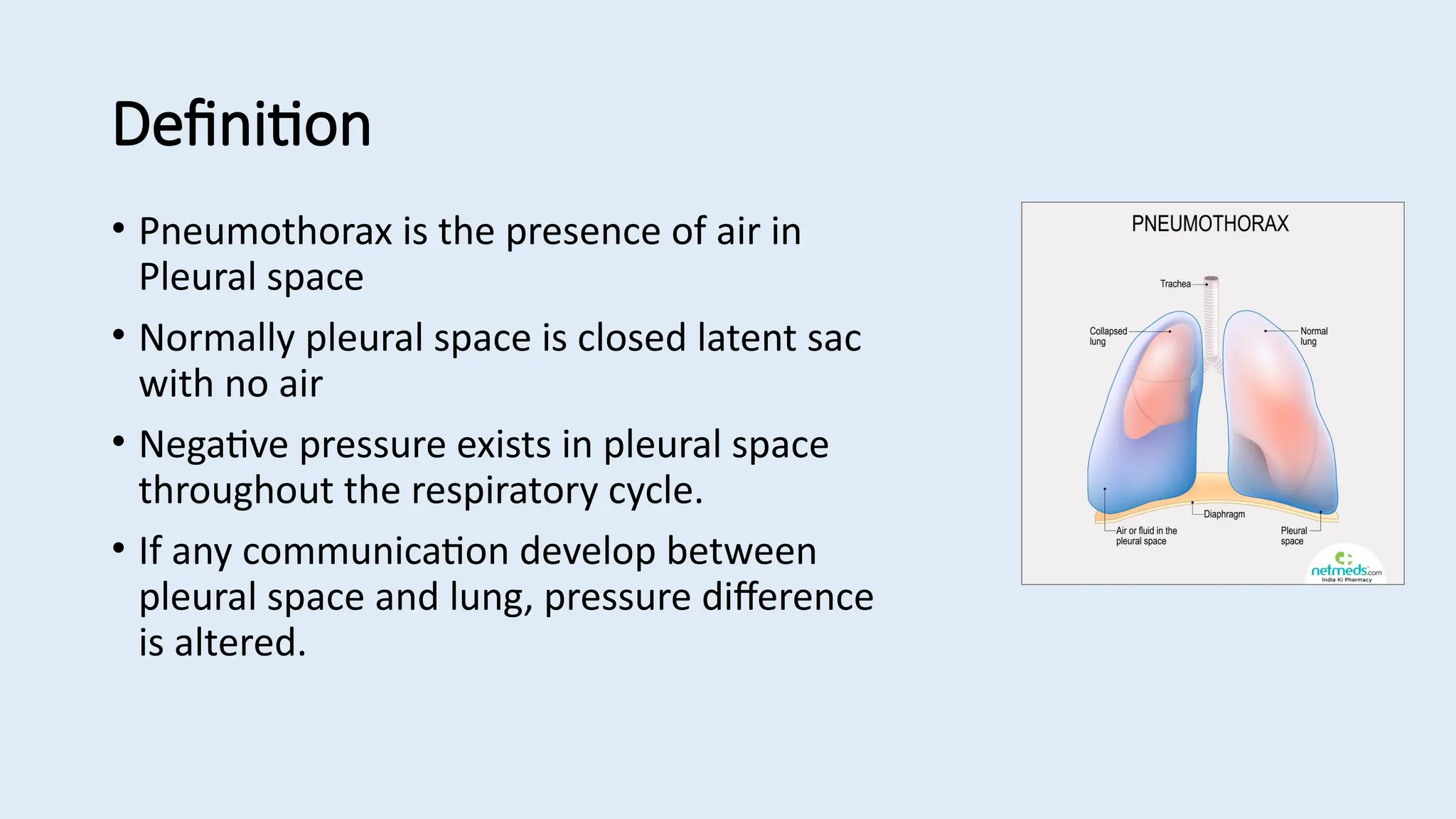
Pneumothorax is defined as the presence of air in the pleural space, which can be classified into spontaneous, traumatic, and tension pneumothorax, each with distinct causes and management strategies. Clinical features include pleuritic chest pain, breathlessness, and signs of shock in severe cases; diagnosis primarily involves chest X-ray, CT, and ultrasound. Management includes observation, decompression for tension pneumothorax, intercostal drain insertion, and potential surgical intervention for persistent cases.