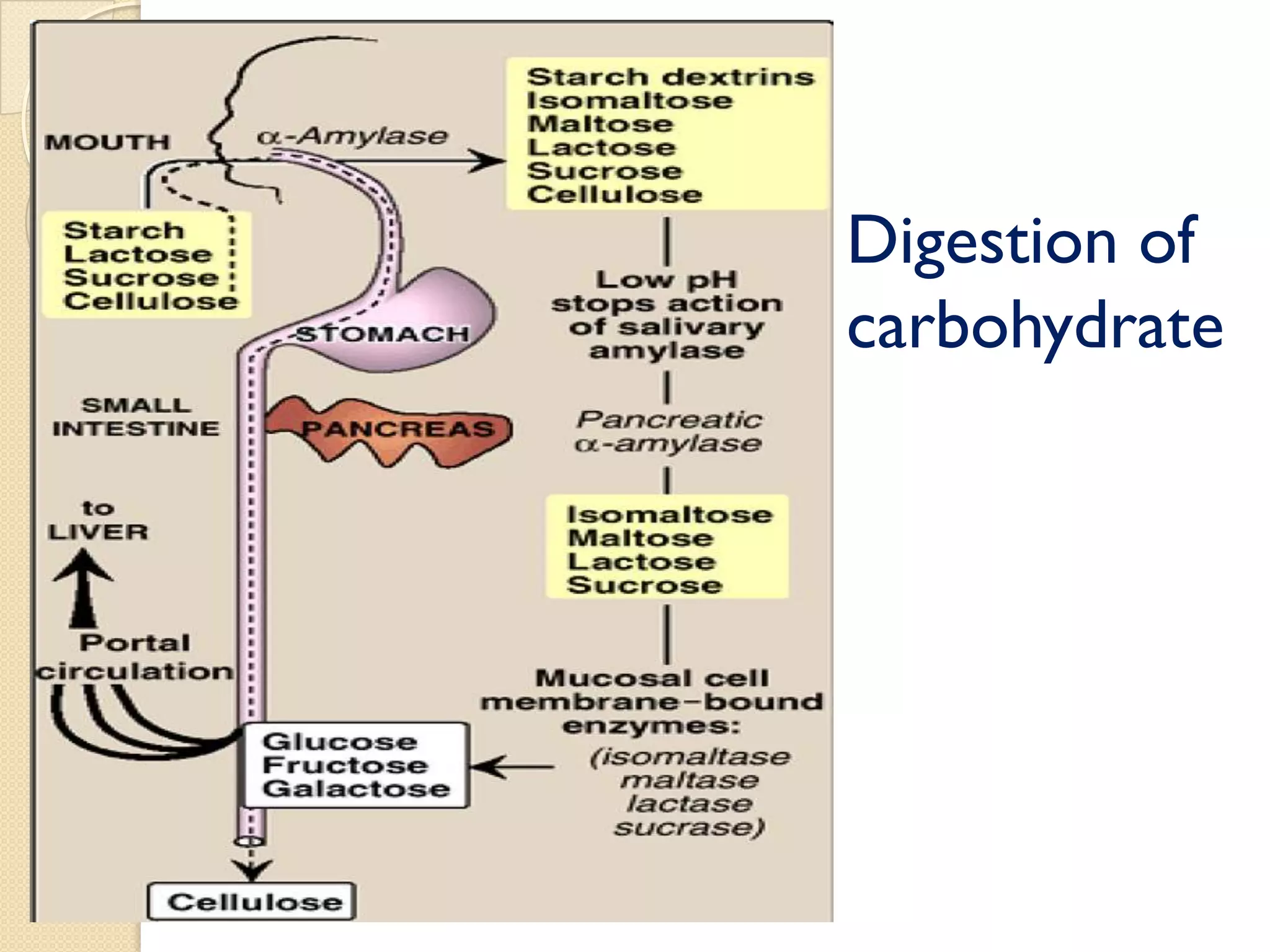
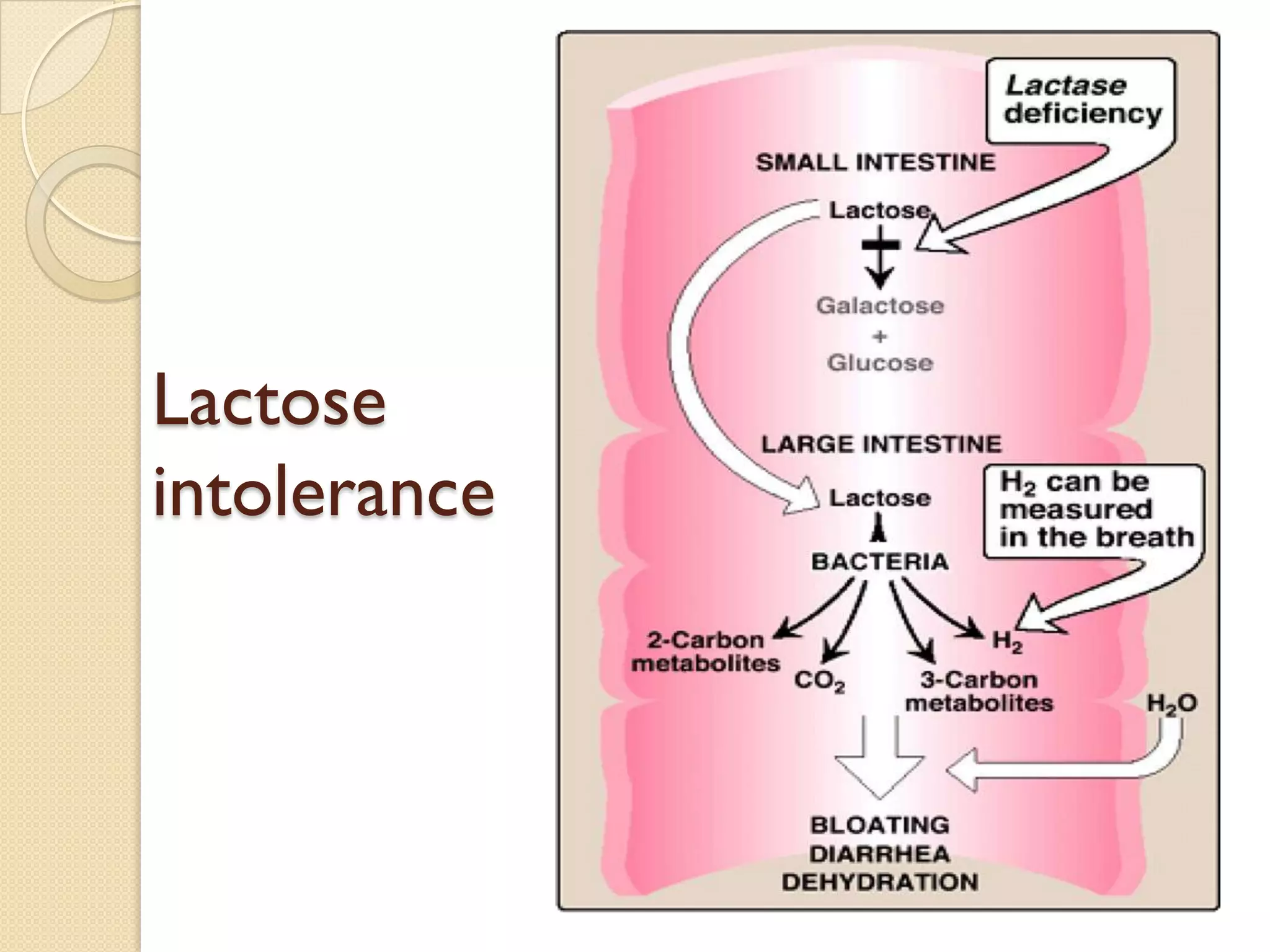
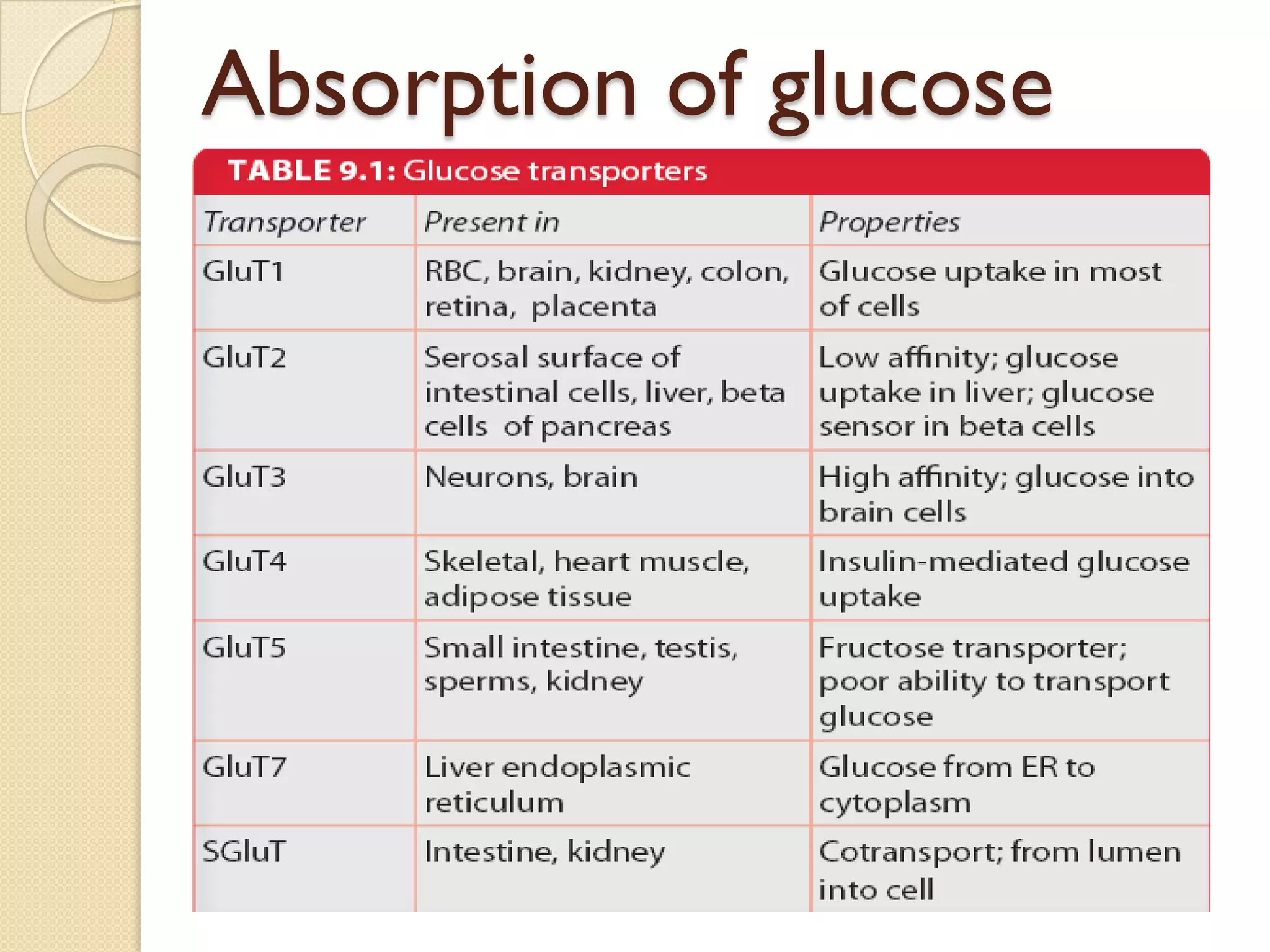
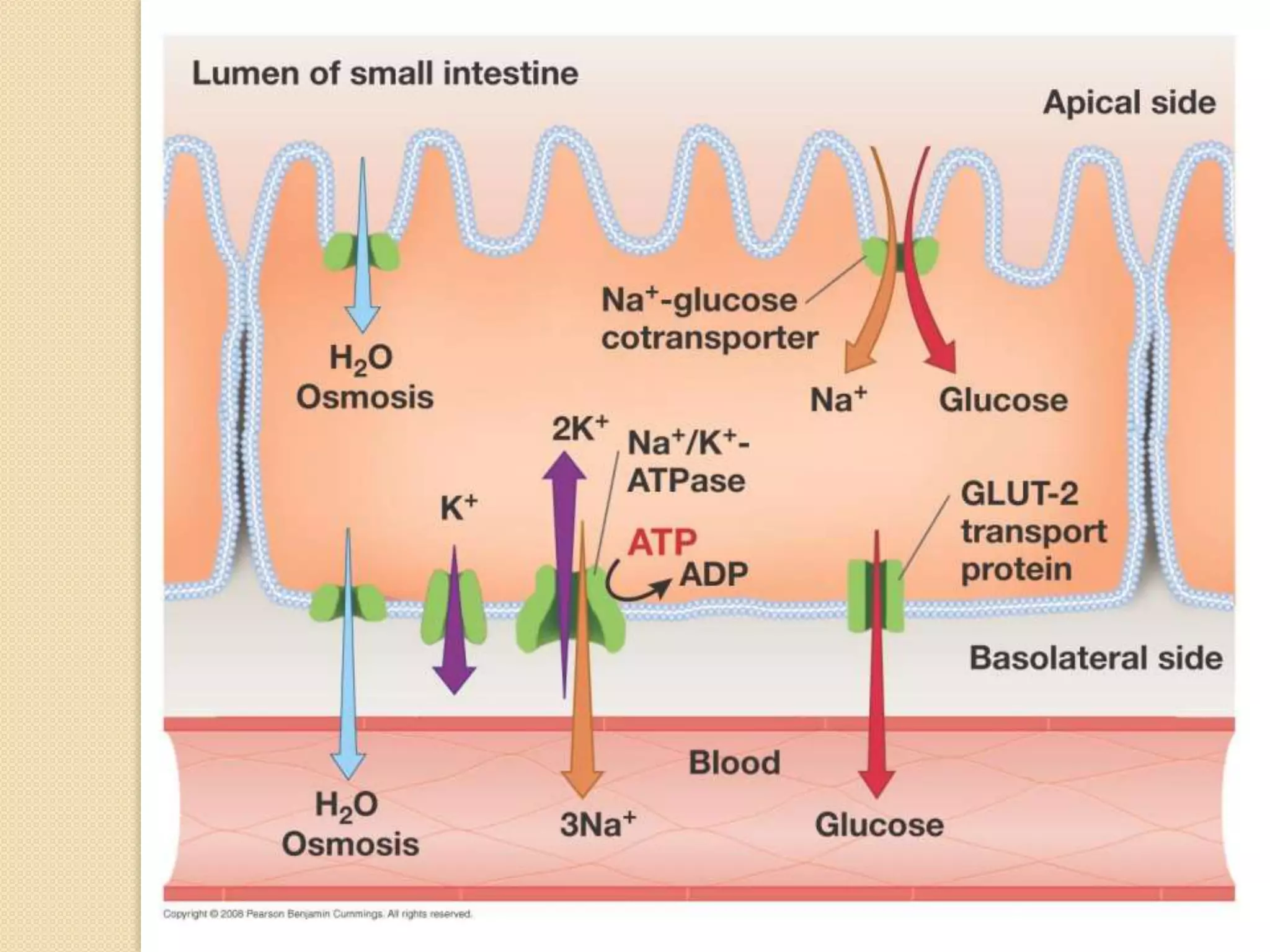
