1) An approximation is an inexact representation of something that is still close enough to be useful as it reduces complexity while still yielding an accurate solution.
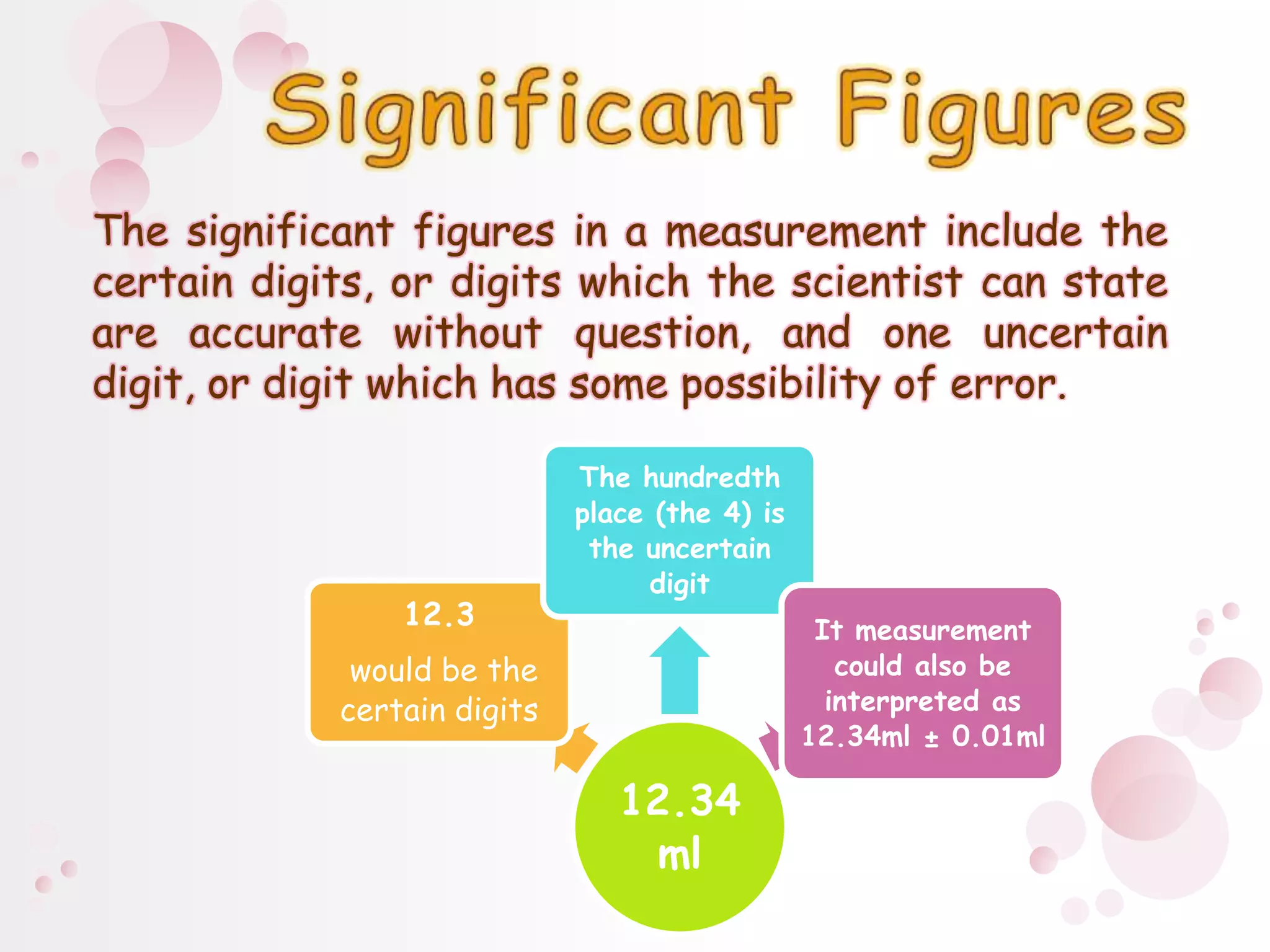
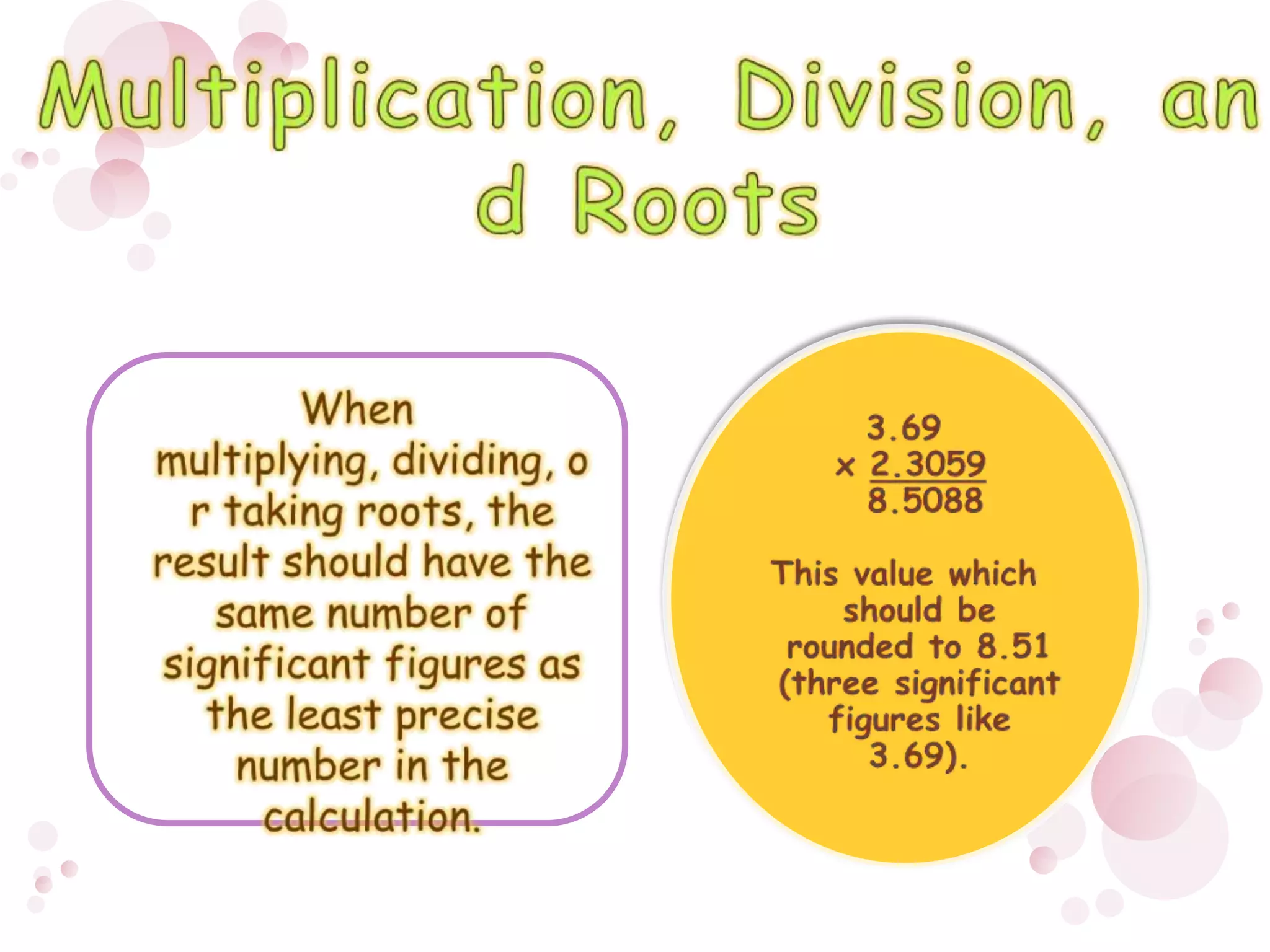
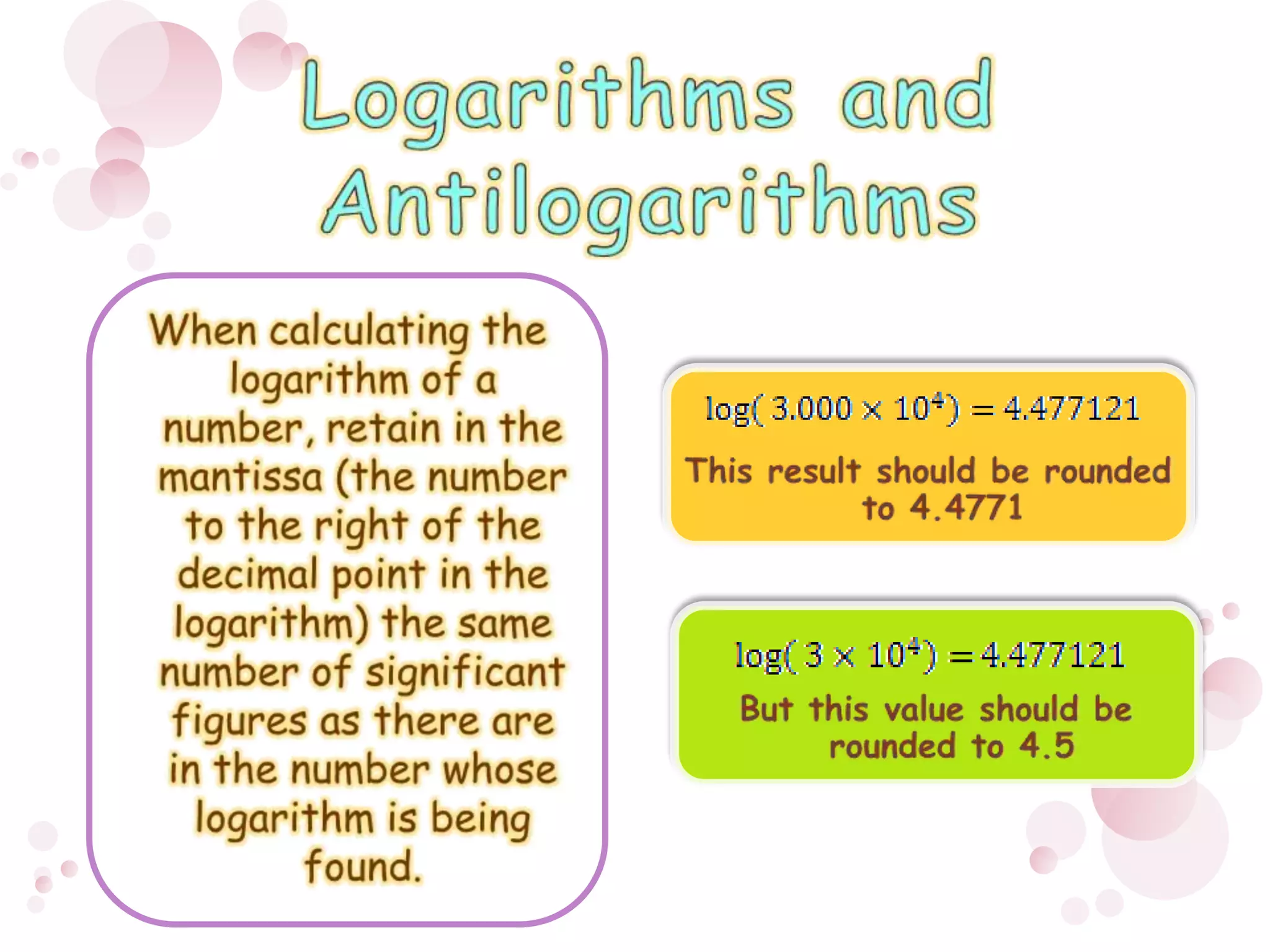
