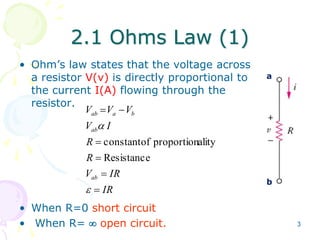
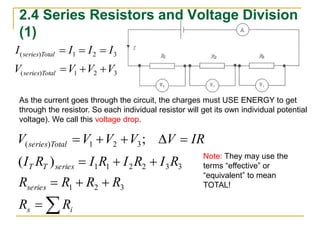
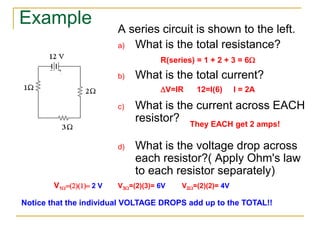
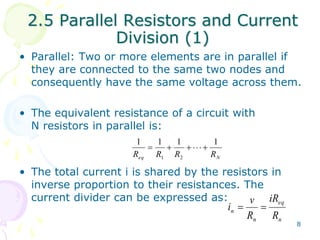
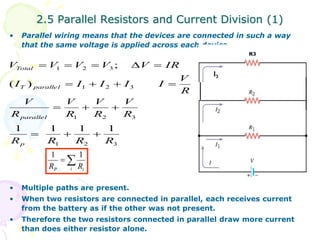
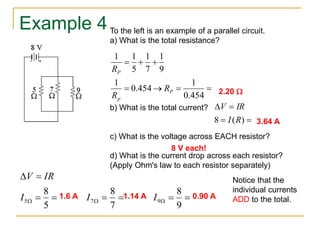
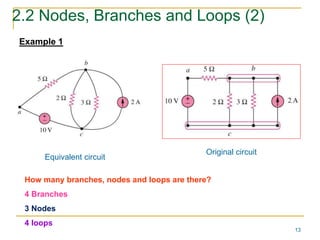
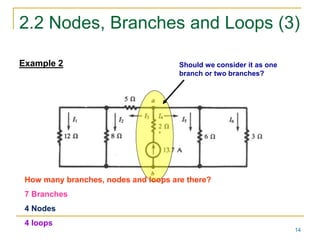
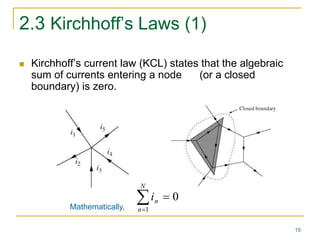
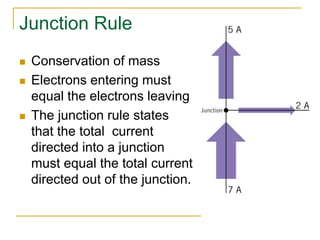
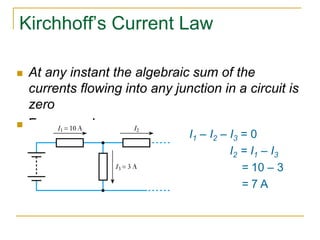
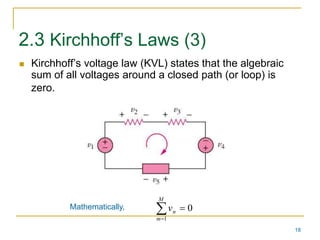
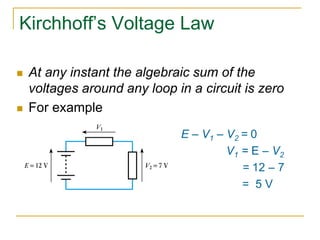
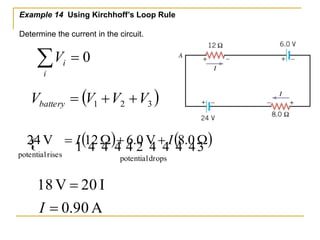
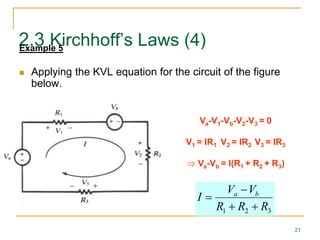
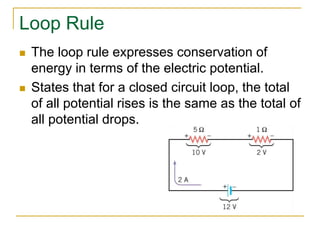
This document provides an overview of basic circuit laws including Ohm's law, Kirchhoff's laws, and analysis of series and parallel circuits. Ohm's law states that voltage across a resistor is proportional to current through the resistor. Kirchhoff's laws include the junction rule that the total current entering a node equals the total leaving, and the loop rule that the sum of all potential differences around a closed loop is zero. Series and parallel circuits are analyzed using concepts like equivalent resistance, voltage division, and current division. Examples are provided to demonstrate applying these circuit analysis techniques.