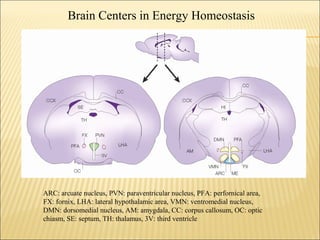
This document discusses obesity and energy balance regulation in the body. It covers topics such as the definition of BMI, types of adipose tissue, health risks of obesity, and trends in obesity worldwide. It then discusses factors contributing to the current obesogenic environment like increased food availability and decreased physical activity. The remainder of the document details the biological mechanisms of energy homeostasis, including hormones like leptin that regulate appetite and metabolism, as well as brain centers involved in energy balance. Potential future therapies for obesity that target these biological pathways are also mentioned.

![BMI = weight [kg]/(height [m])2
• At a given BMI, women, on average, have more body fat.
• Morbidity and mortality increase with BMI similarly for men and women.
• Risk at a given BMI can vary between populations.
Body Mass Index (BMI): Medically Significant Adiposity](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/obesity-140327085933-phpapp01/85/Obesity-2-320.jpg)