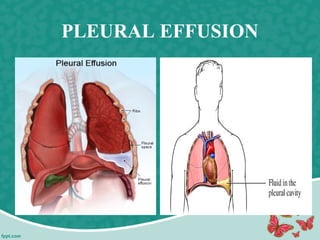
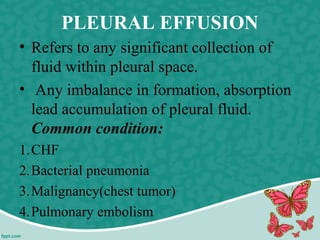
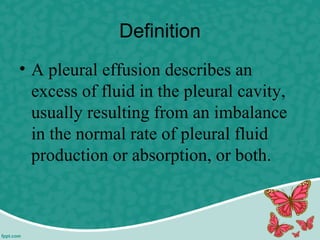
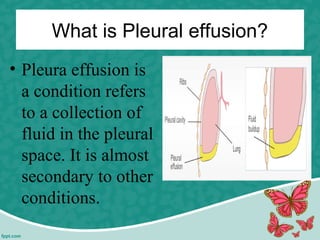
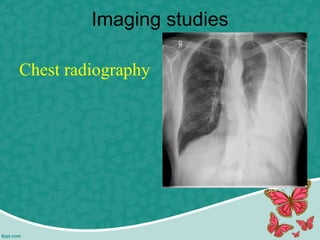
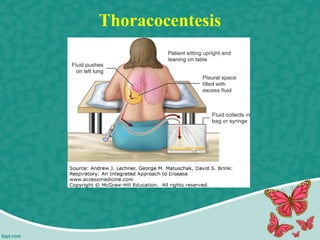
Pleural effusion is the accumulation of excess fluid in the pleural cavity, which can impair breathing and is usually caused by conditions such as congestive heart failure, pneumonia, or malignancy. There are two main types of pleural effusion – transudative and exudative – distinguished by their characteristics and underlying causes. Diagnosis involves history, physical exam, and imaging, while management includes thoracentesis and nursing interventions to support respiratory function and prevent complications.