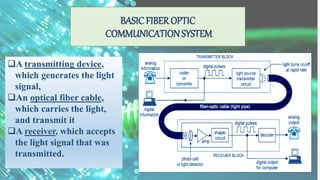
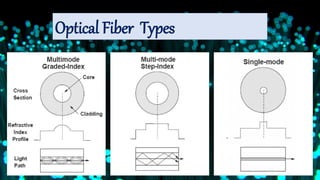
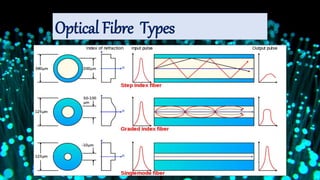
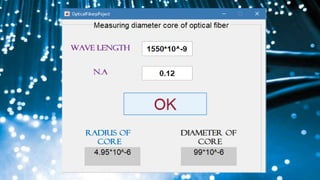
Optical fibers are thin glass rods that transmit information as light pulses through total internal reflection, allowing for high-speed communication. They consist of a core, cladding, and protective outer jacket, offering advantages like greater bandwidth and longer transmission distances compared to ordinary cables. Despite being expensive and requiring skilled installation, optical fibers are widely used in various applications, including communication, military, and medical fields.