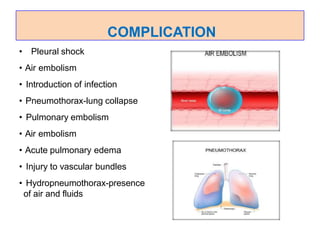
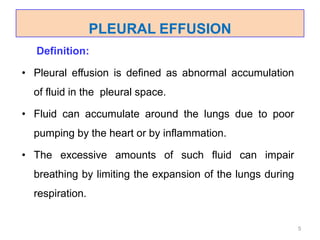
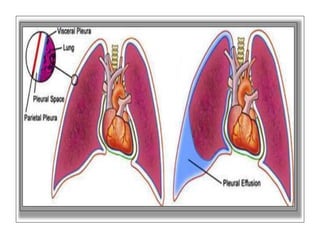
This document discusses pleural effusion, which is an accumulation of fluid in the pleural space between the lungs and chest wall. It can be caused by conditions like heart failure, infections, cancer, or autoimmune disorders. The fluid is classified as a transudate or exudate based on its composition. Symptoms include shortness of breath and chest pain. Diagnosis involves x-rays, ultrasound, or thoracentesis to analyze the fluid. Treatment depends on the underlying cause but may include draining fluid, treating the infection or heart condition, or surgery in severe cases. Nurses monitor for respiratory distress and manage chest tubes if used to drain the fluid.



![PLEURAL EFFUSION
Introduction:
• Pleural effusions are accumulations of fluid
within the pleural space. They are classified as
transudates or exudates.
• TRANSUDATES-fluid buildup caused by systemic
conditions[ due to cardiac or renal problem]
• EXUDATES-fluid buildup caused by tissue leakage due
to inflammation or local cellular damage.
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitiii3-230325072411-0059d3da/85/Unit-III-3-Pleural-Effusion-ppt-4-320.jpg)


![.Clear ultra filtrate of plasma
•Volume - 0.3 ml/kg[eg.50kg=12ml]
•Cells/ mm3 -1000 – 5000
•Mesothelial cells - 60%
•Monocytes - 30%
•Lymphocytes - 5%
•Protein - 1-2 g/dl
COMPOSITION OF PLEURAL FLUID](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitiii3-230325072411-0059d3da/85/Unit-III-3-Pleural-Effusion-ppt-9-320.jpg)
![CLASSIFICATION
a)Based on site
Apical
Inter lobar
Sub-pulmonic-base[btw pleura and diaphragm]
Mediastinal-btw the lungs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitiii3-230325072411-0059d3da/85/Unit-III-3-Pleural-Effusion-ppt-10-320.jpg)
![B)Based on mechanism and type of pleural fluid
Transudative
Exudative
Serous fluid[hydrothorax]-accumulation of serous fluid in
pleural cavity
Blood[haemothorax]-blood accumulating in pleural cavity
Pus [pyothorax or empyema]- accumulation of pus in
pleural cavity
Chyle[chylothorax]-milky body fluid contains fatty cells](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitiii3-230325072411-0059d3da/85/Unit-III-3-Pleural-Effusion-ppt-11-320.jpg)
![ETIOLOGY
• A viral infection such as the flu[influenza]
• A bacterial infection,such as pneumonia
• A fungal infection
• Autoimmune disorder eg.rheumatoid arthritis
• Certain medications
• Lung cancer near the pleural surface](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitiii3-230325072411-0059d3da/85/Unit-III-3-Pleural-Effusion-ppt-12-320.jpg)

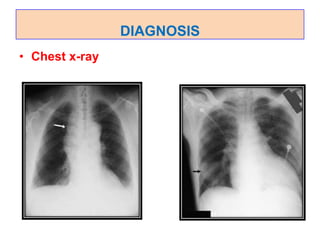
![• CT scan of chest
• Ultrasound of the chest
• Thoracentesis- a needle is inserted between
the ribs to remove a biopsy or to collect fluid]
• Pleural fluid analysis-examination of the fluid
removed from the pleural space.
• Thoracoscopy- minimally invasive technique
allows for a visual evaluation of the pleura
- It is also known as video assisted
thoracoscopic surgery[VATS]
- It is performed under general anesthesia](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitiii3-230325072411-0059d3da/85/Unit-III-3-Pleural-Effusion-ppt-18-320.jpg)
![MANAGEMENT
Treatment of pleural effusion is based on the
underlying condition and whether the effusion is causing
severe respiratory symptoms such as shortness of breath
or difficulty breathing.
Congestive heart failure- treat with diuretics
Thoracentesis [ tube thoracostomy ]- drained through a
chest tube.
Pleural sclerosis performed with sclerosing agents[such
as doxycycline , tetracycline]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitiii3-230325072411-0059d3da/85/Unit-III-3-Pleural-Effusion-ppt-19-320.jpg)