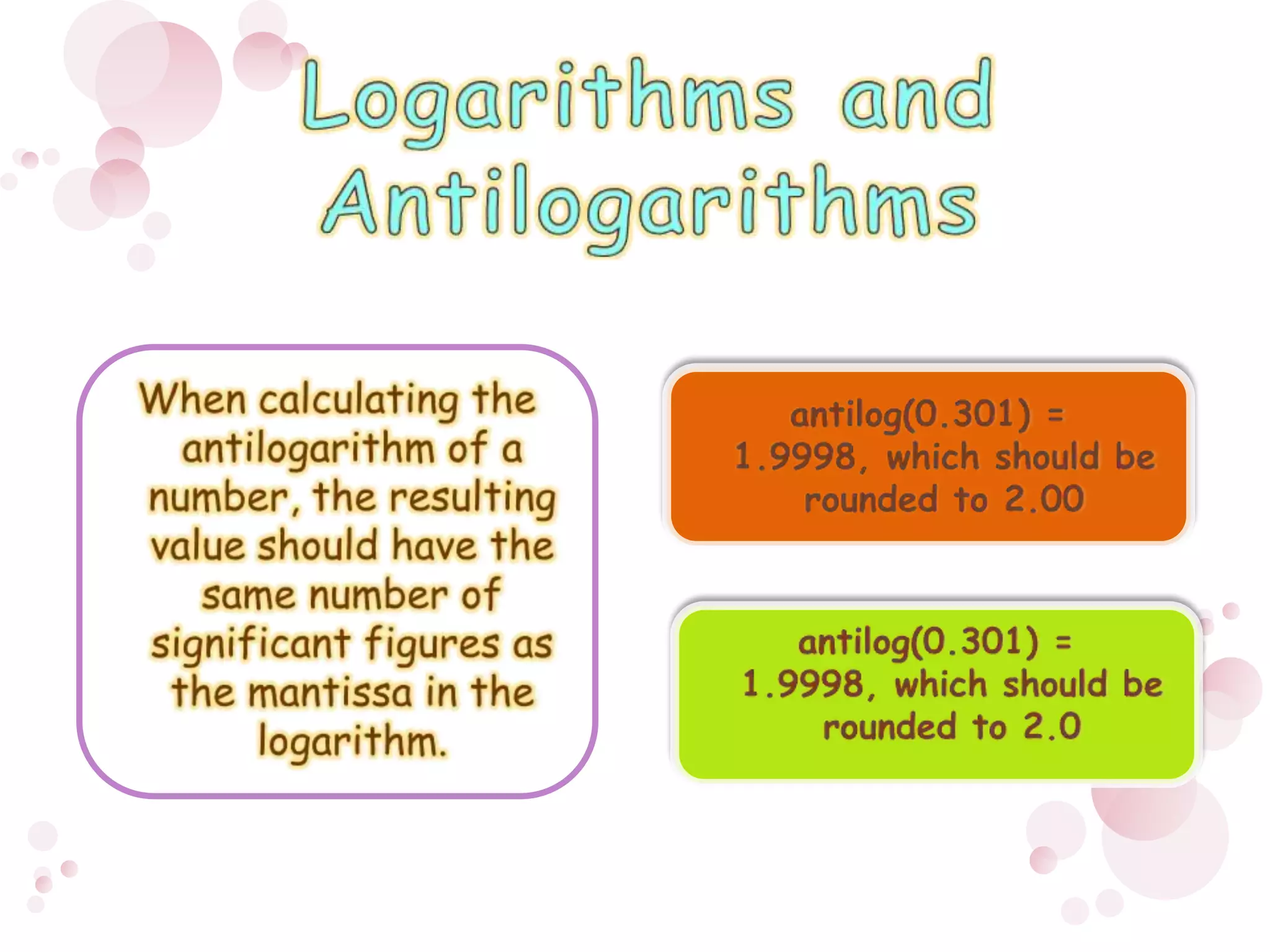
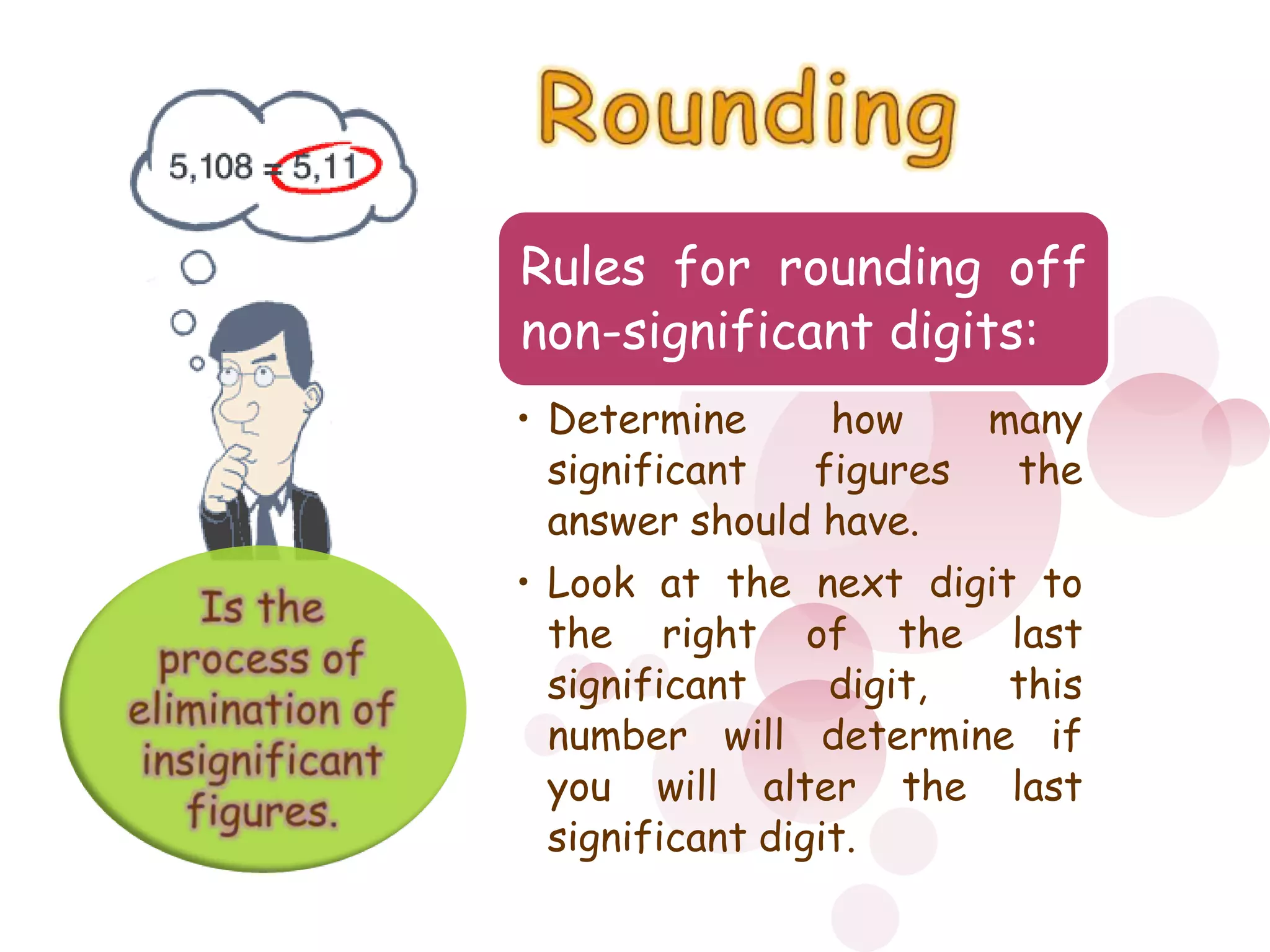
2) When performing calculations with approximations, the number of