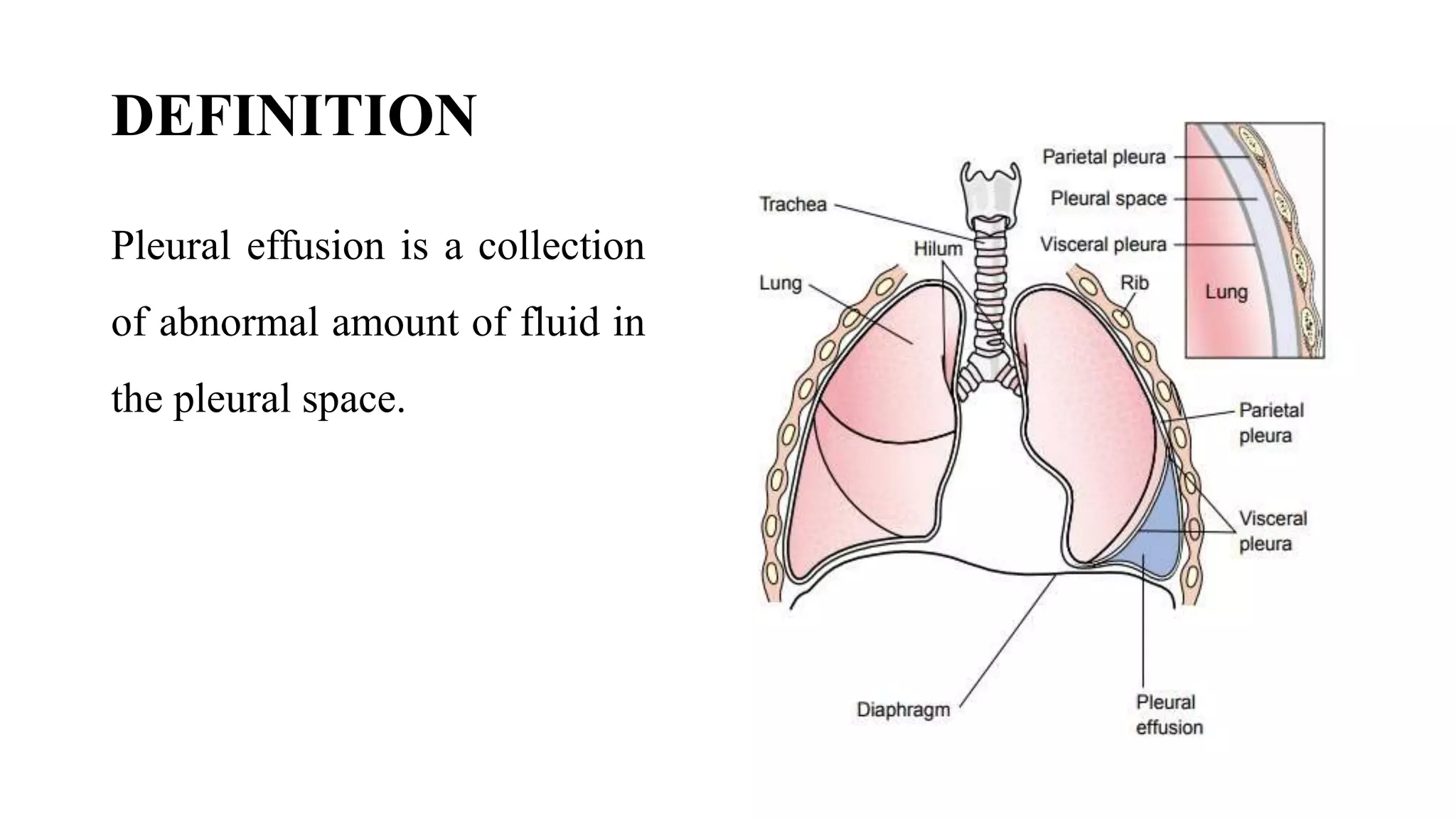
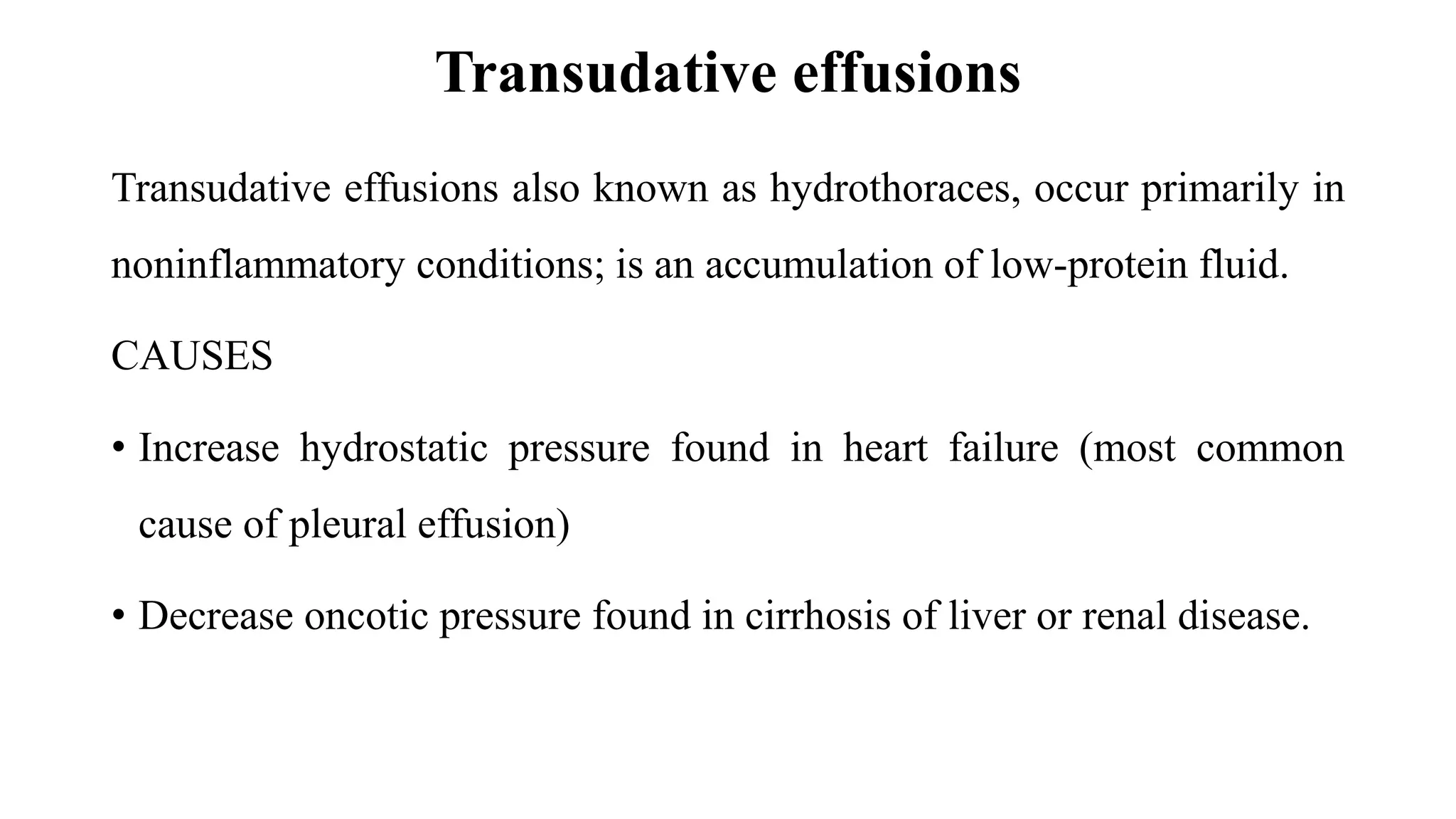
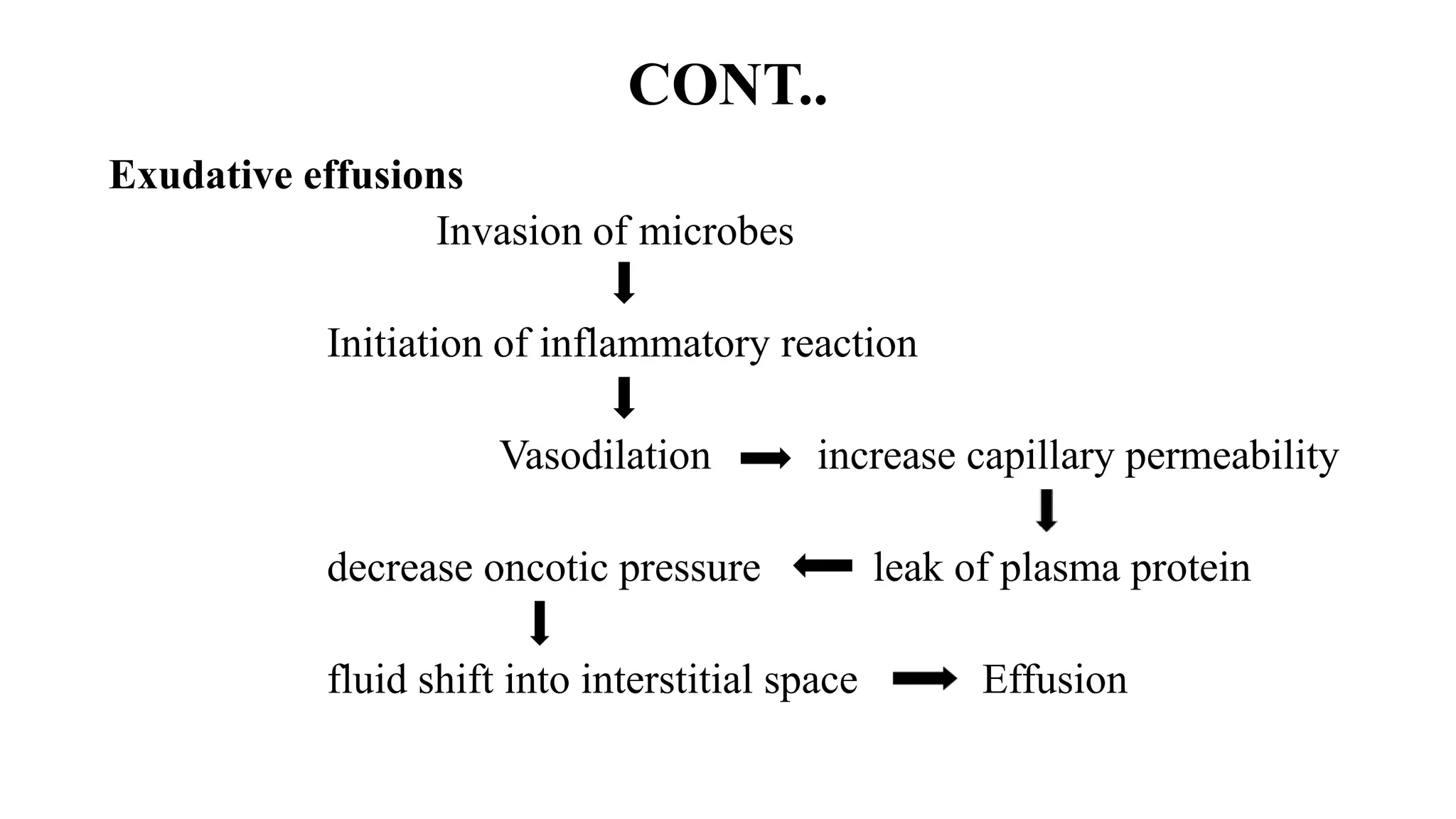
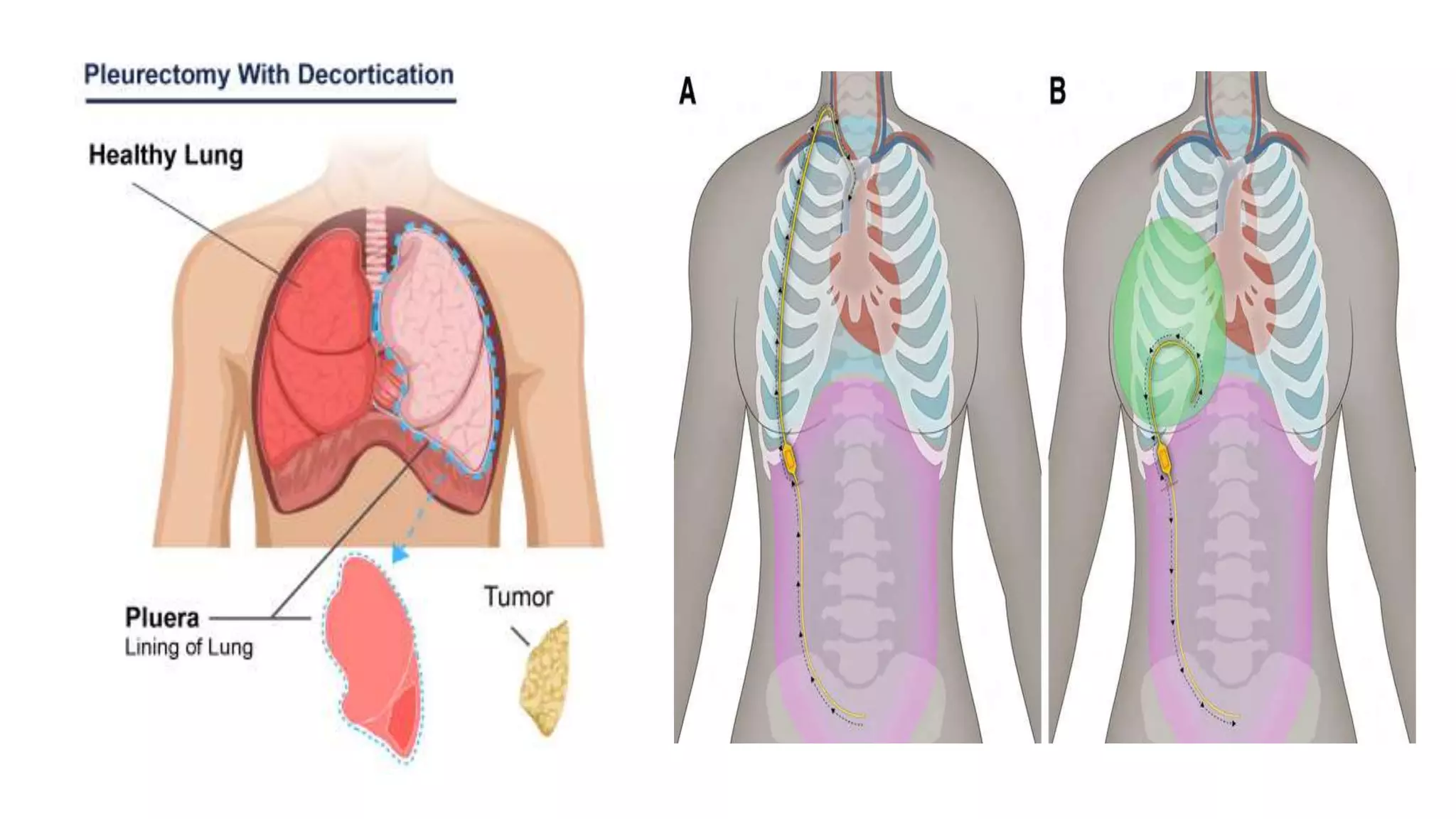
Pleural effusion occurs when an abnormal amount of fluid collects in the pleural space between the lungs and chest wall. There are two main types - transudative effusions which occur without inflammation from conditions like heart failure, and exudative effusions which occur with inflammation from things like infection or cancer. The fluid is evaluated through tests on a sample obtained by thoracentesis to determine the underlying cause. Treatment focuses on addressing the cause, relieving symptoms by draining fluid, and preventing reaccumulation through procedures like pleurodesis. Nursing care involves monitoring for breathing difficulties, providing oxygen, assisting with drainage procedures, and managing pain.