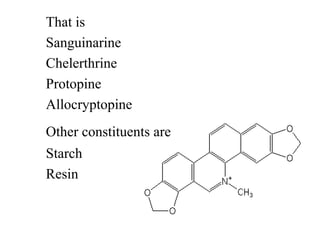
The document discusses two plants from the Papaveraceae family - Papaver somniferum and Sangunaria canadensis. P. somniferum, or opium poppy, is a source of opium which contains alkaloids like morphine and codeine that are used medicinally to relieve pain and as hypnotics. S. canadensis, or bloodroot, contains isoquinoline alkaloids like sanguinarine and is used as an emetic, expectorant, and in toothpaste for gum diseases. Both plants contain various alkaloids that have medical applications but can also be toxic in large doses.