significant figures in the final result should match the least precise initial value. For addition/subtraction, round to the same decimal places, and for multiplication/division/roots round to the same number of significant figures.
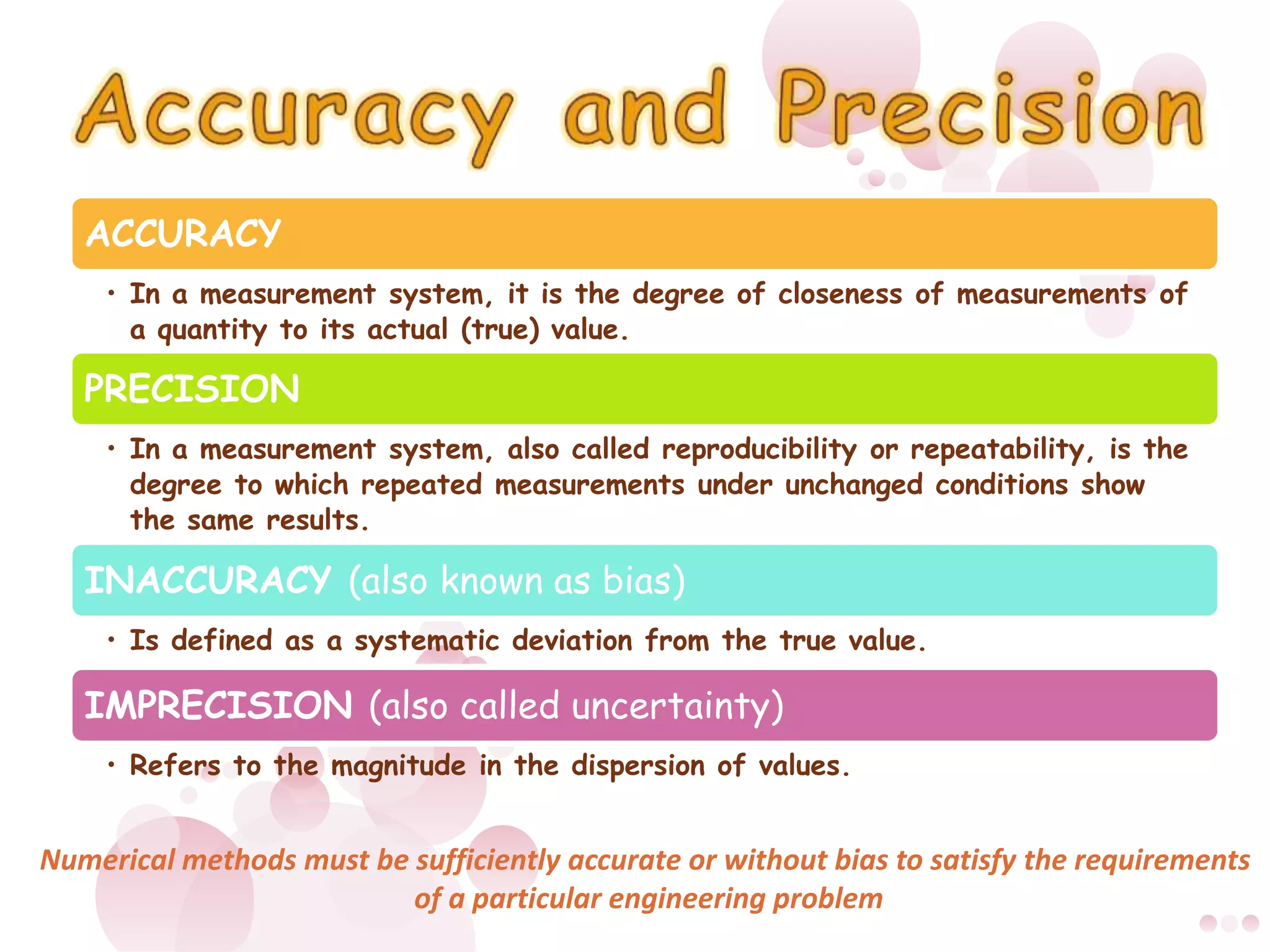
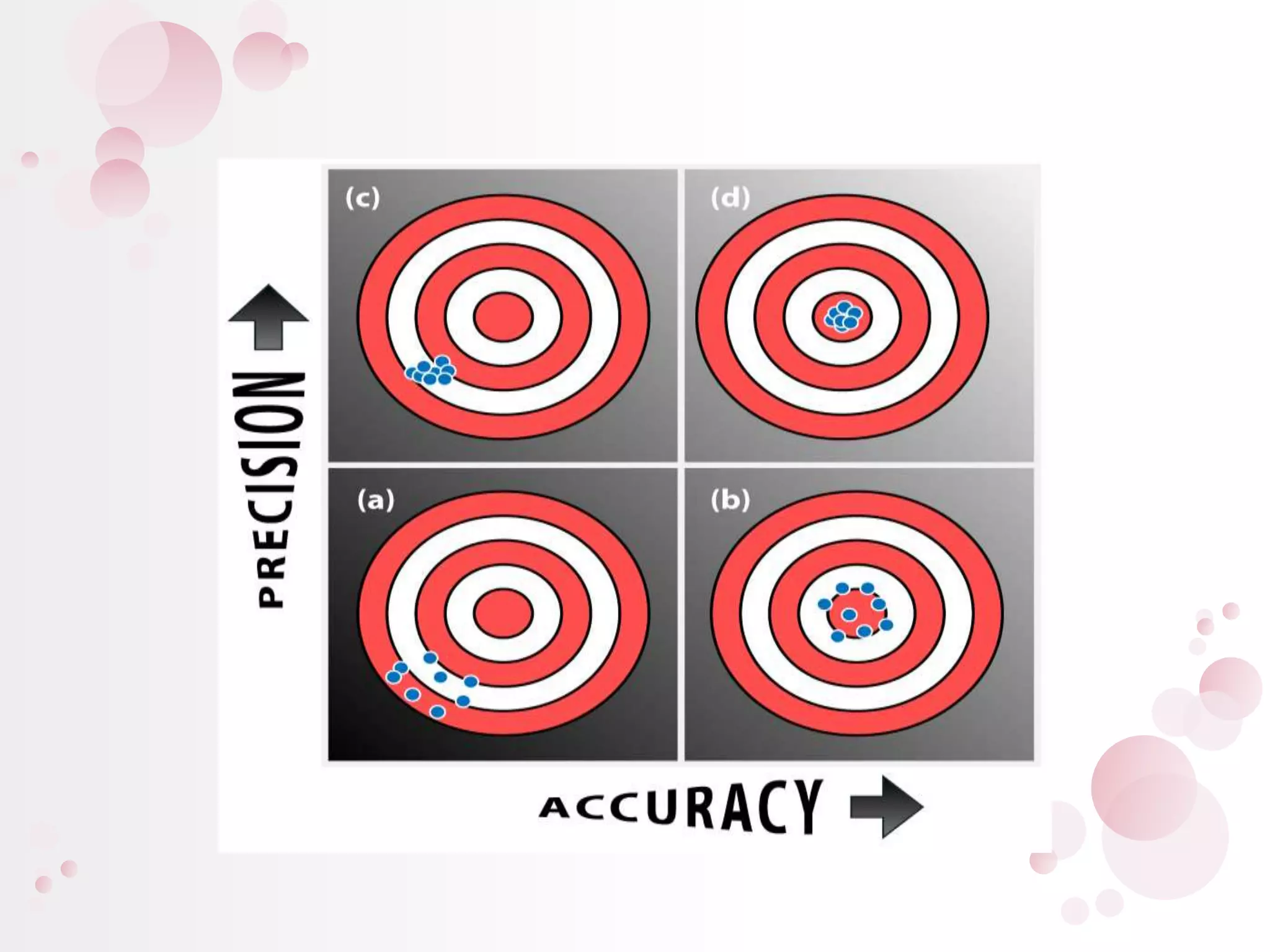
