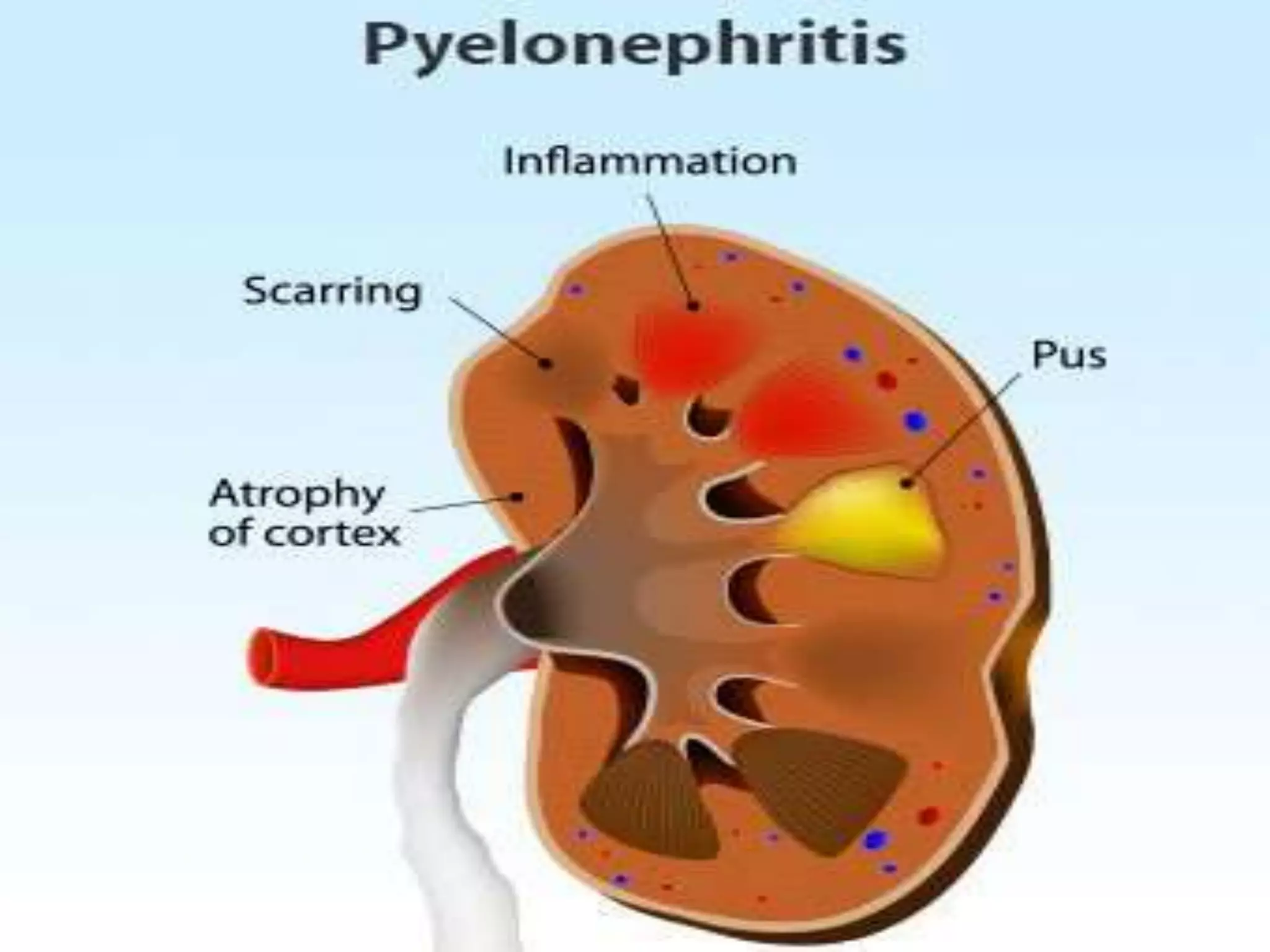
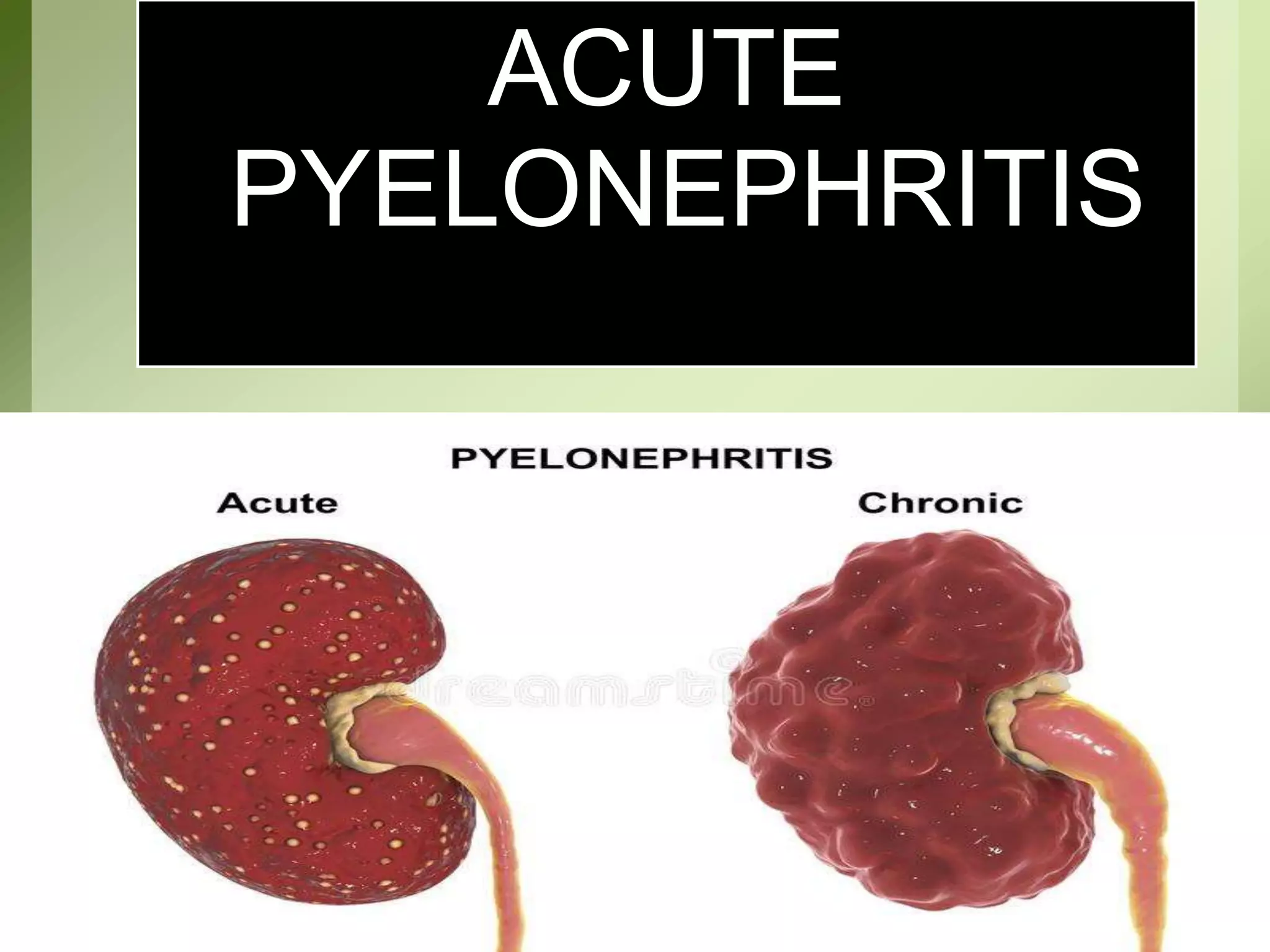
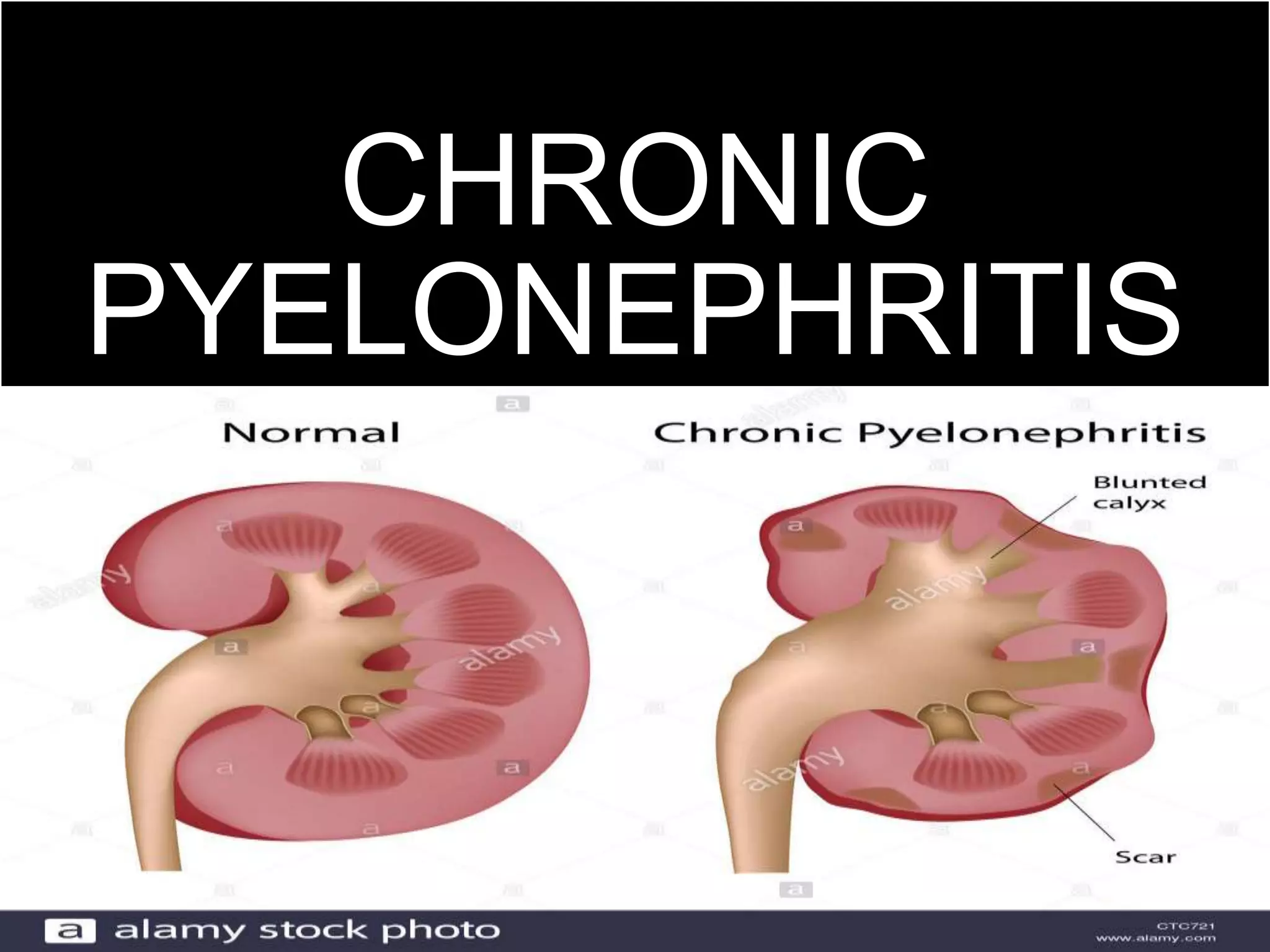
