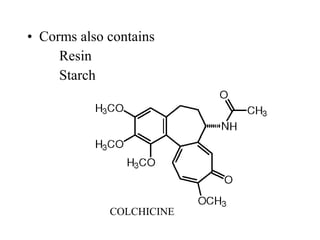
This document provides information on four plants from the Lily family (Liliaceae): Colchicum, Aloe, Garlic. It describes their botanical origins, parts used, constituents, and medical uses. Colchicum contains alkaloids like colchicine used to treat gout and cancer. Aloe gel is used topically for burns and skin issues. Garlic contains volatile oils and is used for various conditions like asthma, cholesterol, infection. The document defines characteristics of Liliaceae plants and provides details on morphology and taxonomy.