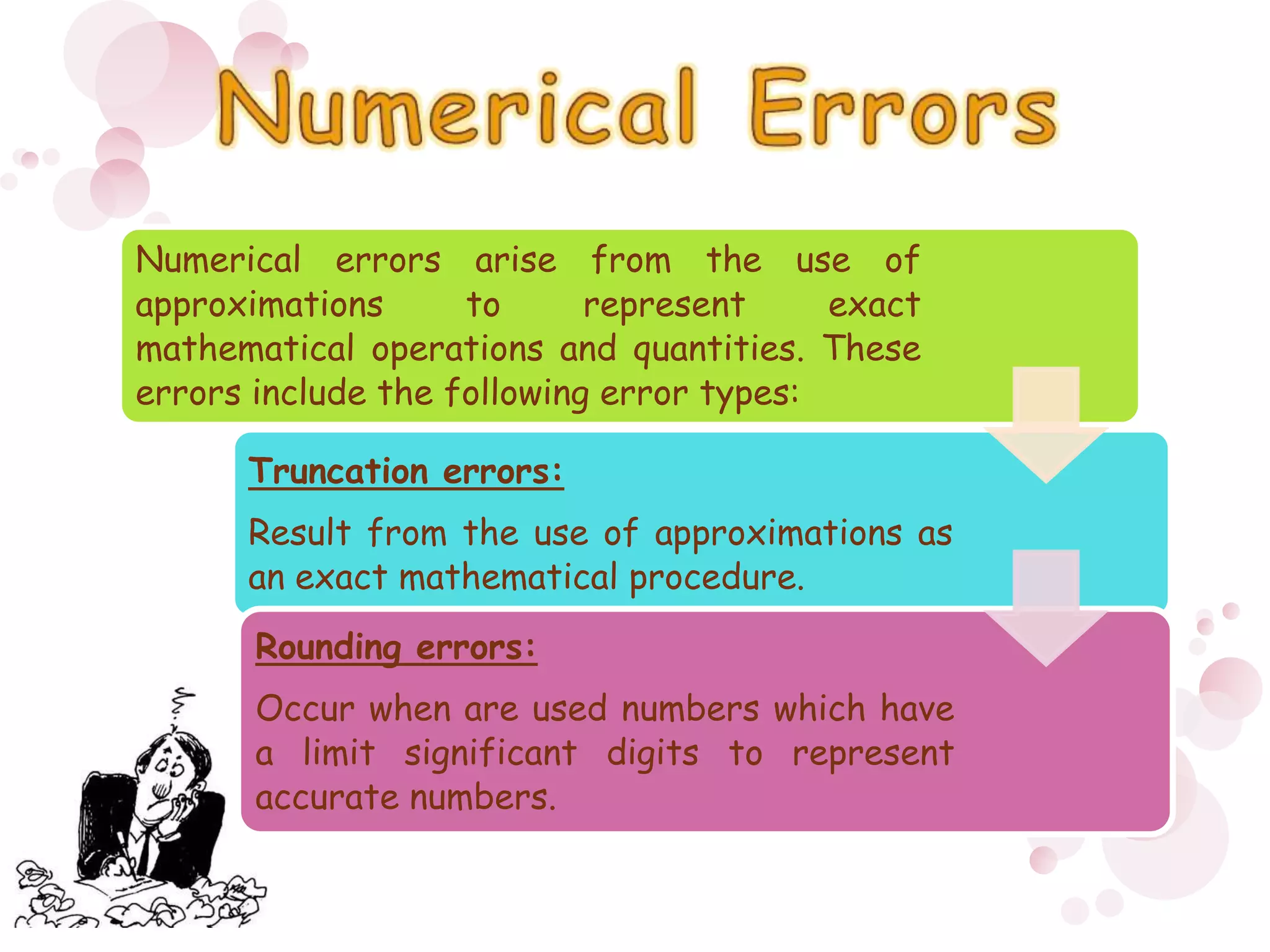
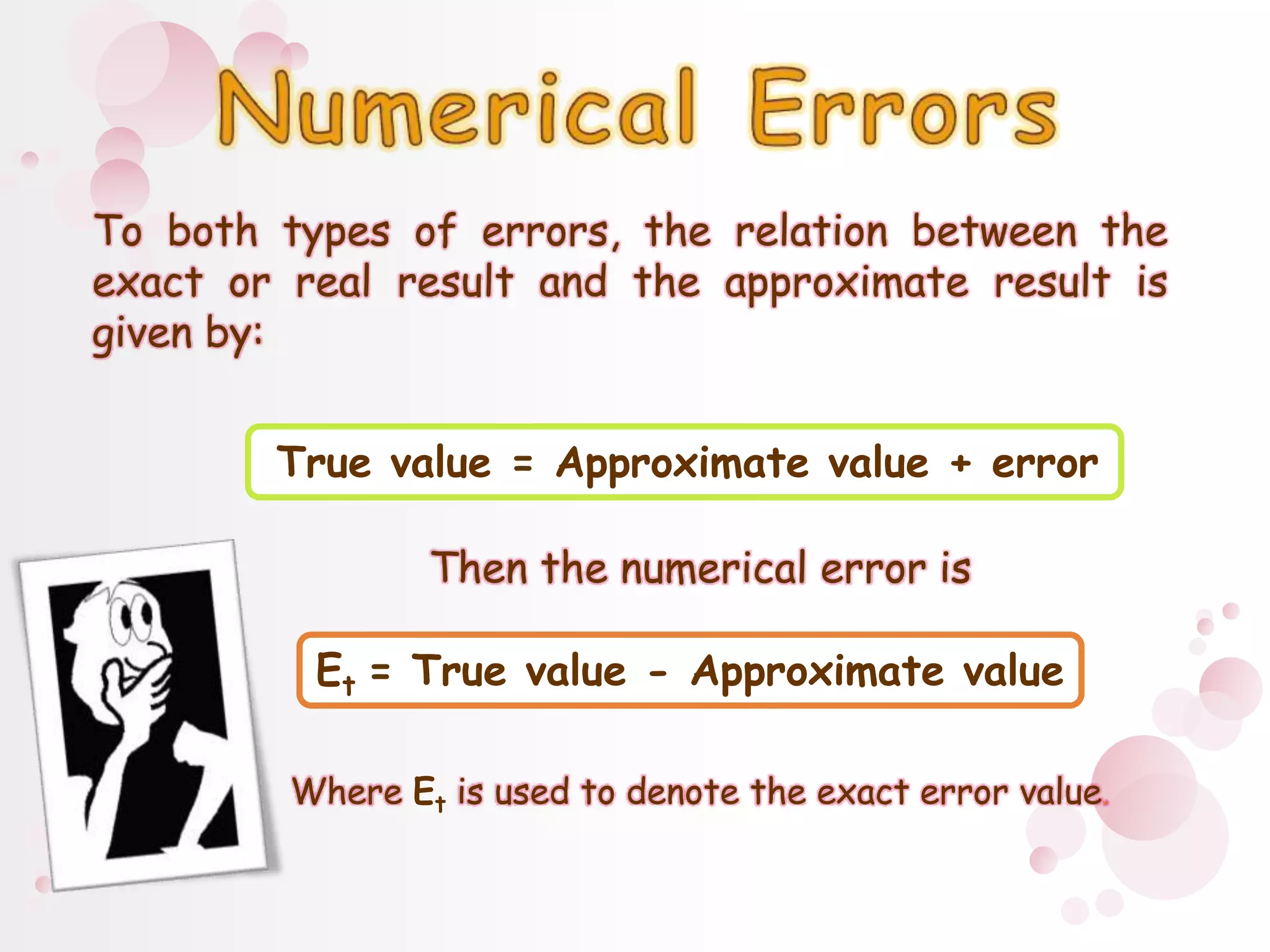
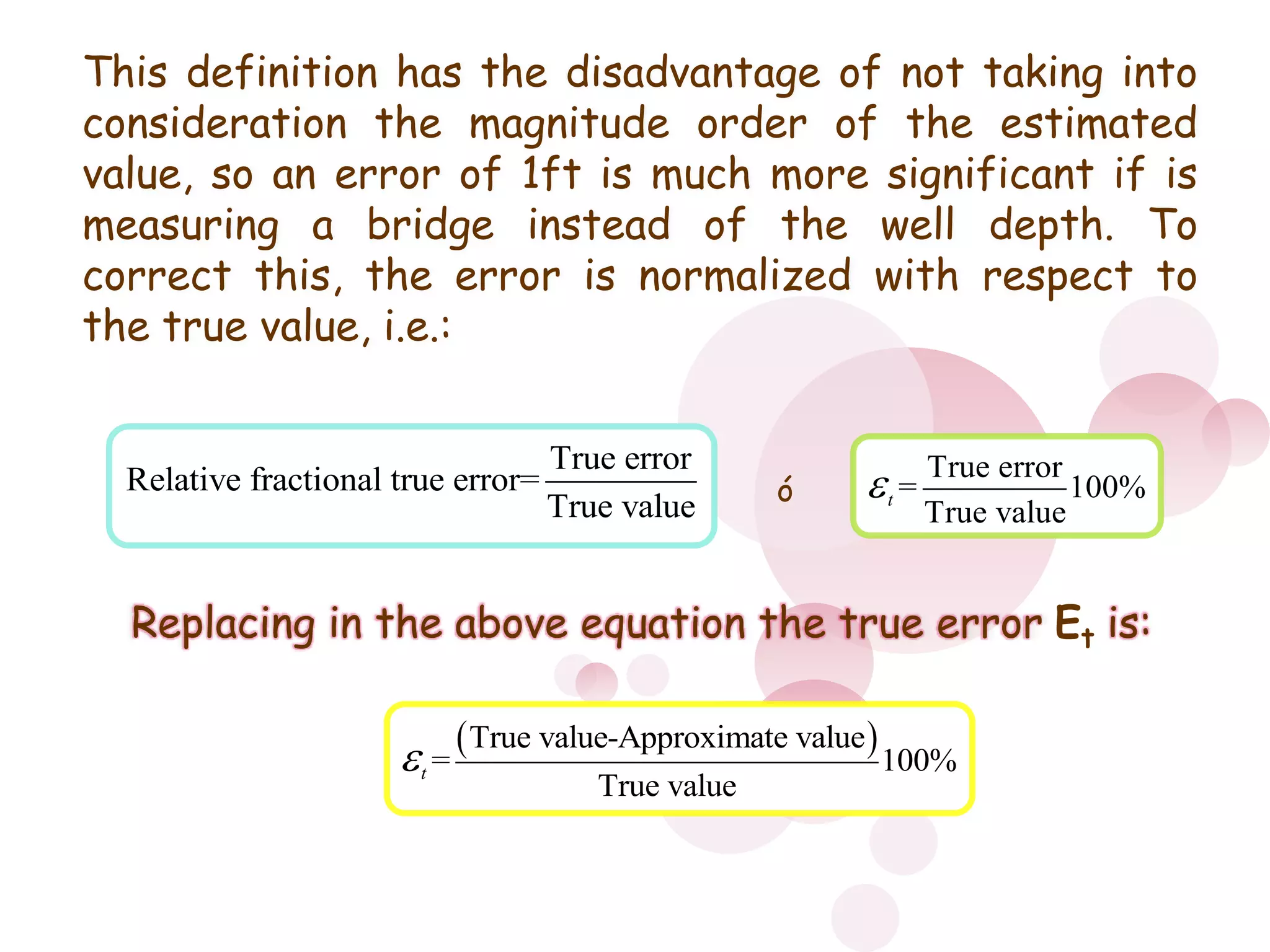
