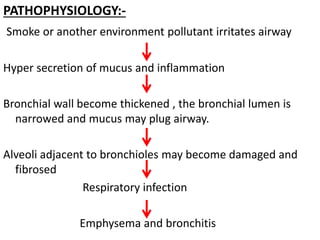
Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes caused by viral or bacterial infection or irritants like smoke. It is classified as acute (lasting days to weeks) or chronic (lasting months). Acute bronchitis is usually caused by cold/flu viruses while chronic bronchitis is often caused by long-term smoke inhalation. Symptoms include cough, wheezing, chest tightness and mucus production. Treatment focuses on reducing inflammation, opening airways, treating infection if present, and addressing underlying causes like smoking.