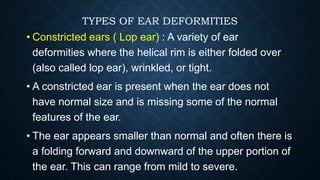
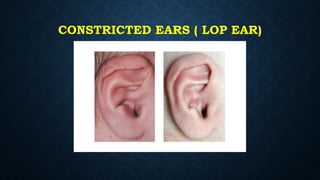
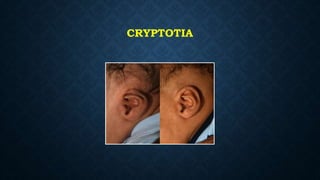
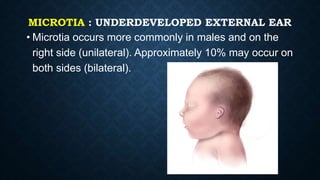
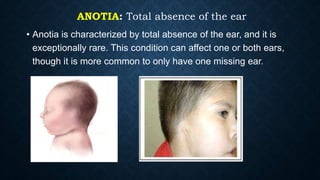
The document discusses various congenital ear deformities, their causes, and types. Conditions such as protruding ears, constricted ears, microtia, and anotia are highlighted, along with potential genetic and environmental factors leading to these deformities. Treatment typically involves a multidisciplinary approach, including surgical and medical interventions, tailored to the specific type and severity of the deformity.