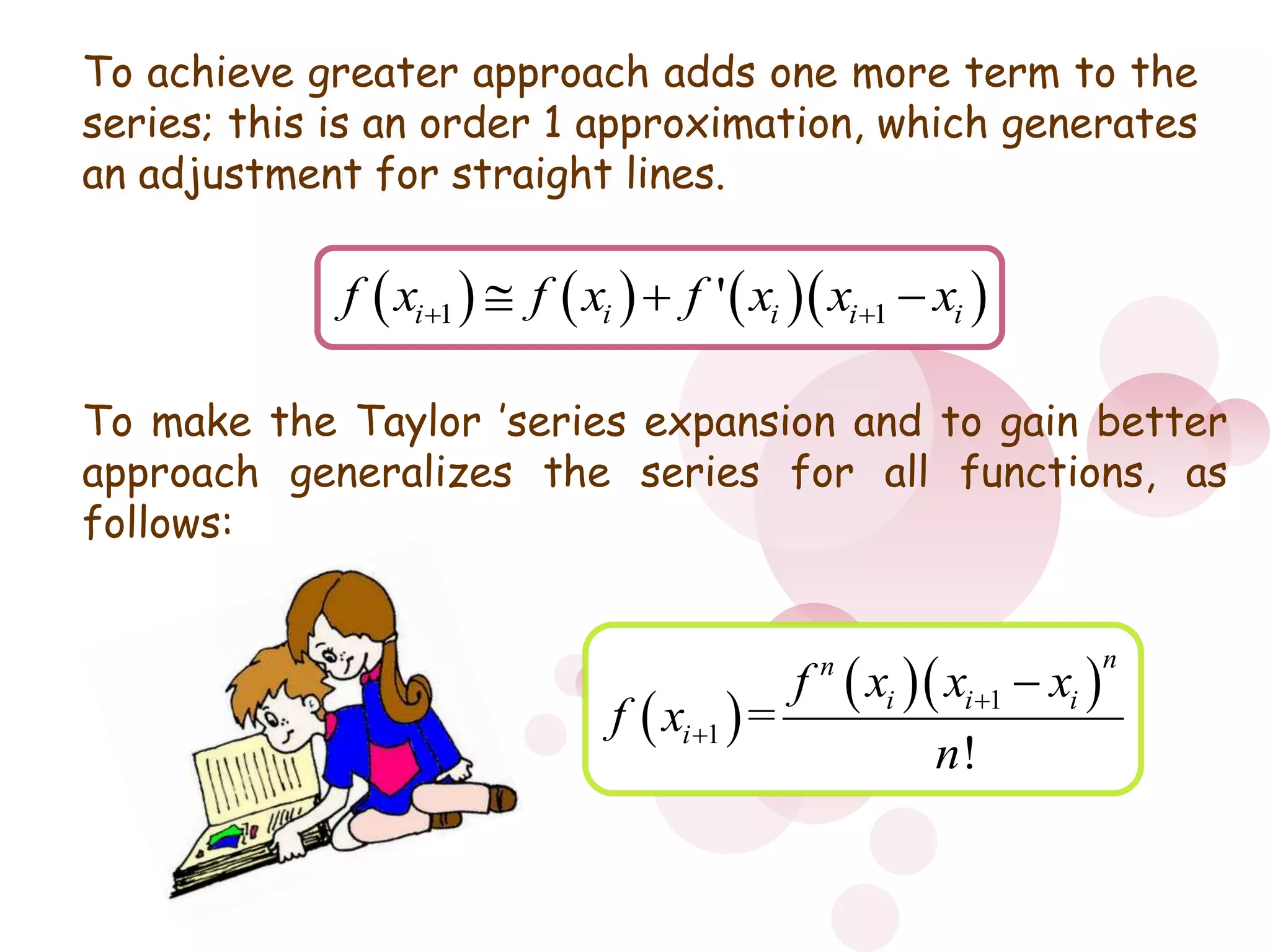
3) Numerical errors are the difference between the true and approximate values. Relative percent error is used to normalize the error by the true value when measuring differences in magnitude. Rounding and truncation errors contribute to the total numerical error.