Embed presentation
Downloaded 19 times





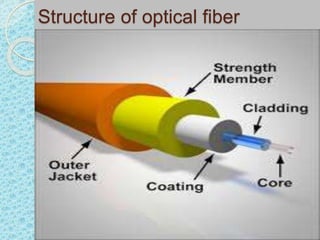

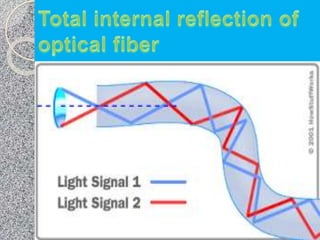
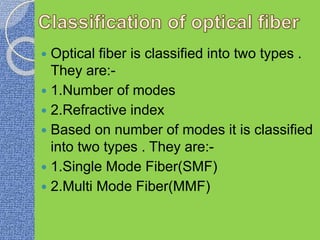










This document discusses the structure and classification of optical fibers. Optical fibers are classified based on the number of modes as either single-mode fiber or multi-mode fiber. The structure of an optical fiber communication system includes an information source, electrical transmitter, optical source, and optical fiber as the transmission medium. The optical source provides electrical-optical conversion, typically using a semiconductor laser or LED.


















