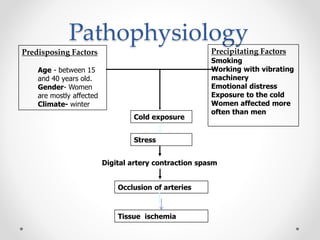
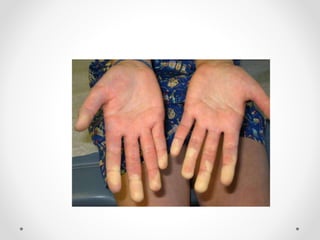
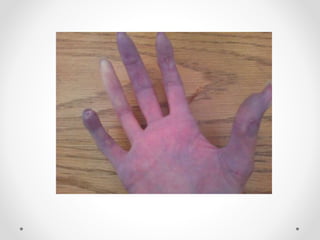
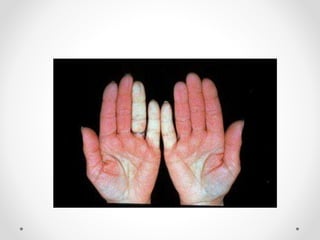
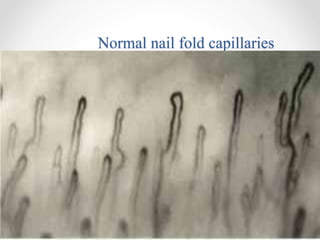
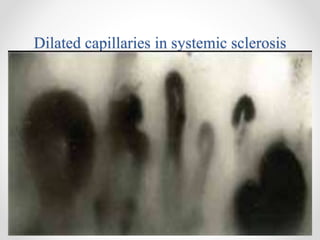
Raynaud's disease is a condition characterized by episodic vasoconstriction of the small arteries in the hands and feet in response to cold or stress. It most commonly affects women ages 16-40. Episodes cause color changes from pale to blue to red as blood flow is reduced and restored. Risk factors include cold exposure, vibratory machinery use, smoking, emotional distress, and autoimmune diseases. Diagnosis involves patient history and physical exam looking for color changes. Treatment focuses on avoiding triggers through lifestyle changes, calcium channel blockers, and topical nitroglycerin.