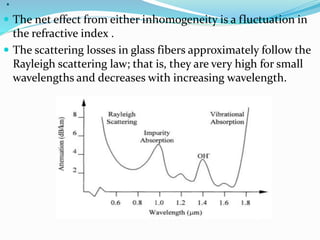
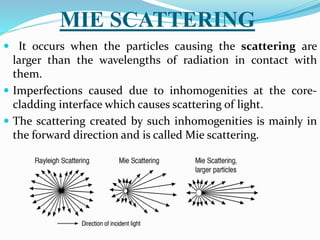
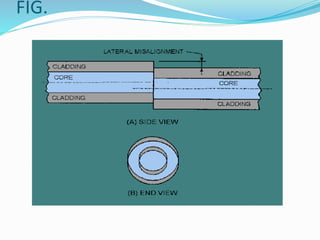
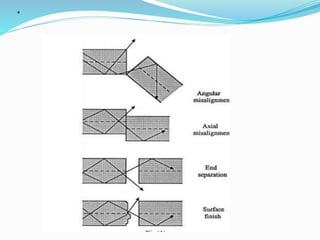
Optical fibers experience various intrinsic and extrinsic losses that limit signal strength over long distances. Intrinsic losses include material absorption and scattering due to fiber imperfections. Absorption is caused by molecular vibrations and impurities, while scattering results from refractive index fluctuations. Extrinsic losses include bending, launching, and connector losses. Bending losses occur from macroscopic or microscopic bends, launching losses are from imperfect coupling into the fiber, and connector losses are due to core misalignments between joined fibers. Together these losses contribute to the overall attenuation of signals transmitted through optical fibers.