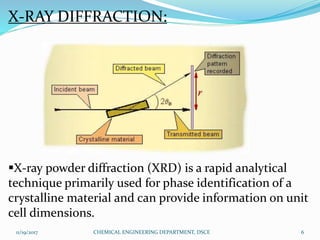
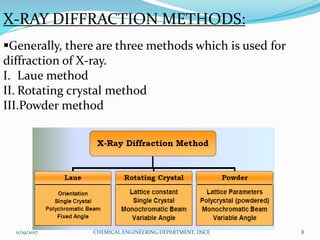
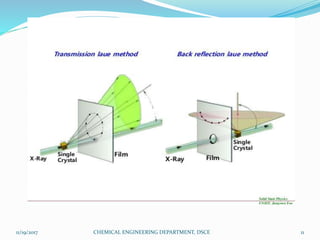
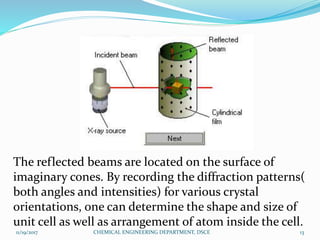
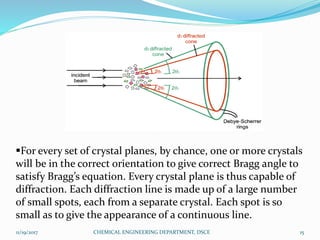
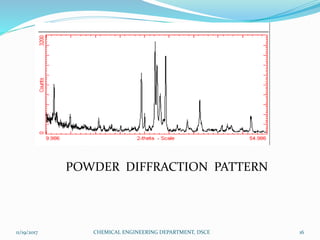
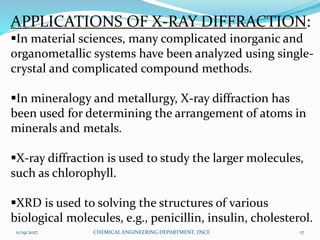
The document summarizes a seminar on X-ray diffraction (XRD) techniques. It introduces Bragg's law which relates the wavelength of X-rays to the diffraction pattern produced when X-rays interact with a crystal lattice. Three common XRD methods are described: the Laue method for single crystals, the rotating crystal method, and the powder method. Applications of XRD include determining crystal structures of minerals, metals, and biological molecules. Limitations are that it has a detection limit of 2% for mixed materials and peak overlap issues.