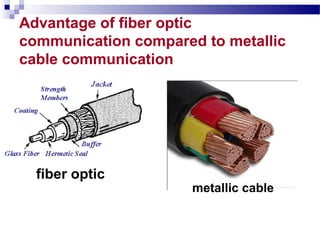
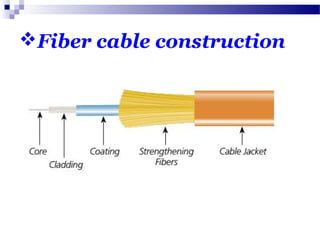
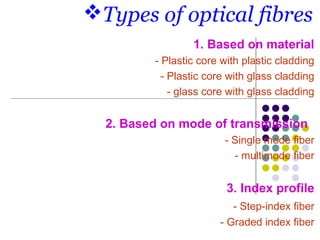
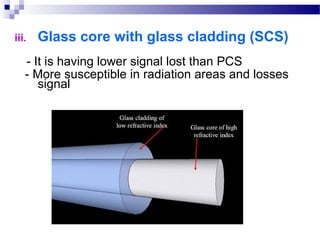
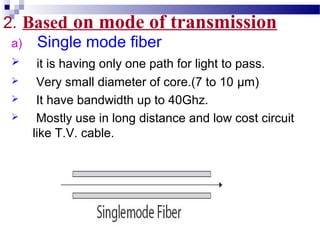
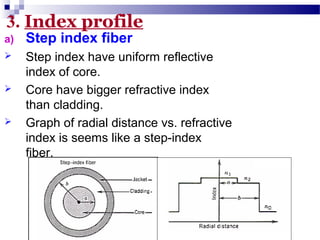
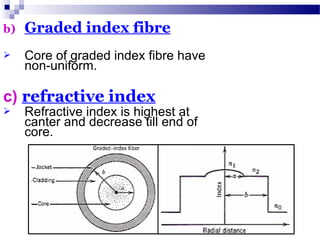
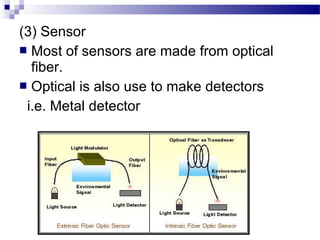
Optical fibers carry information in the form of light. They have several advantages over metallic wires including much higher bandwidth, immunity to electromagnetic interference, lighter weight and smaller size. Optical fibers have a core made of glass or plastic surrounded by a cladding layer. They transmit light using either single mode or multimode transmission. Common applications of optical fibers include telecommunications, local area networks, sensors and computer networks due to their high information carrying capacity and low signal attenuation.