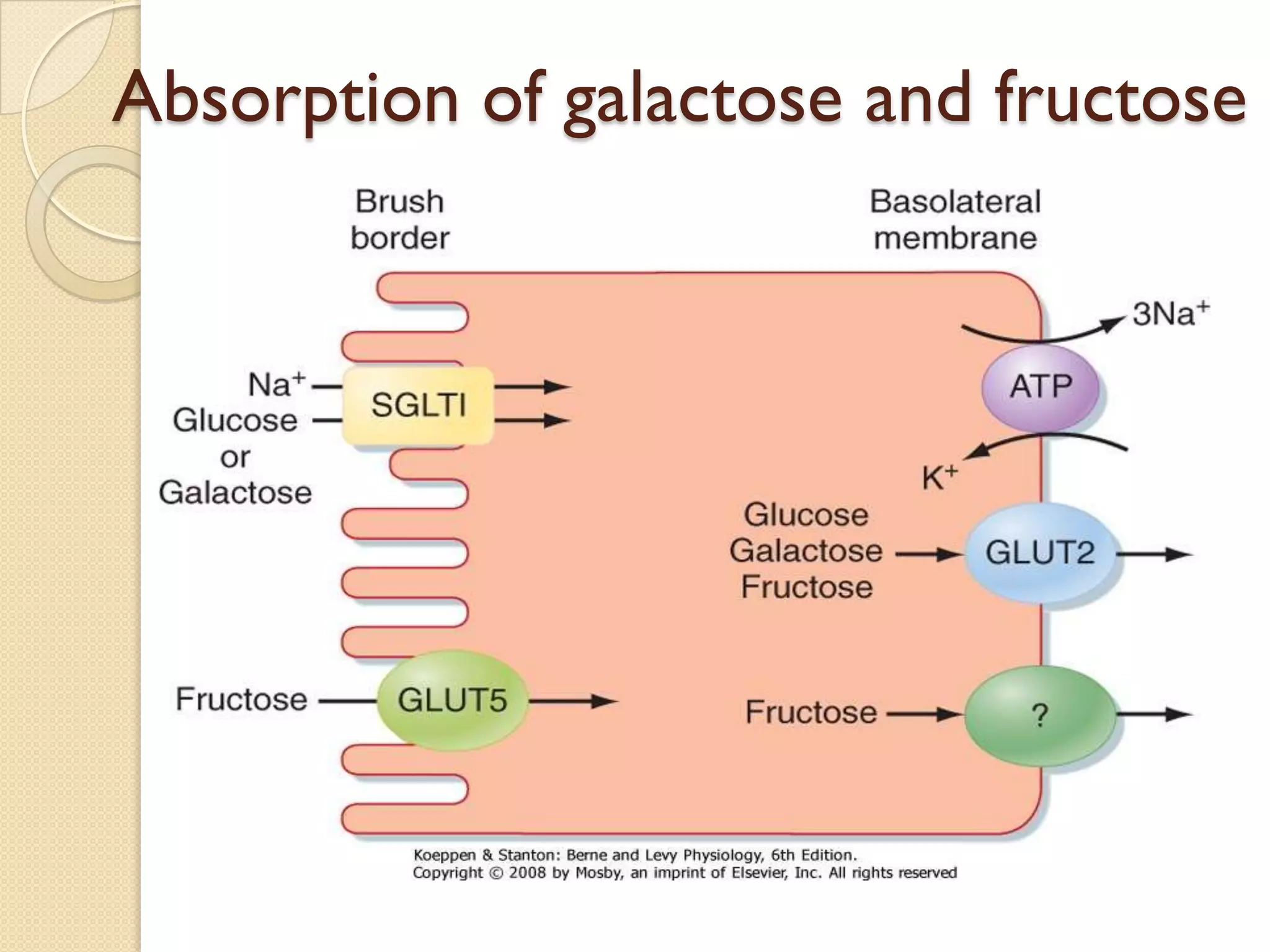
This document summarizes the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates. It states that carbohydrates in the diet are primarily complex polysaccharides that are broken down by enzymes into monosaccharides in the gastrointestinal tract. The breakdown process begins in the mouth with salivary amylase and continues in the pancreas with pancreatic amylase and in the small intestine with enzymes that break down disaccharides into monosaccharides. Only monosaccharides can be absorbed into the intestinal cells, primarily through co-transport with sodium ions. The monosaccharides are then released into the bloodstream through facilitated diffusion transporters.