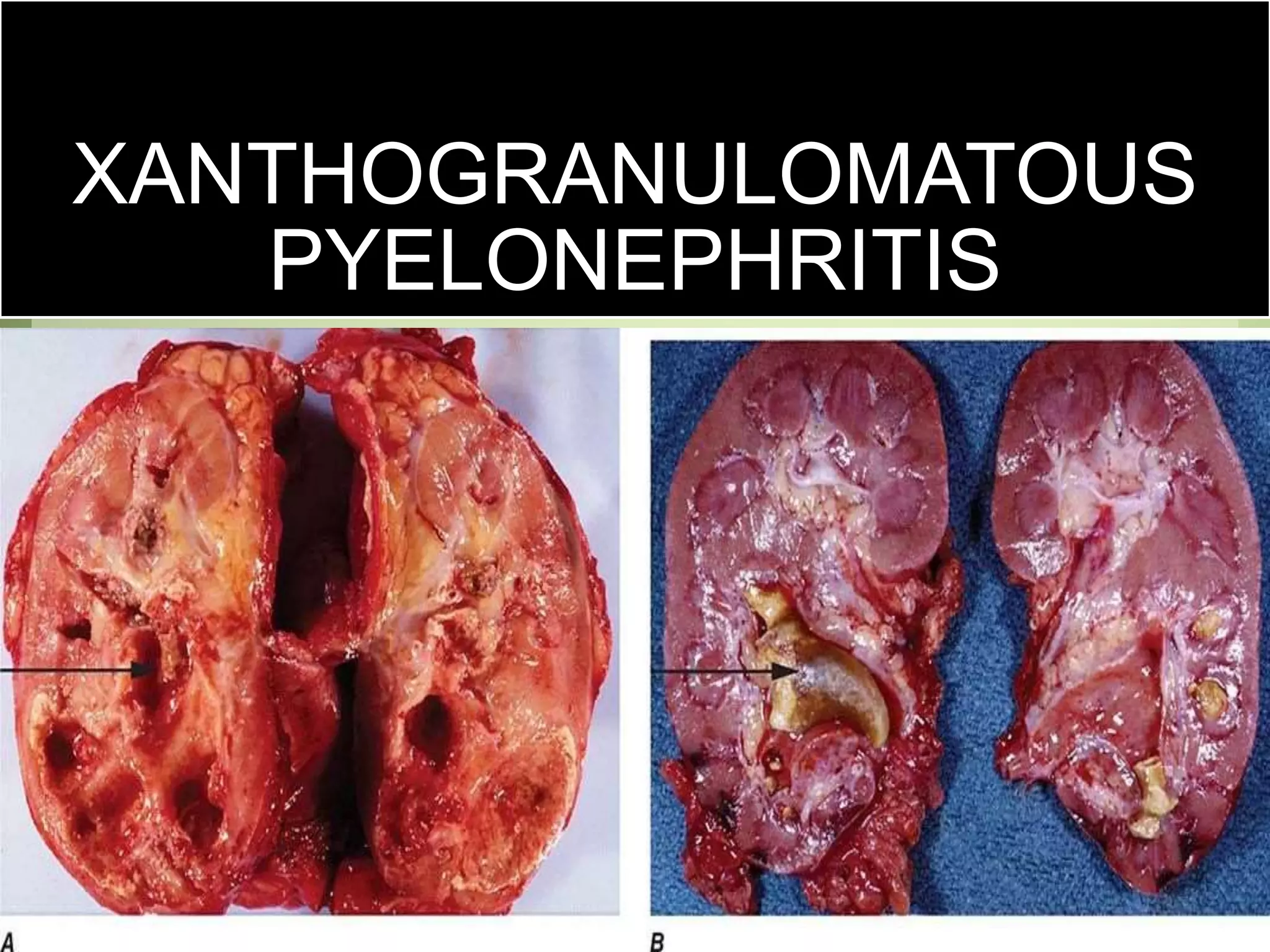
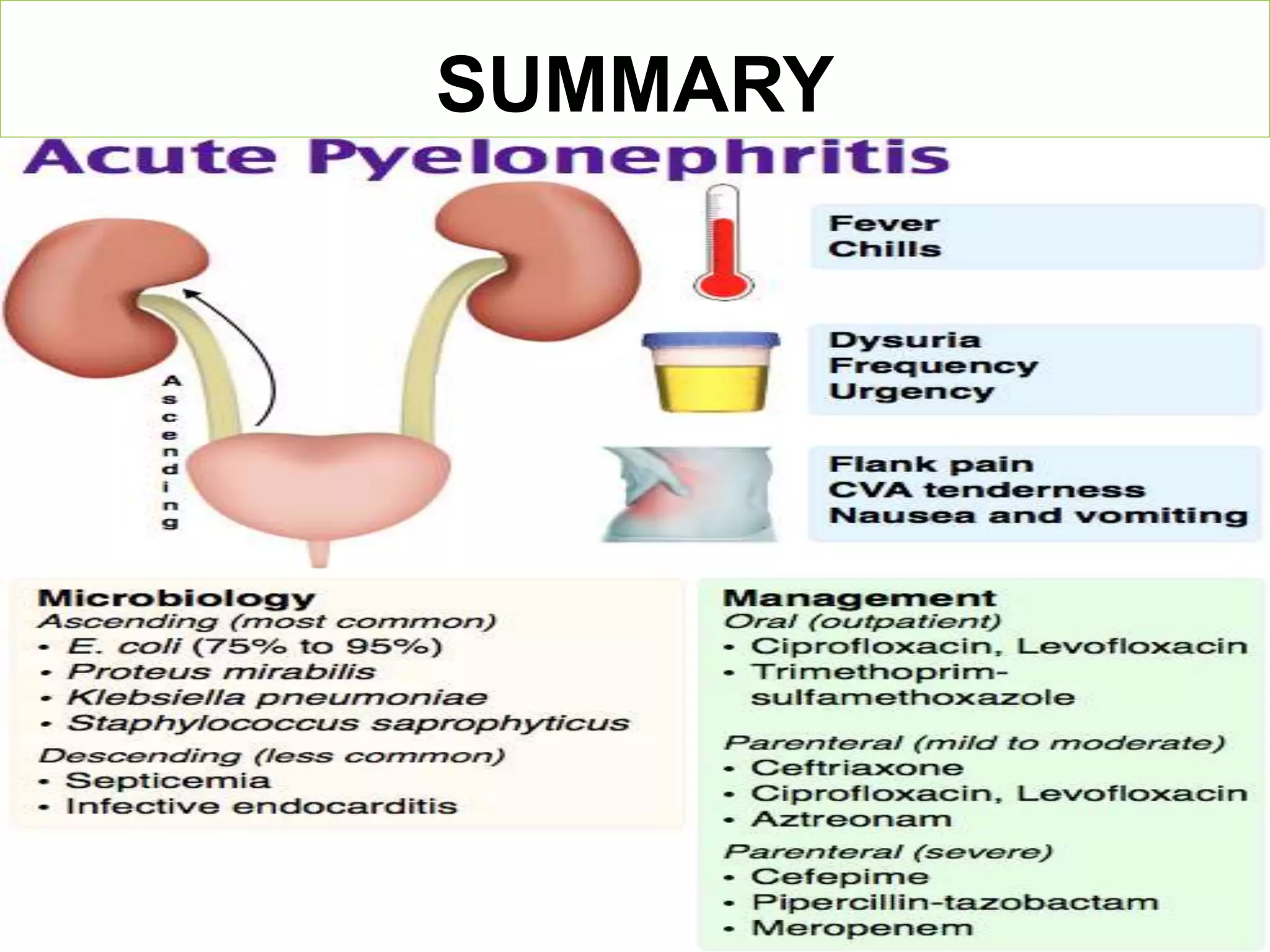
Pyelonephritis is an inflammation of the kidney and upper urinary tract, often caused by bacterial infection from the bladder, classified into acute, chronic, and xanthogranulomatous types. Symptoms include fever, flank pain, dysuria, and complications may arise if untreated, necessitating diagnostic tests and antibiotic management. Prevention strategies include increasing fluid intake and consuming certain foods to inhibit bacterial adherence in the urinary tract.