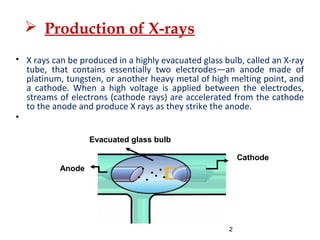
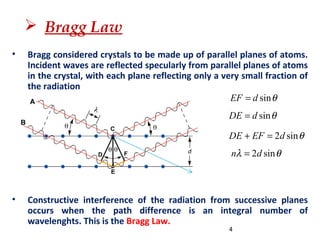
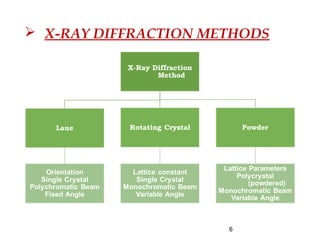
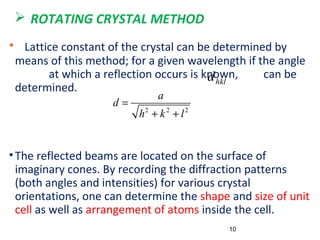
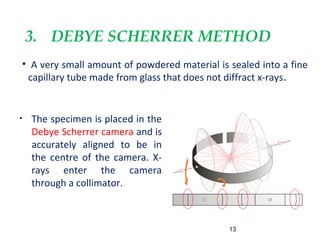
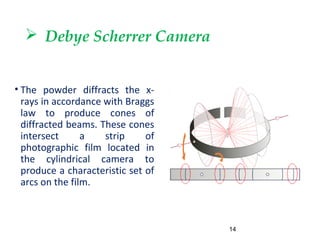
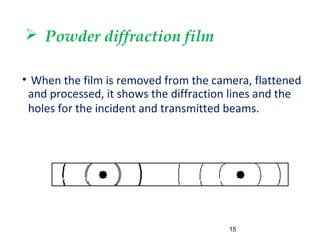
X-rays are produced when high-velocity electrons strike a metal target in an evacuated glass tube. X-ray diffraction occurs when X-rays interact with the regular arrangement of atoms in a crystal lattice, producing diffracted rays. There are three main methods used in X-ray diffraction: the Laue method uses stationary crystals and white radiation to determine crystal orientation; the rotating crystal method uses a monochromatic beam and rotating single crystal to determine structure; and the powder method bombards a powdered sample to identify crystalline materials and determine lattice parameters.
![X-RAY DIFFRACTION
1
[Paper III- Diffraction methods I]
-Jaiswal Priyanka
M.Sc – II [Inorganic]
Mithibai College](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/x-raydiffraction-170615161324/75/X-ray-diffraction-1-2048.jpg)