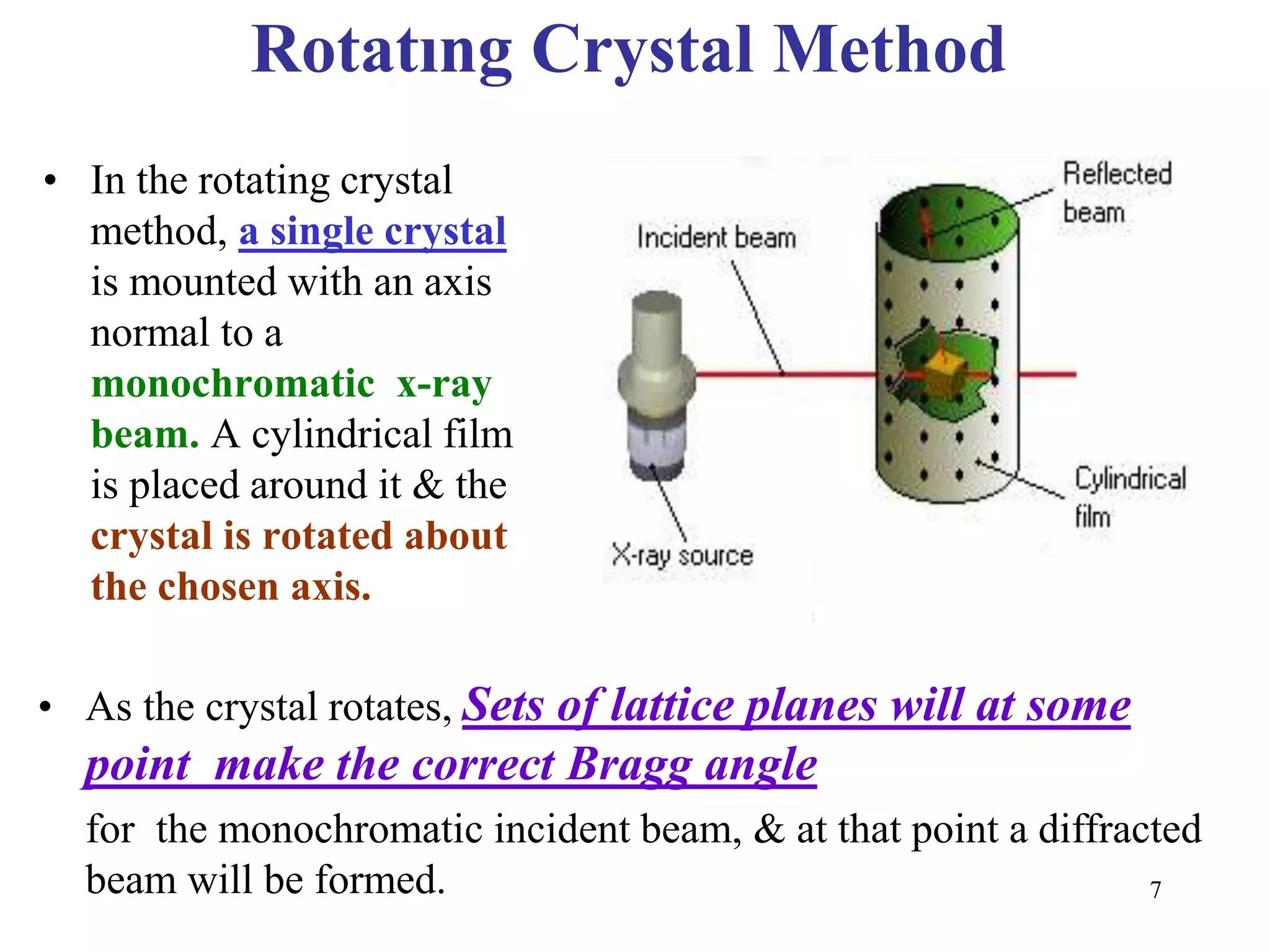
X-ray diffraction is used to analyze the crystal structure of materials. Several methods are described, including Laue, rotating crystal, and powder methods. The Laue method determines crystal orientation using a fixed crystal and white radiation. The rotating crystal method uses a single crystal rotated under a monochromatic beam to determine lattice parameters. The powder method bombards a powdered sample with a monochromatic beam to measure all crystal orientations simultaneously and determine lattice parameters. Bragg's law relates the diffraction pattern to the crystal structure.