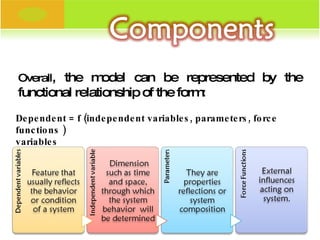
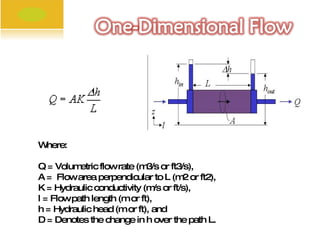
The document discusses mathematical modeling and Darcy's Law. It provides definitions of a mathematical model and its variables. Darcy's Law expresses the volumetric flow rate through porous media as a function of the flow area, elevation difference, fluid pressure, and a proportionality constant. It then gives the specific equations for Darcy's Law in terms of hydraulic head and its components of pressure head and elevation.