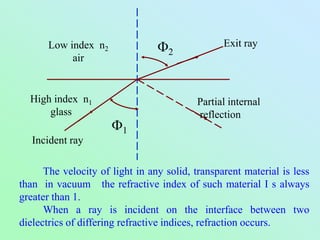
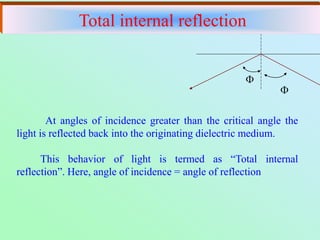
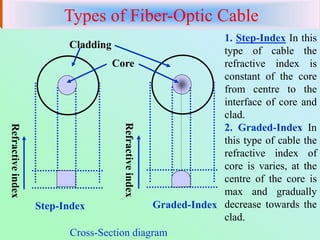
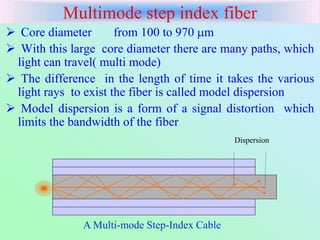
Fibre-optic communication uses glass or plastic fibers to transmit data as light. A fiber-optic cable contains a core that carries the light, surrounded by cladding with a lower refractive index. Total internal reflection within the core allows light to propagate long distances with little attenuation. Fiber-optic cables have several advantages over electrical cables including higher bandwidth, lower losses, lighter weight, and immunity to electromagnetic interference. Common applications include telephone networks, cable television, computer networking, and industrial sensors.