This document discusses optical fiber communication and fiber optic cables. It covers the following key points:
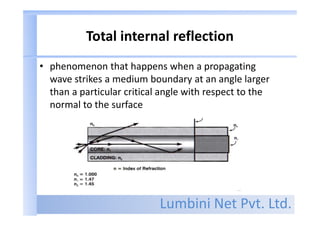
- Fiber optics uses light to transmit information through glass or plastic strands. Unlike copper transmission, it is not electrical in nature.
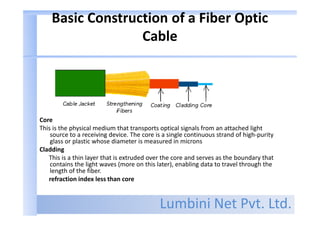
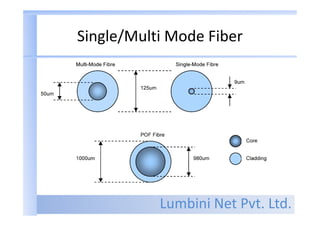
- The basic components of a fiber optic cable are the core that carries light, cladding surrounding the core, a coating for protection, and a cable jacket.
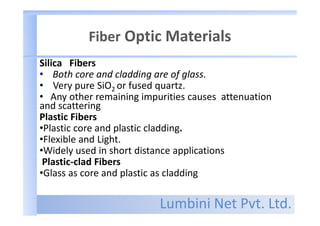
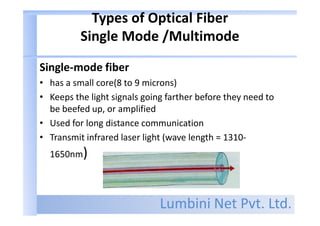
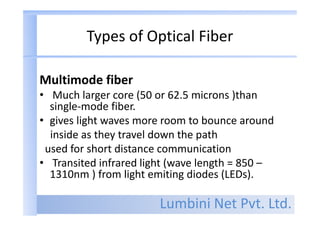
- Fiber materials include silica glass, plastic, and plastic-clad fibers. Single-mode fiber has a small core for long distances, while multimode fiber has a larger core for short distances.
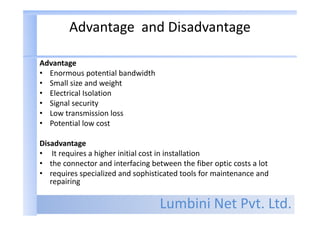
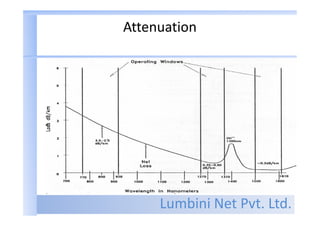
- Fiber optic communication has advantages like large bandwidth, small size, electrical isolation, and low



![Lumbini Net Pvt. Ltd.
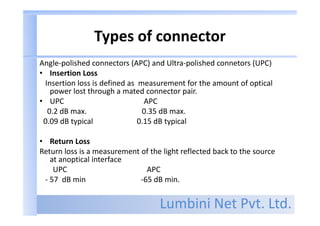
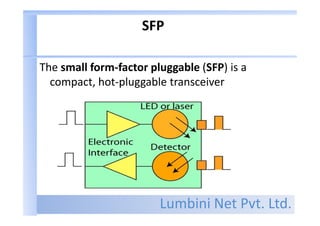
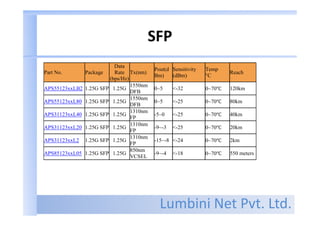
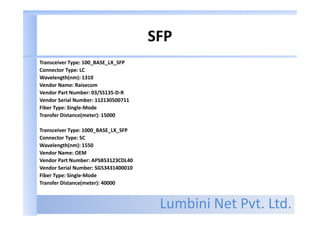
Types of connector
• FC
• Ferrule Connector or Fiber Channel
SC
Subscriber Connector [3] or
square connector [3] or
Standard Connector](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opticalfibercommunication-kirandevkota-140811071042-phpapp02/85/Optical-fiber-communication-Presented-by-Kiran-Devkota-15-320.jpg)